Abstract
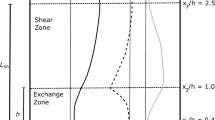
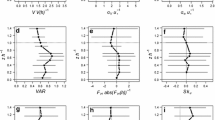
The processes influencing turbulence in a deciduous forest and the relevant length and time scales are investigated with spectral and cross-correlation analysis. Wind velocity power spectra were computed from three-dimensional wind velocity measurements made at six levels inside the plant canopy and at one level above the canopy. Velocity spectra measured within the plant canopy differ from those measured in the surface boundary layer. Noted features associated with the within-canopy turbulence spectra are: (a) power spectra measured in the canopy crown peak at higher wavenumbers than do those measured in the subcanopy trunkspace and above the canopy; (b) peak spectral values collapse to a relatively universal value when scaled according to a non-dimensional frequency comprised of the product of the natural frequency and the Eulerian time scale for vertical velocity; (c) at wavenumbers exceeding the spectral peak, the slopes of the power spectra are more negative than those observed in the surface boundary layer; (d) Eulerian length scales decrease with depth into the canopy crown, then increase with further depth into the canopy; (e) turbulent events below crown closure are more correlated with turbulent events above the canopy than are those occurring in the canopy crown; and (f) Taylor's frozen eddy hypothesis is not valid in a plant canopy. Interactions between plant elements and the mean wind and turbulence alter the processes that produce, transport and remove turbulent kinetic energy and account for the noted observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, L. H., Jr.: 1968, ‘Turbulence and Wind Speed Spectra within a Japanese Larch Plantation’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 7, 73–78.
Anderson, D. E., Verma, S. B., Clement, R. J., Baldocchi, D. D., and Matt, D. R.: 1986, ‘Turbulence Spectra of CO2, Water Vapor, Temperature and Velocity over a Deciduous Forest’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 38, 81–99.
Bache, D. H.: 1986, ‘Momentum Transfer to Plant Canopies: Influence of Structure and Variable Drag’, Atmospheric Environment 20, 1369–1378.
Baldocchi, D. D. and Hutchison, B. A.: 1988, ‘Turbulence in an Almond Orchard: Spatial Variation in Spectra and Coherence’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 293–311.
Baldocchi, D. D. and Meyers, T. P.: 1988, ‘Turbulence Structure in a Deciduous Forest’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 43, 345–365.
Browne, L. W. B., Antonia, R. A., and Shah, D. A.: 1987, ‘Turbulent Energy Dissipation in a Wake’, J. Fluid Mech. 179, 307–326.
Businger, J. A.: 1982, ‘Equations and Concepts’, in F. T. M. Nieuwstadt and H. van Dop (eds.), Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modeling, D. Reidel Pub. Co., Dordrecht, pp. 1–36.
Carter, G. C. and Ferrie, J. F.: 1979, ‘A Coherence and Cross Spectral Estimation Program’, in Digital Processing Committee (eds.), Programs for Digital Signal Processing. IEEE Press, pp. 2.3-1 to 2.3-18.
Caughey, S. J.: 1982, ‘Observed Characteristics of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, in F. T. M. Nieuwstadt and H. van Dop (eds.), Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modeling, D. Reidel Pub. Co., Dordrecht, pp. 107–158.
Corrsin, S.: 1974, ‘Limitations of Gradient Transport Models in Random Walks and in Turbulence’, Adv. Geophys. 18A, 25–60.
Crowther, J. M. and Hutchings, N. J.: 1985, ‘Correlated Vertical Wind Speeds in a Spruce Canopy’, in: B. A. Hutchison and B. B. Hicks (eds.), Forest-Atmosphere Interactions, D. Reidel Pub. Co., Dordrecht, pp.543–562.
Finnigan, J. J.: 1979a, ‘Turbulence in Waving Wheat. I: Mean Statistics and Honami’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 16, 181–212.
Finnigan, J. J.: 1979b, ‘Turbulence in Waving Wheat. II: Structure of Momentum Transfer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 16, 213–236.
Finnigan, J. J. and Raupach, M. R.: 1987, ‘Transfer Processes in Plant Canopies in Relation to Stomatal Characteristics’, in E. Zeiger, G. Farquhar and I. Cowan (eds.), Stomatal Function. Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA, pp. 385–429.
Hicks, B. B.: 1972, ‘Propeller Anemometers as Sensors of Atmospheric Turbulence’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 214–228.
Hutchison, B. A., Matt, D. R., McMillen, R. T., Gross, L. J., Tajchman, S. J., and Norman, J. M.: 1986, ‘The Architecture of an East Tennessee Deciduous Forest Canopy’ J. Ecol. 74, 635–646.
Inoue, K.: 1981, ‘A Model Study of Microstructure of Wind Turbulence of Plant Canopy Flow’, Bull. Natl. Inst. Agric. Sci. Ser A. 27, 69–89.
Isobe, S.: 1972, ‘A Spectral Analysis of Turbulence in a Corn Canopy’, Bull. Natl. Inst. Agric. Sci. Ser. A. 19, 101–113.
Jensen, N. O. and Busch, N. E.: 1982, ‘Atmospheric Turbulence’, in E. J. Plate (ed.), Engineering Meteorology, Elsevier Sci. Pub., pp. 179–231.
Kaimal, J. C., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y., and Cote, O. R.: 1972, ‘Spectral Characteristics of Surface Layer Turbulence’, Quart. J. Roy. Metorol. Soc. 98, 563–589.
