Abstract
-
1.
Projection patterns of olfactory receptor neurons, specifically tuned to the two principal components of the female H. virescens sex pheromone blend, and to a third pheromone-like compound of possible antagonistic significance, were examined using a combined electrophysiological and morphological technique.
-
2.
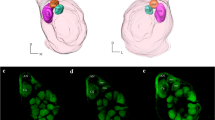
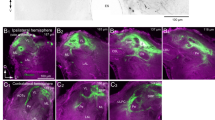
The macroglomerular complex consists of four major glomerular subdivisions.
-
3.
In the sensillum type containing a receptor neuron detecting the main pheromone component, Z11-16: AL, two cells were present. When the sensillum was stimulated with Z11-16:AL, a single axon, stained by a method that selectively stains active neurons, was seen projecting into the large a glomerulus. The b glomerulus was innervated by a second neuron in a few double stainings.
-
4.
In a second sensillum type, one receptor neuron tuned to the second major pheromone component, Z9-14:AL, was found. In these sensilla, one or two receptor neurons of unknown specificity were also observed. When the sensillum was stimulated with Z9-14: AL, a single neuron projecting into glomerulus a or two neurons projecting into glomerulus a were most often observed.
-
5.
In the third sensillum type, one neuron specifically tuned to Z11-16:AC projected to glomerulus c, and a second cell of unknown specificity projected to the same area.
-
6.
The axonal arborizations of different physiological receptor neuron types involved in the detection of the pheromone blend do not display a clearcut morphological separation into different glomeruli in the MGC. A separation between neurons detecting attracting and repelling odours was, however, present.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AN :
-
antennal nerve
- AL :
-
antennal lobe
- MGC :
-
macroglomerular complex
- RN :
-
receptor neuron
- Z9-14 :
-
AL (Z) 9-tetradecenal
- Z11-16 :
-
AL(Z) 1-hexadecenal
- Z11-16 :
-
AC(Z)-11-hexadecenyl acetate
- Z11-16 :
-
OH(Z)-11-hexadecenol
References
Almaas TJ, Mustaparta H (1990) Pheromone reception in tobacco budworm moth, Heliothis virescens. J Chem Ecol 16: 1331–1347
Almaas TJ, Mustaparta H (1991) Heliothis virescens: Response characteristics of receptor neurons in sensilla trichodea type 1 and type 2. J Chem Ecol 17: 953–972
Berg B, Tumlinson, JH, Mustaparta H (1995) Chemical communication in heliothine moths. IV. Receptor neuron responses to pheromone compounds and formate analogues in the tobacco budworm moth Heliothis virescens. J Comp Physiol A 177: 527–534
Boeckh J, Tolbert LP (1993) Synaptic organization and development of the antennal lobe in insects. Microsc Res Tech 24: 260–280
Bretschneider F (1924) Über die Gehirne des Eichenspinners und des Scidenspinners (Lasiocampa querqus L. und Bombyx mori L.). Jena Z Naturwissensch (Zool) 60: 563–570
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1987) Male-specific, sex pheromone-selective projection neurons in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A160: 553–569
Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Hildebrand JG (1989) Discrimination of sex pheromone blends in the olfactory system of the moth. Chem Senses 14: 463–477
Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Hildebrand JG (1991) Chemical communication in Heliothine moths II. Central processing of intraspecific and interspecific olfactory messages in the male corn earworm moth Helicoverpa zea. J Comp Physiol A 169: 259–274
Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Hildebrand, JG (1995) Chemical communication in heliothine moths. VI. Dendritic processing of pheromonal information in antennal lobe neurons in the male tobacco budworm moth Heliothis virescens. J Comp Physiol A 177: 545–557
Christensen TA, Waldrop B, Harrow ID, Hildebrand JG (1993) Local interneurons and information processing in the olfactory glomeruli of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 173: 385–399
