Abstract
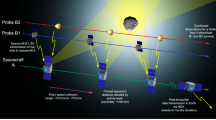
The Genesis spacecraft will collect solar wind samples from a halo orbit about the Sun-Earth L1 point for two years, returning those samples to Earth in 2003 for analysis and examination. The solar wind will imbed itself into a set of ultra-pure material collectors that will be deployed throughout the collection phase of the mission. Analysis of the samples collected by the mission will contribute to our understanding of the origins of the solar system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RAPP, D. et al. “The Suess-Urey Mission,” Acta Astronautica, Vol. 39, No. 1–4, 1996, 229–238.
GOMEZ, G., LLIBRE, J., MARTINEZ, R., and SIMO, C. “Station Keeping of Libration Point Orbits,” Final Report, November 1985, ESA Contract Report, ESCO Contract No. 5648/83/D/JS (SC).
JORDAN, P. SOHO Mission Description and Flight Dynamics Analysis Reports, Rev. 2, September 1993, GSFC Doc. No. 554-FDD-91/026R0UD0.
FARQUHAR, R., MUHONEN, D., and RICHARDSON, D. “Mission Design for a Halo Orbiter of the Earth,” Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, Vol. 14, No. 3, 1977, pp. 170–177.
FARQUHAR, R., MUHONEN, D., NEWMAN, C., and HEUBERGER, H. “The First Libration-Point Satellite: Mission Overview and Flight History,” Paper 79-126, AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Conference, Provincetown, Massachusetts, June, 1979.
FARQUHAR, R., MUHONEN, D., NEWMAN, C., and HEUBERGER, H. “Trajectories and Orbital Maneuvers for the First Libration-Point Satellite,” Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, Vol. 3, No. 6, 1980, pp. 549–554.
HOWELL, K., BARDEN, B., and LO, M. “Application of Dynamical Systems Theory to Trajectory Design for a Libration Point Mission,” The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, Vol. 45, No. 2, April–June 1997, 161–178.
BARDEN, B. Using Stable Manifolds to Generate Transfers in the Circular Restricted Problem of Three Bodies, Masters Thesis, Purdue University, December 1994.
LO, M. and ROSS, S. “Low Energy Interplanetary Transfers Using the Invariant Manifolds of L1, L2, and Halo Orbits,” Paper No. AAS 98-136, AAS Astrodynamics Conference, Monterey, California, February 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The Genesis spacecraft was successfully launched on August 8, 2001. The vehicle will inject into the libration point orbit on November 16, 2001; the return date is September 8, 2004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, M.W., Williams, B.G., Bollman, W.E. et al. Genesis Mission Design. J of Astronaut Sci 49, 169–184 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03546342
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03546342