Kristensen, L. and Jensen, N. O.: 1979, ‘Lateral Coherence in Isotropic Turbulence and in the Natural Wind’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 17, 353–373.
Legg, B. J. and Raupach, M. R.: 1982, ‘Markov-Chain Simulation of Particle Dispersion in Inhomogeneous Flows: the Mean Drift Velocity Induced by a Gradient in Eulerian Velocity Variance’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 24, 3–13.
Lumley, J. L. and Panofsky, H. A.: 1964, The Structure of Atmospheric Turbulence, Interscience, New York, 239 pp.
Maitani, T.: 1978, ‘On the Downward Transport of Turbulent Kinetic Energy in the Surface Layer over Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 14, 571–584.
Meyers, T. P. and Paw, U. K. T.: 1986, ‘Testing of a Higher Order Closure Model for Modeling Airflow within and above Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 297–311.
Panofsky, H. A.: 1973, ‘Tower Micrometeorology’, in D. A. Haugen (ed.), Workshop on Micro-meteorology, American Meteorological Society, Boston, pp. 151–176.
Panofsky, H. A. and Dutton, J. A.: 1984, Atmospheric Turbulence: Models and Methods for Engineering Applications, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 397 pp.
Raupach, M. R.: 1987, ‘A Lagrangian Analysis of Scalar Transfer in Vegetation Canopies’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 113, 107–120.
Raupach, M. R. and Shaw, R. H.: 1982, ‘Averaging Procedures for Flow within Vegetation Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 22, 79–90.
Raupach, M. R., Coppin, P. A., and Legg, B. J.: 1986, ‘Experiments on Scalar Dispersion within a Model Plant Canopy, Part 1: The Turbulent Structure’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 35, 21–52.
Seginer, I., Mulhearn, P. J., Bradley, E. F., and Finnigan, J. J.: 1976, ‘Turbulent Flow in a Model Plant Canopy’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 10, 423–453.
Seginer, I. and Mulhearn, P. J.: 1978, ‘A Note on Vertical Coherence of Streamwise Turbulence inside and above a Model Plant Canopy’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 14, 515–523.
Shaw, R. H., Silversides, R. H., and Thurtell, G. W.: 1974, ‘Some Observations of Turbulence and Turbulent Transport within and above Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 5, 429–449.
Shaw, R. H.: 1976, ‘Secondary Wind Maxima Inside Plant Canopies’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 16, 514–521.
Shaw, R. H. and Seginer, I.: 1985, ‘The Dissipation of Turbulence in Plant Canopies’, 7th Symp. on Turbulence and Diffusion, Am. Meteorol. Soc., Boston, pp. 200–203.
Silversides, R. H.: 1974, ‘On Scaling Parameters for Turbulence Spectra within Plant Canopies’, Agric. Meteorol. 13, 203–211.
Thompson, N.: 1979, Turbulence Measurements Over a Pine Forest, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 16, 293–310.
Uchijima, Z. and Wright, J. L.: 1964, ‘An Experimental Study of Air Flow in a Corn Plant-air Layer’, Bull. Natl. Inst. Agric. Sci. Ser A. 11, 19–65.
Verma, S. B., Baldocchi, D. D., Anderson, D. E., Matt, D. R., and Clement, R. J.: 1986, ‘Eddy Fluxes of CO2, Water Vapor and Sensible Heat over a Deciduous Forest’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 36, 71–91.
Weiss, A. and Allen, L. H., Jr.: 1976, ‘Air Flow Patterns in Vineyard Rows’, Agric. Meteorol. 16, 329–342.
Wilson, J. D., Thurtell, G. W., and Kidd, G. E.: 1981, ‘Numerical Simulation of Particle Trajectories in Inhomogeneous Turbulence, I: Systems with Constant Turbulent Velocity Scales’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21, 295–313.
Wilson, J. D., Thurtell, G. W., and Kidd, G. E.: 1981, ‘Numerical Simulation of Particle Trajectories in Inhomogeneous Turbulence, I: Systems with Constant Turbulent Velocity Scales’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21, 295–313.
Wilson, J. D., Ward, D. P., Thurtell, G. W., and Kidd, G. E.: 1982, ‘Statistics of Atmospheric Turbulence within and above a Corn Canopy’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 24, 495–519.
Wilson, N. R. and Shaw, R. H.: 1977, ‘A Higher Order Closure Model for Canopy Flow’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 16, 1197–1205.
Wyngaard, J. C.: 1982, ‘Boundary Layer Modeling’, in F. T. M. Nieuwstadt and van Dop (eds.), Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modeling, D. Reidel Pub. Co., Dordrecht, pp. 69–106.
Wyngaard, J. C. and Zhang, S. F.: 1985, ‘Transducer-Shadow Effects on Turbulence Spectra Measured by Sonic Anemometers’, J. Atmos. Oceanic Tech. 2, 548–558.
Yamada, T.: 1982, ‘A Numerical Model Study of Turbulent Airflow in and Above a Forest Canopy’, J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. 60, 439–454.
Yamada, T.: 1982, ‘A Numerical Model Study of Turbulent Airflow in and Above a Forest Canopy’, J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan. 60, 439–454.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldocchi, D.D., Meyers, T.P. A spectral and lag-correlation analysis of turbulence in a deciduous forest canopy. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 45, 31–58 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120814
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120814