Abstract
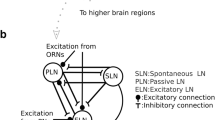
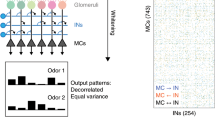
It has been suggested that in the olfactory bulb, odor information is processed through parallel channels and learning depends on the cognitive environment. The synapse’s spike effective time is defined as the effective time for a spike from pre-synapse to post-synapse, which varies with the type of synapse. A learning model of the olfactory bulb was constructed for synapses with varying spike effective times. The simulation results showed that such a model can realize the multi-channel processing of information in the bulb. Furthermore, the effect of the cognitive environment on the learning process was also studied. Different feedback frequencies were used to express different attention states. Considering the information’s multi-channel processing requirement for learning, a learning rule considering both spike timing and average spike frequency is proposed. Simulation results showed that habituation and anti-habituation of an odor in the olfactory bulb might be the result of learning guided by a common local learning rule but at different attention states.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laurent, G., Dynamical representation of odors by oscillating and evolving neural assemblies, Trends in Neurosciences, 1996, 19: 489–496.
Laurent, G., Wehr, M., Davidowitz, H., Temporal representations of odors in an olfactory network, J. Neuroscience, 1996, 16: 3837–3847.
Laurent, G., Macleod, K., Stopfer, M. et al., Spatiotemporal structure of olfactory inputs to the mushroom bodies, Learning & Memory, 1998, 5: 124–132.
Laurent, G., A systems perspective on early olfactory coding, Science, 1999, 286: 723–728.
MacLeod, K., Laurent, G., Distinct mechanisms for synchronization and temporal patterning of odor-encoding neural assemblies, Science, 1996, 274: 976–979.
Mori, K., Relation of chemical structure to specificity of response in olfactory glomeruli, Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 1995, 5: 467–474.
Mori, K., Nago, H., Yohihara, Y., The olfactory bulb: Coding and processing of odor molecule information, Science, 1999, 286: 711–715.
Stopfer, M., Bhagavan, S., Smith, B. H. et al., Impaired odour discrimination on desynchronization of odour-ecoding neural assemblies, Nature, 1997, 390: 70–74.
Buonviso, N., Chaput, M., Olfactory experience decreases responsiveness of the olfactory bulb in the adult rat, Neuroscience, 2000, 95(2): 325–332.
Faber, T., Joerges, J., Menzel, R., Associative learning modifies neural representations of odors in the insect brain, Nature Neuroscience, 1999, 2: 74–78.
Wilson, D. A., Sullivan, R. M., Leon, M., Odor familiarity alters mitral cell response in the olfactory bulb of neonatal rats, Brain Research, 1985, 22: 314–317.
Gray, C. M., Skinner, J. E., Field potential response change in the rabbit olfactory bulb accompany behavioral habituation during the repeated presentation of unreinforced odors, Experimental Brain Research, 1998, 73: 189–197.
Hiroshi, Fujii, Hiroyuki, Ito, Kazuyuki, Aihara et al., Dynamical cell assembly hypothesis theoretical possibility of spa- tio-temporal coding in the cortex, Neural Networks, 1996, 9(8): 1303–1350.
Hendin, O., Horn, D., Tsodyks, M. V., Associative memory and segmentation in an oscillatory neural model of the olfactory bulb, Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 1998, 5(2): 157–169.
Nicoll, R. A., Jahr, C. E., Self-excitation of olfactory bulb neurons, Nature, 1982, 296(5856): 441–444.
Davison, A. P., Feng, J., Brown, D., Structure of lateral inhibition in an olfactory bulb model, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1999, 1606: 189–196.
Bi, G. Q., Poo, M. M., Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type, J. Neuroscience, 1998, 18(24): 10464–10472.
Sejnowski, T. J., The book of Hebb, Neuron, 1999, 24(4): 773–776.
Tsien, J. Z., Linking Hebb’s coincidence-detection to memory formation, Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 2000, 10(2): 266–273.
Turrigiano, G. G., Nelson, S. B., Hebb and homeostasis in neuronal plasticity, Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 2000, 10(3): 358–364.
Viana, D., Prisco, G., Hebb synaptic plasticity, Progress in Neurobiology, 1984, 22(2): 89–102.
Hendin, O., Horn, D., Tsodyks, M. V., The role of inhibition in an associative memory model of the olfactory bulb, Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 1997, 4(2): 173–182.
Linster, C., Hasselmo, M., Modulation of inhibition in a model of olfactory bulb reduces overlap in the neural representation of olfactory stimuli, Behavioural Brain Research, 1997, 84(1–2): 117–127.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, B., Wang, S., Li, Y. et al. Function of attention in learning process in the olfactory bulb. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 46, 358–369 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192579
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192579