Abstract
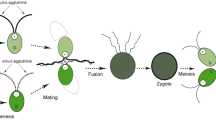
Chlamydomonas gametes of opposite mating types interact through flagellar adhesion molecules called agglutinins leading to a signal transduction cascade that induces cell wall loss and activation of mating structures along with other cellular responses that ultimately result in zygote formation. To identify molecules involved in these complex cellular events, we have employed subtractive and differential hybridization with cDNA from mt+ gametes activated for fertilization and non-signaling, vegetative (non-gametic) cells. We identified 55 cDNA clones whose transcripts were regulated in activated gametes. Here we report the molecular cloning and characterization of the complementary DNA (cDNA) for one clone whose transcripts in activated gametes were several-fold higher than in normal gametes. Regulation of the transcript was not related simply to protein synthesis because it was not increased in cells synthesizing new cell wall proteins. The cDNA contained a single open reading frame (ORF) of 815 amino acids encoding a polypeptide of calculated relative mass of 87 kDa. Database search analysis and sequence alignment indicated that the deduced amino acid sequence exhibited 42% identity and 62% similarity to a class of prokaryotic methyl transferases (5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyl transferase; EC 2.1.1.14) known to be involved in the terminal step of de novo biosynthesis of methionine. This enzyme catalyzes transfer of a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate to homocysteine resulting in methionine formation. Affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies raised against a bacterially produced GST-fusion protein identified a 85 kDa soluble protein in Chlamydomonas gametes. Southern blot hybridization indicated that the enzyme is encoded by a single-copy gene. The evidence presented in this paper raises the possibility that, in addition to its participation in de novo biosynthesis and regeneration of methionine, Chlamydomonas methionine synthase may play a role in adhesion-induced events during fertilization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair WS, Apt KE: Cell wall regeneration in Chlamydomonas: accumulation of mRNAs encoding cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 7355–7359 (1990).
Banerjee RV, Matthews RG: Cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase. FASEB J 4: 1450–1459 (1990).
Buchanan MJ, Snell WJ: Biochemical studies on lysin, a cell wall degrading enzyme released during fertilization in Chlamydomonas. Exp Cell Res 179: 181–193 (1988).
Clarke S: Protein isoprenylation and methylation at carboxy-terminal cysteine residues. Annu Rev Biochem 61: 355–386 (1992).
Dobberstein B, Blobel G, Chua N: In vitro synthesis and processing of a putative precursor for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 1082–1085 (1977).
Drennan CL, Huang S, Drummond JT, Matthews RG, Ludwig ML: How a protein binds B12 A 3.0 Å X-ray structure of B12-binding domains of methionine synthase. Science 266: 1669–1674 (1994).
Dworkin MB, Dawid IB: Use of a cloned library for the study of abundant poly(A)+ RNA during Xenopus laevis development. Devel Biol 76: 449–464 (1980).
Emini EA, Hughes JV, Perlow DS, Boger J: Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol 55: 836–839 (1985).
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132: 6–13 (1984).
Ferris PJ, Goodenough UW: Transcription of novel genes including a gene linked to the mating type locus induced by Chlamydomonas fertilization. Mol Cell Biol 7: 2360–2366 (1987).
Frangioni JV, Neel BG: Solubilization and purification of enzymatically active glutathione S-transferase (pGEX) fusion proteins. Anal Biochem 210: 179–187 (1993).
Frohman MA, Dush MK, Martin GR: Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 8998–9002 (1988).
Goodenough UW: Mating interactions in Chlamydomonas. In: Reissig JL (ed) Microbial Interactions, pp. 323–350. Chapman and Hall, London (1977).
Goodenough UW, Adair WS, Collin-Osdoby P, Heuser JE: Chlamydomonas cells in contact. In: Edelman GM, Thiery JP (eds) The Cell in Contact: Adhesions and Junctions as Morphogenetic Determinants, pp. 111–135. John Wiley, New York, (1985).
