Abstract
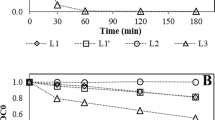
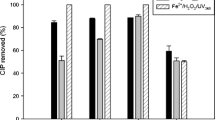
Ultraviolet photolysis and ultraviolet and hydrogen peroxide oxidation of fourteen commonly used pharmaceutical compounds and two personal care products in mixed solution using low pressure ultraviolet lamp was investigated in laboratory batch experiments. Removal of the compounds followed the first-order reaction kinetic. Three distinct impacts of hydrogen peroxide on ultraviolet and hydrogen peroxide oxidation of the compounds (positive, negative and no significant effect) were observed. Removal behavior of the several tested compounds in mixed solution varied significantly than their respective behavior in absence of coexisting compounds. Clofibric acid, diclofenac, fenoprofen, isopropylantipyrine, ketoprofen, phenytoin and triclosan were removed very efficiently (> 96 %) by ultraviolet photolysis alone. Residual hydrogen peroxide during ultraviolet and hydrogen peroxide oxidation was quantitated for the first time. Hydrogen peroxide addition to ultraviolet photolysis was not worthy for majority of the tested compounds as their removal did not increase significantly and very big fractions (> 85 %) of the added hydrogen peroxide (0.29 ∼ 1.47 mM) remained unused presumably due to small fluence of the lamp, very small molar absorption for hydrogen peroxide at 254 nm (27.06 /M.cm) and acidic pH of reaction solution (< 5.7). Further exploration on ultraviolet and hydrogen peroxide oxidation with higher fluence lamp and alkaline solution pH will clarify usefulness of the method to treat pharmaceutical contaminated waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, F. H.; Fauf, M. A.; Ashraf, S. S., (2007). Photolytic oxidation of Safranin-O with H2O2. Dyes Pigm., 72(3), 349–352 (4 pages).
Aina, M.; Matejka, G.; Mama, D.; Yao, B.; Moudachirou, M., (2009). Characterization of stabilized waste: Evaluation of pollution risk. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(1), 59–165 (7 pages).
Alshamsi, F. A.; Albadwawi, A. S.; Alnuaimi, M. M.; Rauf, M. A.; Ashraf, S. S., (2007). Comparative efficiencies of the degradation of crystal violet using UV/hydrogen peroxide and fenton’s reagent. Dyes Pigm., 74(2), 283–287 (5 pages).
Andreozzi, R.; Capiro, V.; Marotta, R.; Radovnikovic, A., (2003). Ozonation and H2O2/UV treatment of clofibric acid in water: a kinetic investigation. J. Hazard. Mater., 103(3), 233–246 (14 pages).
Baumgarten, S.; Schroder, H. F.; Charwath, C.; Lange, M.; Beier, S.; Pinnekamp, J., (2007). Evaluation of advanced treatment technologies for the elimination of pharmaceutical compounds. Water Sci. Tech., 56(5), 1–8 (8 pages).
Canonica, S.; Meunier, L.; Gunten, U. V., (2008). Phototransformation of selected pharmaceuticals during UV treatment of drinking water. Water Res., 42(1-2), 121–128 (8 pages).
Fagbote, E. O.; Olanipekun, E. O., (2010). Levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediment of bitumen deposit impacted area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(3), 561–570 (10 pages).
Giri, R. R.; Ozaki, H.; Ishida, T.; Takanami, R.; Taniguchi, S., (2007). Synergy of ozonation and photocatalysis to mineralize low concentration 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, 66(9), 1610–1617 (8 pages).
Giri, R. R.; Ozaki, H.; Ota, S.; Takanami, R. Taniguchi, S., (2010). Degradation of common pharmaceuticals and personal care products in mixed solutions by advanced oxidation techniques. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(2), 251–260 (10 pages).
Igwe, J. C.; Abia, A. A.; Ibeh, C. A., (2008). Adsorption kinetics and intraparticulate diffusivities of Hg, As and Pb ions on unmodified and thiolated coconut fiber. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(1), 83–92 (10 pages).
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R. M.; Guwy, A. J., (2009). The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Res., 43(2), 363–380 (18 pages).
Kim, I. H.; Tanaka, H.; Iwasaki, T.; Takubo, T.; Morioka, T.; Kato, Y., (2008). Classification of the degradability of 30 pharmaceuticals in water with ozone, UV and H2O2. Water Sci. Tech., 57(2), 195–200 (6 pages).
Lin, A. Y.; Reinhard, M., (2005). Photodegradation of common environmental pharmaceuticals and estrogens in river water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 24(6), 1303–1309 (7 pages).
Lopez, A.; Bozzi, A.; Mascolo, G.; Kiwi, J., (2003). Kinetic investigation on UV and UV/H2O2 degradations of pharmaceutical intermediates in aqueous solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A., 156(1-3), 121–126 (6 pages).
Pereira, V. J.; Linden, K. G.; Weinberg, H. S., (2007b). Evaluation of UV irradiation for photolytic and oxidative degradation of pharmaceutical compounds in water. Water Res., 41(19), 4413–4423 (11 pages).
Pereira, V. J.; Weinberg, H. S.; Linden, K. G.; Singer, P. C., (2007a). UV degradation kinetics and modeling of pharmaceutical compounds in laboratory grade and surface water via direct and indirect photolysis at 254 nm. Environ. Sci. Tech., 41(5), 1682–1688 (7 pages).
Perkowski, J.; Ledakowicz, S., (2002). Decomposition of anthraquinone dye in the aqueous solution during advanced oxidation processes. Fibres and Textiles in Eastern Europe, October/December, 68–72 (5 pages).
Qiao, R. P.; Ma, Y. M.; Qi, X. H.; Li, N.; Jin, X. C.; Wang, Q. S.; Zhuang, Y. Y., (2005). Degradation of microcystin-RR by combination of UV/H2O2 technique. Chin. Chem. Lett., 16(9), 1271–1274 (4 pages).
Rauf, M. A.; Ashraf, S.; Alhadrami, S. N., (2005). Photolytic oxidation of Coomassie brilliant blue with H2O2. Dyes Pigm., 66(3), 197–200 (4 pages).
Samarghandi, M. R.; Nouri, J.; Mesdaghinia, A. R.; Mahvi, A. H.; Nasseri, S.; Vaezi, F., (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/ TiO2/ H2O2 processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 19–26 (8 pages).
Shah, B. A.; Shah, V. A.; Singh, R. R., (2009). Sorption isotherms and kinetics of chromium uptake from wastewater using natural sorbent material. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(1), 77–90 (14 pages).
Shu, H. Y.; Chang, M. C., (2006). Development of a rate expression for predicting decolorization of C. I. Acid Black 1 in a UV/H2O2 process. Dyes Pigm., 70(1), 31–37 (6 pages).
Vonga, D.; Marotta, R.; Napolitano, A.; Andreozzi, R.; d’lschia, M., (2004). Advanced oxidation of the pharmaceutical drug diclofenac with UV/H2O2 and ozone. Water Res., 38(2), 414–422 (9 pages).
Yuan, F.; Hu, C.; Hu, X.; Qu, J.; Yang, M., (2009). Degradation of selected pharmaceuticals in aqueous solution with UV and UV/H2O2. Water Res., 43(6), 1766–1774
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giri, R.R., Ozaki, H., Takayanagi, Y. et al. Efficacy of ultraviolet radiation and hydrogen peroxide oxidation to eliminate large number of pharmaceutical compounds in mixed solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 19–30 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326192
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326192