Abstract
Two fixed-bed loop reactors were used to evaluate singleand separated-phase anaerobic treatments of a high strength waste-water from ethanol fermentation. The one-phase system consisted of an anaerobic fixed-bed loop reactor containing both acidogenic as well as methanogenic populations allowing a complete conversion of the carbon source into gaseous end products and biomass.
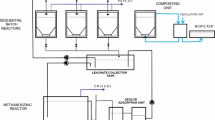
The two-phase system consisted of a second fixed-bed loop reactor operated as a methanogenic unit, which was proceeded by a CSTR for acidification, both connected in series allowing sequential acidogenesis and methanogenesis of the organic components. The reactors were operated under steady state and variable process conditions. By gradually increasing the feed supply in both systems, maximum turnover of COD was determined.
The separated-phase system consistently gave a better quality effluent with lower suspended solids and total COD. Maximum loading rates and COD elimination of the methanogenic phase of the two-phase system was over two times higher than that of the one-phase system. Process stability was also higher.
On overloading the methane reactor of the two phase system accumulation of different fatty acids within the reactor was observed. Hydrogen concentration in the biogas can be used as a reliable indicator for system overloadings. At least, continuous online monitoring of hydrogen in the methanogenic reactor gas should provide a convenient alternative to other analyses for process control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryant, M. P.; Wolin, M. J.: Rumen bacteria and their metabolic interactions. In: Hasegawa, T. (Ed.): Proc. of the First Intersectional Congress of the Intern. Assoc. Microbiol. Soc. 2 (1975) 297, Developmental Microbiology, Ecology. Science Council of Japan, Tokyo
Lettinga, G.; van Velsen, A. F. M.; de Zeeuw, W.; Hobma, S. W.: The application of anaerobic digestion to industrial pollution treatment. In: First International Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion, Cardiff, England (1979)
Ianotti, E. L.; Kafkewitz, D.; Wolin, M. J.; Bryant, M. P.: Glucose fermentation products of Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: Changes caused by interspecies transfer of hydrogen. J. Bact. 114 (1973) 1231–1240
Lathmann, M. J.; Wolin, M. J.: Fermentation of cellulose by Ruminococcus flavefaciens in the presence and absence of Methanobacterium ruminantium. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 34 (1977) 297–301
Weimer, P. J.; Zeikus, J. G.: Fermentation of cellulose and cellobiose by Clostridium thermocellum in the absence and presence of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 33 (1977) 289–297
Winter, J. U.; Wolfe, R. S.: Methane formation from fructose by syntrophic associations of Acetobacterium woodii and different strains of methanogens. Arch. Microbiol. 124 (1980) 73–79
Normann, J.; Frostell, B.: Anaerobic wastewater treatment in a two-stage reactor of a new Design. Proceedings of the 32nd Purdue Industrial Waste Conference (1977) 387
Ghosh, S.; Conrad, J. R.; Klass, D. L.: Anaerobic acidogenesis of wastewater sludge. J. Wat. Poll. Cont. Fed. 47 (1975) 30–45
Massey, M. L.; Pohland, F. G.: Phase separation of anaerobic stabilization by kinetic controls. J. Wat. Poll. Cont. Fed. 50 (1978) 9, 2204
Kunst, S.; Mudrack, K.: Untersuchungen zum anaeroben Abbau von Stärke unter besonderer Berücksichtigung einer Optimierung der Hydrolyse- und Versäuerungsstufe. gwf-wasser/abwasser 124 (1983) 2, 77–86
Bull, M. A.; Sterritt, R. M.; Lestert, J. N.: An evaluation of single- and separated phase anaerobic industrial wastewater treatment in fluidized bed reactors. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 26 (1984) 1054–1065
Cohen, A.; Breure, A. M.; van Andel, J. G.; van Deursen, A.: Influence of phase separation on the anaerobic digestion of Glucose-(I)-Maximum COD turnover rate during continuous operations. Water research 14 (1980), Pergamon Press, 1439–1448
Cohen, A.; Breure, A. M.; van Andel, J. G.; van Deursen, A.: Influence of phase separation of the anaerobic digestion of Glucose-(II) (Stability and kinetic responses to shock loadings). Water research 16, Pergamon Press 1445–1454
Sutton, P. M.; Li, A.: Single phase and two phase anaerobic stabilization in fluidized bed reactors. Wat. Sci. Tech. 15 (1983)
Wulfert, K.; Weiland, P.: Betriebsverhalten von Festbettreaktoren zur Biomethanisierung von Abläufen der Gärungsindustrie. Chem. Ing. Tech. 57 (1985) 5
Aivasidis, A.; Wandrey, C.: Process and apparatus for the continuous anaerobic decomposition of organic compounds. U.S. Patent Nr.: 4, 532, 042 from Jul. 30th (1985)
Aivasidis, A.; Wandrey, C.: Anaerober Abbau von Essigsäure mittels trägerfixierten Methanosarcinen. Wissenschaft und Umwelt 4 (1983) 181–187
Aivasidis, A.; Wandrey, C.: Anaerober Abbau von Essigsäure und Brüdenkondensaten in einem Festbett-Umlaufreaktor. Poster presentation at the Conference on „Verfahrenstechnik der biologischen Abwasserreinigung“, Krefeld (1983) Reprints 290
Aivasidis, A.: Anaerobic treatment of acetic acid containing industrial effluents in a fixed bed loop reactor. Proc. of IAWPRC Symp. on Forest Industry Wastewaters, Tampere 1984
Aivasidis, A.; Wandrey, C.: Ein Glasschwamm als Bakterienspeicher — Abwasserreinigung ohne Sauerstoff. KFA Jülich Report, No. 1900
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aivasidis, A., Wandrey, C. & Hilla, E. Studies on reaction techniques concerning reactor design for the anaerobic degradation of complex substrates with the example of the methanation of effluents in the fermentation industry. Bioprocess Engineering 4, 63–74 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373733
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373733