Goodenough UW: Green yeast. Cell 70: 533–538 (1992).
Gonzalez JC, Banerjee RV, Huang S, Sumner JS, Matthews RG: Comparison of cobalamin-independent and cobalamin-dependent methionine synthases from Escherichia coli: two solutions to the same chemical problem. Biochemistry 31: 6045–6056 (1992).
Harris EH: The Chlamydomonas sourcebook. A comprehensive guide to biology and laboratory use. Academic Press, San Diego, CA (1989).
Horwich AL, Low KB, Fenton WA, Hirshfield IN, Furtak K: Folding in vivo of bacterial cytoplasmic proteins: role for GroEL. Cell 74: 909–917 (1993).
Klar A, Baldassare M, Jessell TM: F-spondin: A gene expressed at high levels in the floor plate encodes a secreted protein that promotes neural cell adhesion and neurite extension. Cell 69: 95–110 (1992).
Kurvari V, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Snell W: A novel protein kinase in Chlamydomonas: An element of a new signaling pathway in fertilization Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, in press.
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685 (1974).
Lefebvre PA, Silflow CD, Wieben ED, Rosenbaum JL: Increased levels of mRNAs for tubulin and other flagellar proteins after amputation or shortening of Chlamydomonas flagella. Cell 20: 469–477 (1980).
Lelias J, Adra CN, Wulf GM, Gruillemot J, Khagad M, Caput D, Lim B: cDNA cloning of a human mRNA preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and with homology to a GDP-dissociation inhibitor for the rho GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 1479–1483 (1993).
Mathur M, Saluja D, Sachar RC: Post-trascriptional regulation of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase from its stored mRNA in germinated wheat embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta 1078: 161–170 (1991).
Matthews RG: Methionine biosynthesis. In: Blakley RL, Benkovic SJ (eds) Folates and Pterins, pp. 497–554, John Wiley, New York (1984).
Pasquale SM, Goodenough UW: Cyclic AMP functions as a primary sexual signal in gametes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol 105: 2279–2292 (1987).
Peleman J, Boerjan W, Engler G, Seurinck J, Botterman J, Alliotte T, Van Montagu M, Inze D: Strong cellular preference in the expression of a housekeeping gene of Arabidopsis thaliana encoding S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. Plant Cell 1: 81–93 (1989).
Peleman J, Saito K, Cottyn B, Engler G, Seurinck J, Van Montagu M, Inze D: Structure and expression of the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene 84: 359–369 (1989).
Pijst HLA, van Driel R, Janssens PMW, Musgrave A, van den Ende H: Cyclic AMP is involved in sexual reproduction of Chlamydomonas eugametos. FEBS Lett 174: 132–136 (1984).
Rognes SE, Lea PJ, Miflin BJ: S-adenosylmethionine, a novel regulator of aspartate kinase. Nature 287: 257–359 (1980).
Rutherford SL, Zuker CS: Protein folding and the regulation of signaling pathways. Cell 79: 1129–1132 (1994).
Sager R, Granick S: Nutritional control of sexuality in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Gen Physiol 37: 729–742 (1954).
Saito T, Small L, Goodenough UW: Activation of adenylyl cyclase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by adhesion and by heat. J Cell Biol 122: 137–147 (1993).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467 (1977).
Sapperstein S, Berkower C, Michaelis S: Nucleotide sequence of the yeast STE14 gene which encodes farnesyl-cysteine carboxyl methyltransferase and demonstration of its essential role in a-Factor export. Mol Cell Biol 14: 1438–1449 (1994).
Schloss JA, Silflow CD, Rosenbaum JL: mRNA abundance changes during flagellar regeneration in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Cell Biol 4: 424–434 (1984).
Schmidt A, Rennenberg H, Wilson LG, Filner P: Formation of methanethiol from methionine by leaf tissue. Phytochemistry 24: 1181–1185 (1985).
