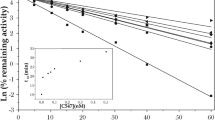
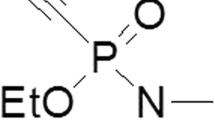
Abstract
The bispyridinium oxime HI-6, 1-((((4-amino-carbonyl) pyridinio)methoxy) methyl)-2-(hydroxyimino)-methyl) pyridinium dichloride monohydrate, combined with atropine is an effective treatment for soman (pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate) poisoning but is relatively ineffective against tabun (ethyl N-dimethyl phosphoroamidocyanidate) poisoning in mice. This contrasts with those results obtained using the bispyridinium oxime obidoxime [1,1′-(oxy bis(methylene)) bis(4-(hydroxyimino)-methyl) pyridinium dibromide]. The purpose of this study was to investigate the efficacy of the combination of HI-6 and obidoxime plus atropine against poisoning by tabun and soman in mice. The combination of ineffective single doses of obidoxime (5 or 10 mg/kg) and HI-6 (25 or 50 mg/kg) improved the treatment of tabun poisoning over either oxime alone. Combinations employing higher concentrations of obidoxime (25 or 50 mg/kg) and HI-6 (100 or 200 mg/kg) resulted in significant toxicity in the absence of organophosphate poisoning. Against soman poisoning the addition of obidoxime to HI-6 did not attenuate the efficacy of HI-6. The half-life of elimination and peak serum concentrations of HI-6 and obidoxime were not altered following administration of the combined injection. Reactivation of tabun-inhibited acetylcholinesterase was found consistently in the diaphragm but not in the brain. Using response surface methods it was possible to estimate the optimal therapy against soman and tabun poisoning (74.5 mg/kg HI-6+31.9 mg obidoxime against 1052 μg/kg challenge of tabun and 129 mg/kg HI-6 +0 mg/kg obidoxime against 390 μg/kg challenge of soman). It is proposed that reactivation of tabun inhibited acetylcholinesterase at the diaphragm may be responsible for the increased efficacy of the combination of HI-6 and obidoxime against tabun poisoning in mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benschop HP, Konings CAG, Van Genderen J, De Jong LPA (1984) Isolation, in vitro activity and acute toxicity in mice of the four stereoisomers of soman. Fundam Appl Toxicol 4: S84-S95
Borbely AA, Junod U, Hoff W, Hofmann A, Vaney R, Waser PG (1975) Studies on the protective action of atropine and obidoxime against sarin poisoning in mice. In: Waser PG (ed) Cholinergic Mechanisms. Raven Press, New York, pp 427–432
Bošković B (1979) The influence of 2-/0-Cresyl/-4 H/1∶3∶2-ben zodioxaphosphorin-2-oxide (CBDP) on organophosphate poisoning and its therapy. Arch Toxicol 42: 207–216
Bošković B, Kovacević V, Jovanović D (1984) PAM-2 CL, HI-6 and HGG-12 in soman and tabun poisoning. Fundam Appl Toxicol 4: S106-S115
Carter WH, Jr, Wampler GL, Stablin DM, Campell ED (1982) Drug activity and therapeutic synergism in cancer treatment. Cancer Res 42: 2963–2971
Carter WH, Jr, Jones DE, Carchman RA (1985) Application of response surface methods for evaluating the interactions of soman, atropine and pralidoxime chloride. Fundam Appl Toxicol 5: S232-S241
Cetkovic S, Cvetkovic M, Jandric D, Cosic M, Bošković B (1984) Effect of PAM-2 CL, HI-6 and HGG-12 in poisoning by tabun and its thiocholine-like analog in the rat. Fundam Appl toxicol 4: S116-S123
Clement JG (1979) Efficacy of Pro-PAM (N-methyl-1,6-dihydro-pyridine-2-carbaldoxime hydrochloride) as a prophylaxis against organophosphate poisoning. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 47: 305–311
Clement JG (1981) Toxicology and pharmacology of bispyridinium oximes — insight into the mechanism of action vs soman poisoning in vivo. Fundam Appl toxicol 1: 193–202
Clement JG (1982) HI-6: Reactivation of central and peripheral acetylcholinesterase following inhibition by soman, sarin and tabun in vivo in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol 31: 1283–1287
