Abstract
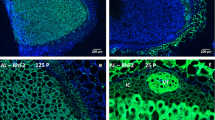
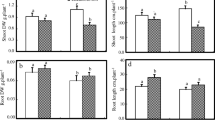
Changes in growth, symbiotic nitrogen fixation (SNF), acid phosphatase (ACP), and phytase activities to phosphorus availability (15 and 60 μmol KH2PO4 plant−1 week−1) were compared in two recombinant lines (115 and 147) of common bean. Plant growth, nodulation and SNF were genotype and P level-dependent. 147 was more affected by P shortage (15 μmol P) than 115. Four ACP types were revealed in the nodules of both lines, ACP1 exhibiting a higher specific activity under P shortage as compared to the 60 μmol P treatment, especially in 115. A single phytase was revealed for the nodules of both lines and was significantly enhanced by P deficiency. Three ACP types were found in roots and leaves, showing increasing activity under P deficiency, especially in 115. Regardless of P supply, leaf ACP specific activity was higher than that of nodules and roots in the both lines. Interestingly, phosphorus use efficiency for N2 fixation significantly correlated to nodule ACP activity under P shortage in the both lines. The relatively better performance of 115 as compared to 147 under P deficiency could be partly ascribed to the ability of 115 to maintain higher ACP activity. This enzyme might be involved in the remobilization of the plant Pi and its utilization for SNF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriotis, V.M.E and Ross, J.D. 2003. Isolation and characterisation of phytase from dormantCorylus avellana seeds.Phytochemistry 64: 689–699.
Araújo, A.P., Plassard, C., and Drevon, J.J. 2008. Phosphatase and phytase activities in nodules of common bean genotypes at different levels of phosphorus supply.Plant and Soil DOI 10.1007/s11104--008-9595-3.
Broughton, W.J., Hernández, G., Blair, M., Beebe, S., Gepts, P., and Vanderleyden, J. 2003. Beans (Phaseolus spp.) — model food legume.Plant and Soil 252: 55–128.
Chen, W.S., Huang, Y.F., and Chen, Y.R. 1992. Localization of acid phosphatase in root cap of rice plant.Botany Bulletin Academy Sin 33: 233–239.
Coello, P. 2002. Purification and characterization of secreted acid phosphatase in phosphorus-deficientArabidopsis thaliana.Physiologia Plantarum 116: 293–298.
Doremus, H.D. and Blevins, D.G. 1988. Nucleoside diphosphatase and 5′-nucleotidase activities of soybean root nodules and other tissues.Plant Physiology 87: 36–40.
Duff, S.M.G., Sarath, G., and Plaxton, W.C. 1994. The role of acid phosphatases in plant phosphorus metabolism.Physiologia Plantarum 90: 791–800.
Fernandez, D.S. and Ascencio, J. 1994. Acid phosphatase activity in bean and cowpea plants grown under phosphorus stress.Journal of Plant Nutrition 17: 229–241.
George, T.S., Richardson, A.E., Hadobas, P., and Simpson, R.J. 2004. Characterisation of transgenicTrifolium subterraneum L. which expresses phyA and releases extracellular phytase: growth and P nutrition in laboratory media and soil.Plant Cell Environment 27: 1351–1361.
Goldstein, A.H. 1992. Phosphate starvation inducible enzymes and proteins in higher plants. In: Society for Experimental Biology Seminar Series 49:Inducible Plant Proteins. Wray, J.L., ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambrige, UK. pp. 25–44.
Graham, P.H., Rosas, J.C., Estevez de Jensen, C., Peralta, E., Tlusty, B., Acosta-Gallegos, J., and Arraes Pereira, P.A. 2003. Addressing edaphic constraints to bean production: the bean/cowpea CRSP project in perspective.Field Crop Research 82: 179–192.
Guranowski, A. 1982. Purine catabolism in plants.Plant Physiology 70: 344–349.
Gustafsson, E. and Sandberg A.S. 1995. Phytate reduction in brown beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L).Journal of Food Science 60: 149–152.
Hardarson, G., Bliss, F.A., Cigales-Rivero, M.R., Henson, R.A., Kipe-Nolt, J.A., Longeri, L., Manrique, A., Pena-Cabrieles, J.J., Pereira, P.A.A., Sanabria, C.A., and Tsai, S.M. 1993. Genotypic variation in biological nitrogen fixation by common bean.Plant and Soil 152: 59–70.
Haran, S., Logendra, S., Seskar, M., Bratanova, M., and Raskin, I. 2000. Characterization ofArabidopsis acid phosphatase promoter and regulation of acid phosphatase expression.Plant Physiology 124: 615–626.
Hayes, J.E., Richardson, A.E., and Simpson, R.J. 1999. Phytase and acid phosphatase activities in extracts from roots of temperate pasture grass and legume seedlings.Australian Journal of Plant Physiology 26: 801–809.
Hernández, G., Ramírez, M., Valdés-López, 0., Tesfaye, M., Graham, M.A., Czechowski, T., Schlereth, A., Wandrey, M., Erban, A., Cheung, F., Wu, H.C., Lara, M., Town, C.D., Kopka, J., Udvardi, M.K., and Vance, C.P. 2007. Phosphorus stress in common bean: Root transcript and metabolic responses.Plant Physiology 144: 752–767.
Hinsinger, P. 2001. Bioavailability of soil inorganic phosphorus in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes — a review.Plant and Soil 13: 173–195.
