Summary
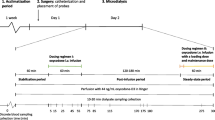
Pregabalin [PGB, (S)-3-isobutyl GABA, CI-1008] is a derivative of the inhibitory neurotransmitter g-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It has shown anticonvulsant, analgesia and anxiety activity in animal models. In this report, blood-brain barrier (BBB) influx and efflux of PGB were investigated with microdialysis at efficacious doses in rats.
BBB influx (CLin) and efflux (CLout) permeability for pregabalin were 4.8 and 37.2 μL/min/g brain, respectively, following an intravenous infusion to rats. The results indicate that PGB is brain pentrable, supporting its anti-epilepsy and other CNS pharmacology. Significant anticonvulsant action of PGB was detected between 2 and 8 hr post oral dose, which is lag behind ECF drug concentrations lees. A PK/PD link model was used to describe the counter-clockwise hysteresis relationship between pregabalin brain ECF concentration and the anticonvulsant effect in rats. The resulting Ce (concentration in effect compartment) versus effect profile exhibits a sigmoidal curve and the calculated ECe50 and Keo values were 95.3 ng/mL and 0.0092 min-1, respectively. The small Keo value suggests that the effect is not directly proportional to the amount of pregabalin in the ECF compartment possibly due to inherent delay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- (BBB):
-
blood-brain barrier
- (CLin):
-
influx
- (CLout):
-
and efflux
- (ECF):
-
permeability, brain extracellular fluid
- (IV):
-
intravenous
- (CNS):
-
central nervous system
References
Su T. Z., Lunney E., Campbell G., and Oxender D. (1995). Transport of Gabapentin, a g-amino acid drug, by system L a-amino acid transporters: a comparative study in astrocytes, synaptosomes, and CHO cells. J. Neurochem. 64:2125–2131.
Wang Y. and Welty D. E. (1996). The simultaneous estimation of influx and efflux blood-brain barrier permeability of gabapentin using a microdialysis-pharmacokinetic approach. Pharm. Res. 3, 398–403.
Wang Y. and Wong L., and Sawchuck R. (1993). Microdialysis calibration using retrodialysis and zero-net influx: Application to a study of the distribution of zidovudine in rabbit CSF and thalamus. Pharm. Res. 10, 1411–1419.
Triguero D., Buciak J., Pardridge M. (1990). Capillary depletion method for quantification of blood-brain barrier transport of circulating peptide and plasma proteins. J. Neurochem., 6: 1882–1888.
Welty D., Schielke G., Vartanian M., and Taylor C. (1993). Gabapentin anticonvulsant action in rats: disequilibrium with peak drug concentrations in plasma and brain microdialysate. Epilepsy Res. 16: 175–181.
Sheiner L., Stanski D., Vozeh S., Miller R., and Ham J. (1979) Simultaneous modeling of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic: application to d-tubocurarine. Clin. Pharmacol Ther 3:358–371.
Verotta D. and Sheiner L. (1995). A general conceptual model for non-steady state pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic data. J Pharmacokin Biopharm 23(1):1–4.
Radukovic L., Türck D., Von Hodenberg A., Vollmer K., McNally M., Drhart P., Hanson B., Bockbrader H., Chang T. (1995). Disposition of gabapentin (Neurotin) in mice, rats, dogs, and monkeys. Drug Met. Disp. 23:441–448.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, M.R., Turluck, D., Burleigh, J. et al. Brain microdialysis and PK/PD correlation of pregabalin in rats. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 26, 123–128 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190385
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190385