Clement JG (1983) Efficacy of mono- and bis-pyridinium oximes versus soman, sarin and tabun poisoning in mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol 3: 533–535
Clement JG, Simons KJ, Briggs CJ (1987) Effect of poisoning by soman (pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate) on the serum half-life of the cholinesterase reactivator, HI-6, in mice. Biopharm Drug Dispos (in press)
De Jong LPA, Wolring GZ (1984) Stereospecific reactivation by some Hagedorn-oximes of acetylcholinesterase from various species including man inhibited by soman. Biochem Pharmacol 33: 1119–1125
Heilbronn E, Sundwall A (1964) Studies on reactivation and ageing of blood cholinesterases of tabun intoxicated dogs. Biochem Pharmacol 13: 59–67
Heffron PF, Hobbiger F (1980) Does reactivation of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase (AchE) in the brain enhance the antidotal actions of pyridinium aldoximes? Br J Pharmacol 69: 313–314
Inns RH, Leadbeater L (1983) The efficacy of bispyridinium derivatives in the treatment of organophosphonate poisoning in the guinea pig. J Pharm Pharmacol 35: 427–433
Kusić R, Bošković B, Vojvodić V, Jovanović D (1985) HI-6 in man: Blood levels, urinary excretion and tolerance after intramuscular administration of the oxime to healthy volunteers. Fundam Appl Toxicol 5: 589–597
Lundy PM, Shih T-M (1983) Examination of the role of central cholinergic mechanisms in the therapeutic effects of HI-6 in organophosphate poisoning. J Neurochem 40: 1321–1328
Maksimović M, Bošković B, Radović L, Tadić V, Deljać V, Binenfeld Z (1980) Antidotal effects of bispyridinium-2-monooxime carbonyl derivatives in intoxications with highly toxic organophosphorus compounds. Acta Pharm Jugosl 30: 151–160
Meselson M, Robinson JP (1980) Chemical warfare and chemical disarmament. Sci Am 242: 34–43
Nelder JA, Mead RA (1965) A simplex method for function minimization. Computer J 7: 308–313
Puu G, Artursson E, Bucht G (1986) Reactivation of nerve agent inhibited acetylcholinesterase by HI-6 and toxogonin. Biochem Pharmacol 35: 1505–1510
Rickett DL, Glenn JF, Beers ET (1986) Central respiratory effects versus neuromuscular actions of nerve agents. Neuro Toxicol 7: 225–236
Siakotos AN, Filbert M, Hester R (1969) A specific radioisotopic assay for acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase in brain and plasma. Biochem Med 3: 1–12
Schoene K, Oldiges J (1973) The effects of pyridinium salts in tabun and sarin intoxications in vivo and in vitro. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 204: 110–123
Van Helden H, Wolthuis OL (1983) Evidence for an intramuscular depot of the cholinesterase inhibitor soman in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 59: 271–274
Wilhelm F, Fajdetić A, Deljać V, Binenfeld Z (1979). Protective effect of dexetimide and HI-6 poisoning with highly toxic organophosphorus compounds. Arch Hig Rada Toxsikol 30: 147–151
Wolthuis OL, Kepner LA (1978) Successful oxime therapy one hour after soman intoxication in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 49: 415–425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clement, J.G., Shiloff, J.D. & Gennings, C. Efficacy of a combination of acetylcholinesterase reactivators, HI-6 and obidoxime, against tabun and soman poisoning of mice. Arch Toxicol 61, 70–75 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324551
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324551
Key words
- HI-6 1-((((4-aminocarbonyl)-pyridinio]metho-xy]methyl)-2-((hydroxyimino)-methyl)pyrindium dichloride
- Obidoxime 1,1−(oxybis(methylene))bis(4-hydroxyimino)-methyl) pyridinium dibromide
- Soman (pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate)
- Tabun (ethyl N-dime-thylphosphoramidocyanidate)
- Bispyridinium
- Oximes
- Reactivation