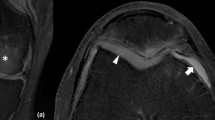
Abstract
High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been used to visualise the changes that occur in both soft tissue and bone during antigen-induced, monoarticular arthritis (AIMA) of the rat knee. Extensive optimisation studies were performed in order to minimise the time of the experiments and to maximise both the signal-to-noise ratio and the contrast in the MR images. The study was cross-sectional rather than longitudinal and at each of the 13 time points studied during the progression of the disease, corresponding X-radiographs and histological sections were obtained. Interpretation of the spin echo MR images was aided by the use of chemical shift-selective imaging, magnetisation transfer contrast and relaxation time experiments, as well as by correlation with the histology and X-radiography data. The MR images clearly show invasion of the synovium by an inflammatory pannus which spreads over the articular cartilage and invades the bone, leading to erosion and later remodelling. Two distinct types of bony erosion were observed: focal erosions, especially at the margins of the joint, and subchondral erosions. It is concluded that MRI provides a sensitive, non-invasive method for investigating both early-stage inflammatory changes and late-stage bony changes in the knee joints of the arthritic rat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badley EM, Tennant G. Which rhematic disorders have the greater impact in the population? Estimates of severity and prevalence from the Calderdale rheumatic disablement survey. Br J Rheumatol 1991; 30 [Suppl 2]: 102.
HG Fassbender. Joint destruction in various arthritic diseases. In: Kuettner KE, Schleyerbach R, Hascall VC, eds: Articular cartilage biochemistry. New York: Raven, 1986: 371–389.
Berquist TH, Ehman RL, Richardson ML, eds. Magnetic resonance of the musculoskeletal system. New York: Raven, 1987.
König H, Aicher K, Saal J. Quantitative evaluation of hyaline cartilage disorders using FLASH sequence. I. Method and animal experiments. Acta Radiol 1990; 31: 371.
Danon O, Goldstein L, Marikovsky Y, Skutelsky E. Use of cationised ferritin as a label of negative charges on cell surfaces. J Ultrastruct Res 1972; 38: 500–512.
Hodgson RJ. Studies in magnetic resonance imaging of arthritis. Ph D Thesis, University of Cambridge, England, 1993.
Flecknell PA, Mitchell M. Midazolam and fentanyl-fluanisone: assessment of anaesthetic effects in laboratory rodents and rabbits. Lab Anim 1984; 18: 143.
Checkley D, Johnstone D, Taylor K, Waterton JC. High resolution NMR imaging of an antigen-induced arthritis in the rabbit knee. Magn Reson Med 1989; 11: 211–235 and (Erratum) 1990; 13: 529.
Ceckler TL. Quantitative 1H magnetization transfer imaging in vivo. Magn Reson Med 1991; 17: 304–314.
Billingham MEJ. Models of arthritis and the search for antiarthritis drugs. Pharmacol Ther 1983; 21: 389.
Howson P, Shepard N, Mitchell N. The antigen induced arthritis model: the relevance of the method of induction to its use as a model of human disease. J Rheumatol 1986; 13: 379–390.
Gondolf KB, Batsford S, Lassie G, Gurschellas E, Mertz A. Handling of cationic antigens in the joint and induction of chronic allergic arthritis: in vivo studies in the rat. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol 1991; 60: 353.
Terrier F, Hricak H, Revel D, Alpers CE, Reinhold CE, Levin J, Genant HK. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of the periarticular inflammatory soft-tissue changes in experimental arthritis of the rat. Invest Radiol 1985; 20: 813–823.
Terrier F, Revel D, Reinhold CE, Levine J, Grodd W, Genant HK, Brasch RC. Contrast-enhanced MRI of periarticular softtissue changes in experimental arthritis of the rat. Magn Reson Med 1986; 3: 385–396.
Borah B, Szeverenyi NM. Quantification of fluid changes in rat leg joints with adjuvant arthritis by a one-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging experiment. Magn Reson Med 1990; 15: 246–259.
Paul PK, O'Byrne E, Blancuzzi V, Wilson D, Gunson D, Douglas FL, Wang JZ, Mezrich RS. Magnetic resonance imaging reflects cartilage proteoglycan degradation in the rabbit knee. Skeletal Radiol 1991; 20: 31–36.
Paul PK, O'Byrne E, Blancuzzi V, Grunland Jacobs J, Rakhit A, Dunton AW, Douglas FL, Wilson D. 3-D MRI of rabbit knee: localization of intra-articular infusion site and evaluation of pathology induced by inflammatory agents. Works in Progress, 10th Annual Meeting, Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 1991: 1129.
Adams ME, Li DKB. MR imaging of joint lesions. In: Kuettner KE, Schleyerbach R, Hascall VC, eds: Articular cartilage biochemistry. New York: Raven, 1986: 331–348.
Paul Sabiston C, Adams ME, Li DKB. Magnetic resonance imaging of osteoarthritis: correlation with gross pathology using an experimental model. J Orthop Res 1987; 5: 164–172.
Mink JH, Reicher MA, Crues JV. Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee. New York: Raven, 1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carpenter, T.A., Everett, J.R., Hall, L.D. et al. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of arthritic pathology in the rat knee. Skeletal Radiol. 23, 429–437 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204603
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00204603