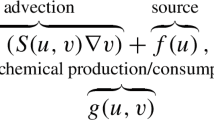Abstract
The Bonhoeffer-van der Pol (BVP) oscillator is a valuable dynamical system model of pacemaker neurons. Isochrons, phase transition curves (PTC), and two dimensional bifurcation diagrams served to analyze the neuron's response to periodic pulse stimuli. Responses are described and explained in terms of the nonlinear dynamical system theory. An important issue in the generation of spikes by pacemaker neurons is the existence of both slow and fast dynamics in the state point's trajectory in the phase plane. It is this feature in particular that makes the BVP oscillator a faithful model of living pacemaker neurons. Comparison of the model's responses with those of a living pacemaker was based also on return maps of interspike intervals. Analyzed in detail were the complex discharges called ‘stammering’ which involve interspike intervals that arise unpredictably and exhibit histograms with several modes separated by the equal intervals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara K, Matsumoto G, Ikegaya Y (1984) Periodic and non-periodic responses of a periodically forced Hodgkin-Huxley oscillator. J Theor Biol 109:249–269
Bonhoeffer KF (1948) Activation of passive iron as a model for the excitation of nerve. J Gen Physiol 32:69–91
Chialvo DR, Apkarian AV (1993) Modulated noisy biological dynamics: three examples. J Stat Phys 70:375–391
Ermentrout GB (1981) n:m phase locking of weakly coupled oscillators. J Math Biol 12:327–342
Ermentrout GB, Rinzel J (1984) Beyond a pacemaker's entrainment limit: Phase walk-through. Am J Physiol 246 (Regul Integrative Comp Physiol 15):R102-R106
FitzHugh R (1961) Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophy J 1:445–466
Guttman R, Lewis S, Rinzel J (1980) Control of repetitive firing in squid axion membrane as a model for a neuroneoscillator. J Physiol 305:377–395
Hayashi H, Ishizuka S (1992) Chaotic nature of bursting discharges in the Onchidium pacemaker neuron. J Theor Biol 156:269–291
Jensen MH (1983) Complete devil's staircase, fractal dimension, and universality of mode-locking structure in the circle map. Phys Rev Lett 50.21:713–747
Kawato M (1981) Transient and steady state phase response curve of limit cycle oscillators. J Math Biol 12:13–30
Keener JP, Glass L (1984) Global bifurcation of a periodically forced nonlinear oscillator. J Math Biol 21:175–190
Kepler TB, Abbott LF, Marder E (1992) Reduction of conductance-based neuron models. Biol Cybern 66:381–387
Kiemel T, Holmes P (1987) A model for the periodic synaptic inhibition of a neuronal oscillator. IMA J Math Appl Med Biol 4:150–169
Koch C, Segev I (1989) Methods in neuronal modeling: from synapse to networks. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass
Kohn AF, Freitas da Rocha A, Segundo JP (1981) Presynaptic irregularity and pacemaker inhibition. Biol Cybern 41:5–18
Longtin A (1993) Stochastic resonance in neuron models. J Stat Phys 70:309–327
Matsumoto G, Aihara K, Hanyu Y, Takahashi N, Yoshizawa S, Nagumo J (1987) Chaos and phase locking in normal squid axons. Phys Lett A 123:162–166
Morris C, Lecar H (1981) Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys J 35:193–213
Nagumo J, Arimoto S, Yoshizawa S (1962) An active pulse transmission line stimulating nerve axon. Proc IRE 50:2061–2070
Nagumo J, Sato S (1972) On a response characteistic of a mathematical neuron model. Kybernetik 10:155–164
Nomura T, Sato S, Doi S, Segundo JP, Stiber MD (1993) A Bonhoeffer-van der Pol oscillator model of locked and non-locked behaviors of living pacemaker neurons. Biol Cybern 69:429–437
Parlitz U, Lauterborn W (1987) Period-doubling cascades and devil's staircases of the driven van der Pol oscillator. Phys Rev A 36:1428–1434
Pérez R, Glass L (1982) Bistability, period doubling bifurcations and chaos in a periodically forced oscillator. Phys Lett 90 A:441–443
Perkel DH, Bullock TH (1968) Neural coding. Neurosci Res Prog Bull 6:221–248
Perkel DH, Schulman JH, Bullock TH, Moore GP, Segundo JP (1964) Pacemaker neurons: effects of regularly spaced synaptic inputs. Science 145:61–63
Pomeau Y, Manneville P (1980) Intermittent transition to turbulence in dissipative dynamical systems. Commun Math Phys 74:184–197
Sato S, Doi S (1992) Response characteristics of the BVP neuron model to periodic stimuli. Math Biosci 112:243–259
Segundo JP, Altshuler E, Stiber M, Garfinkel A (1991a) Periodic inhibition of living pacemaker neurons. I. Locked, intermittent, messy and hopping behaviors. Int J Bifurcation Chaos 1:549–581
Segundo JP, Altshuler E, Stiber M, Garfinkel A (1991b) Periodic inhibition of living pacemaker neurons. II. Influences of driver rates, of transients and of non-driven post-synaptic rates. Int J Bifurcation Chaos 1:873–890
Siegel RM, Read HL (1993) Models of the temporal dynamics of visual processing. J Stat Phys 70:297–308
Stiber MD (1992) Dynamics of synaptic integration. PhD thesis, University of California, Los Angeles
Stiber MD, Segundo JP (1993) Dynamics of synaptic transfer in living and simulated neurons. IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, San Franisco, pp 75–80
Takahashi N, Hanyu Y, Musha T, Kubo R, Matsumoto G (1990) Global bifurcation structure in periodically simulated giant axons of squid. Physica D 43:318–334
Yasin S, Friedman M, Goshen S, Rabinovitch A, Thieberger R (1993) Intermittency and phase locking of the Bonhoeffer van der Pol model. J Theor Biol 160:179–184
Yoshizawa S, Osada H, Nagumo J (1982) Pulse sequences generated by a degenerate analog neuron model. Biol Cybern 45:23–33
Winfree AT (1974) Patterns of phase compromise in biological cycles. J Math Biol 1:73–95
Winfree AT (1980) The geometry of biological time. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Trent H. Wells Jr. Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nomura, T., Sato, S., Doi, S. et al. Global bifurcation structure of a Bonhoeffer-van der Pol oscillator driven by periodic pulse trains. Biol. Cybern. 72, 55–67 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206238
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00206238