Silflow CD, Chisholm RL, Conner TW, Ranum LPW: The two alpha-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii code for slightly different proteins. Mol Cell Biol 5: 2389–2398 (1985).
Sive HL, John TS: A simple subtractive hybridization technique employing photoactivatable biotin and phenol extraction. Nucl Acids Res 16: 10937 (1988).
Snell WJ: Gamete induction and flagellar adhesion in Chlamydomonas reinhardi In: Gantt E (ed) Developmental and Cytological Methods, pp. 37–45. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK (1976).
Snell WJ: Study of the release of cell wall degrading enzymes during adhesion of Chlamydomonas gametes. Exp Cell Res 138: 109–119 (1982).
Snell WJ: Adhesion and signaling in multicellular and unicellular organisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2: 821–832 (1990).
Snell WJ: Signal transduction during fertilization in Chlamydomonas. In: Kurjan J, Taylor BL (eds) Signal Transduction: Procaryotic and Simple Eucaryotic Systems, pp. 255–277, Academic Press, New York (1993).
Snell WJ, Moore WS: Aggregation-dependent turnover of flagellar adhesion molecules in Chlamydomonas gametes. J Cell Biol 84: 203–210 (1980).
Stock J, Surette MG, McCleary WR, Stock AM: Signal transduction in bacteria. J Biol Chem 267: 19753–19756 (1992).
Tabor CW, Tabor H: Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem 53: 749–790 (1984).
Thomas D, Rothstein R, Rosenberg N, Surdin-Kerjan Y: SAM2 encodes the second methionine S-adenosyltransferase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: physiology and regulation of both enzymes. Mol Cell Biol 8: 5132–5139 (1988).
Travis GH, Milner RJ, Sutcliffe JG: Preparation and use of subtractive cDNA hybridization probes for cDNA cloning. In: Boulton AA, Baker GB, Campagnoni AT (eds) Neuromethods, pp. 49–78. Humana Press, Clifton, NJ (1989).
Urbanowski ML, Stauffer LT, Plamann LS, Stauffer GV: A new methionine locus metR that encodes a trans-acting protein required for activation of metE and metH in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bact 169: 1391–1397 (1987).
Urbanowski ML, Stauffer GV: The metH gene from Salmonella typhimurium LT2: cloning and initial characterization. Gene 44: 211–217 (1986).
van den Ende H: Sexual signaling in Chlamydomonas. In: Callow JA, Green JR (eds) Perspectives in Plant Cell Recognition, pp. 1–19, Cambridge University Press, London, (1992).
Weeks DP: Chlamydomonas: an increasingly powerful model plant cell system. Plant Cell 3: 451–456 (1992).
Wegener D, Beck CF: Identification of novel genes specifically expressed in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii zygotes. Plant Mol Biol 16: 937–946 (1991).
Yang SF, Hoffman NE: Ethylene biosynthesis and its regulation in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35: 155–189 (1984).
Youngblom J, Schloss JA, Silflow CD: The two β-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii code for identical proteins. Mol Cell Biol 4: 2686–2696 (1984).
Yu LM, Selman BR: cDNA sequence and predicted primary structure of the γ subunit from the ATP synthase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Chem 263: 19342–19345 (1988).
Zhang Y, Ross EM, Snell WJ: ATP-dependent regulation of flagellar adenylylcyclase in gametes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Chem 266: 22954–22959 (1991).
Zhang Y, Snell WJ: Differential regulation of adenylylcyclases in vegetative and gametic flagella of Chlamydomonas. J Biol Chem 268: 1786–1791 (1993).
Zhang Y, Snell WJ: Flagellar adhesion-dependent regulation of Chlamydomonas adenylyl cyclase in vitro: a possible role for protein kinases in sexual signaling. J Cell Biol 125: 617–624 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurvari, V., Qian, F. & Snell, W.J. Increased transcript levels of a methionine synthase during adhesion-induced activation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii gametes. Plant Mol Biol 29, 1235–1252 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020465
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020465