Hansson BS, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1991) Functionally distinct subdivisions of the macroglomerular complex in the antennal lobe of the male sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 312: 264–278
Hansson BS, Ljungberg H, Hallberg E, Löfstedt C (1992) Functional specialization of olfactory glomeruli in a moth. Science 256: 1313–1315
Kaissling KE (1974) Sensory transduction in insect olfactory receptors. In: Jaenicke L (ed) Biochemistry of sensory functions. Springer, Berlin, pp 243–273
Kaissling KE (1987) Chemo-electrical transduction in insect olfactory receptors. Ann Rev Neurosci 9: 121–145
Koontz MA, Schneider D (1987) Sexual dimorphism in neuronal projections from the antennae of silk moths (Bombyx mori, Antheraea polyphemus) and the gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar). Cell Tissue Res 249: 39–50
Lucas P, Renou M (1989) Responses to pheromone compounds in Mamestra suasa (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) olfactory neurones. J Insect Physiol 35: 837–845
Malun D (1991a) Inventory and distribution of synapses of identified uniglomerular projection neurons in the antennal lobe of Periplaneta americana. J Comp Neurol 305: 348–360
Malun D (1991b) Synaptic relationships between GABA-immunoreactive neurons and an identified uniglomerular projection neuron in the antennal lobe of Periplaneta americana: a double-labeling electron microscopic study. Histochemistry 96: 197–207
Matsumoto SG, Hildebrand JG (1981) Olfactory mechanisms in the moth Manduca sexta: Response characteristics and morphology of central neurons in the antennal lobes. Proc R Soc London B213: 249–277
Mustaparta H (1984) Olfaction. In: Bell WJ, Cardé RT (eds) Chemical ecology of insects. University Press, Cambridge, pp 37–70
Ramaswamy SB, Randle SA, Keung MW (1985) Field evaluation of the sex pheromone components of Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in cone traps. Environ Entomol 14: 293–296
Roelofs WL, Hill AS, Cardé RT, Baker TC (1974) Two sex pheromone components of the tobacco budworm moth, Heliothis virescens. Life Sci 14: 1555–1562
Rospars JP (1983) Invariance and sex-specific variations of the glomerular organization in the antennal lobes of a moth, Mamestra brassicae, and a butterfly, Pieris brassicae. J Comp Neurol 220: 80–96
Rospars JP, Hildebrand JG (1992) Anatomical identification of glomeruli in the antennal lobes of the male sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Cell Tissue Res 95: 223–248
Serby MJ, Chobor KL (1992) Science of olfaction. Springer, Berlin.
Teal PEA, Heath RR, Tumlinson JH, McLaughlin JR (1981) Identification of a sex pheromone of Heliothis subflexa (GN.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and field trapping studies using different blends of components. J Chem Ecol 7: 1011–1022
Timm F (1958) Zur Histochemie der Schwermetalle. Das sulfid-Silber-Verfahren. Dtsch Z Gesamte Gerichtl Med 46: 706–711
Tolbert LP, Hildebrand JG (1981) Organization and synaptic ultrastructure of glomeruli in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta: a study using thin sections and freeze-structure. Proc R Soc London B 213: 279–301
Tumlinson JH, Hendricks PE, Mitchell ER, Doolittle RE, Brennan MM (1975) Isolation, identification and synthesis of the sex pheromone of the tobacco budworm. J Chem Ecol 1: 203–214
Van der Pers JNC, Den Otter CJ (1978) Single cell responses from olfactory receptors of small ermine moths to sex-attractants. J Insect Physiol 24: 337–343
Vickers NJ, Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Baker TC (1991) Chemical communication in heliothine moths. III. Flight behavior of male Helicoverpa zea and Heliothis virescens in response to varying ratios of intraspecific and interspecific sex pheromone components. J Comp Physiol A 169: 275–280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hansson, B.S., Almaas, T.J. & Anton, S. Chemical communication in heliothine moths. J Comp Physiol A 177, 535–543 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207183
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207183