Ingestad, T. 1981. Nutrition and growth of birch and grey alder seedlings in low conductivity solutions and at varied relative rates of nutrient addition.Physiologia Plantarum 52: 454–466.
Lee, D.H. 1998. Phosphorus use efficiency in anthocyanin-free tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.).Journal of Plant Biology 41: 86–92.
Li, S.M., Li, L., Zhang, F.S., and Tang, C. 2004. Acid phosphatase role in chickpea/maize intercropping.Annals of Botany 94: 297–303.
Loewus, R.A., Everard, J.D., and Young, K.A. 1990. Inositol metabolism: Precursor role and breakdown. In:Inositol Metabolism in Plants. Morre, D.J., Boss, W.F., and Loewus, F.A., eds. Wiley-Liss, New York. pp. 21–45.
Lynch, J. 1995. Root architecture and plant productivity.Plant Physiology 109: 7–13.
McLachlan, K.D., Elliott, D.E., De Marco, D.G., and Garran, J.H. 1987. Leaf acid phosphatase isozymes in the diagnosis of phosphorus status in field-grown wheat.Australian Journal of Agriculture Research 38: 1–13.
Mikulska, M., Bomsel, J.L., and Rychter, A.M. 1998. The influence of phosphate deficiency on photosynthesis, respiration and adenine nucleotide pool in bean leaves.Photosynthetica 35: 79–88.
Mudge, S.R., Smith, F.W., and Richardson, A.E. 2003. Root specific and phosphate regulated expression of phytase under the control of a phosphate transporter promoter enablesArabidopsis to grow on phytate as a sole P source.Plant Science 165: 871–878.
Penheiter, A.R., Duff, S.M.G., and Sarath, G. 1997. Soybean root nodule acid phosphatase.Plant Physiology 114: 597–604.
Plaxton, W.C. and Carswell, M.C. 1999. Metabolic aspects of the phosphate starvation response in plants. In:Plant Responses to Environmental Stresses: From Phytohormones to Genome Reorganization. Lerner, H.R., ed, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp. 349–372.
Ribet, J. and Drevon, J.J. 1995. Increase in permeability to oxygen and in oxygen uptake of soybean nodules under limiting phosphorus nutrition.Physiologia Plantarum 94: 298–304.
Richardson, A.E., George, T.S., Hens, M., and Simpson, R.J. 2004. Utilisation of soil organic phosphorus by higher plants. In:Organic Phosphorus in the Environment. Turner, B.L., Frossard, E., and Baldwin, D., eds. CABI Publishing, Wallingford. pp. 165–184.
Roux, M.R., Ward, C.L., Botha, F.C., and Valentine A.J. 2006. Routes of pyruvate synthesis in phosphorus-deficient lupin roots and nodules.New Phytologist 169: 399–408.
Rychter, A.M. and Randall, D.D. 1994. The effect of phosphate deficiency on carbohydrate metabolism in bean roots.Physiologia Plantarum 91: 383–388.
Sandberg, A.-S. 2002. Bioavailability of minerals in legumes.British Journal of Nutrition 88: 281–285.
Schachtman, D.P., Reid, R.J., and Ayling, S.M. 1998. Phosphorus uptake by plant: from soil to cell.Plant Physiology 116: 447–453.
Schubert, K.R. 1981. Enzymes of purine biosynthesis and catabolism inGlycine max.Plant Physiology 68: 1115–1122.
Scott, J.J. 1991. Alkaline phytase activity in nonionic detergent extracts of legume seeds.Plant Physiology 95: 1298–1301.
Shang, C., Stewart, J.W.B., and Huang, P.M. 1992. pH effect on kinetics of adsorption of organic and inorganic phosphates by short-range ordered aluminium and iron precipitates.Geoderma 53: 1–14.
Sprent, J.I. 1988.The Ecology of the Nitrogen Cycle. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Steiner, T., Mosenthin, R., Zimmermann, B., Greiner, R., and Roth, S. 2007. Distribution of phytase activity, total phosphorus and phytate phosphorus in legume seeds, cereals and cereal by-products as influenced by harvest year and cultivar.Animal Feed of Science Technology 133: 320–334.
Tarafdar, J.C. and Claasen, N. 1988. Organic phosphorus compounds as a phosphorus source for higher plants through the activity of phosphatases produced by plant roots and microorganisms.Biology of Fertile Soils 5: 3308–3312.
Turner, B.L., Mahieu, N., and Condron, L.M. 2003. Quantification of myoinositol hexaphosphate in alkaline soil extracts by solution 31P-NMR spectroscopy and spectral deconvolution.Soil Science 168: 469–478.
Vadez, V., Rodier, F., Payre, H., and Drevon, J.J. 1996. Nodule permeability to O2 and nitrogenase-linked respiration in bean genotypes varying in the tolerance of N2 fixation to P deficiency.Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 34: 871–878.
Vadez, V., Lasso, J.H., Beck, D.P., and Drevon, J.J. 1999. Variability of N2-fixation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under P deficiency is related to P use efficiency.Euphytica 106: 231–242.
Wasaki, J., Omura, M., Osaki, M., Ito, H., Matsui, H., Shinano, T., and Tadano, T. 1999. Structure of a cDNA for an acid phosphatase from phosphate-deficient lupin (Lupinus albus L.) roots.Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science 45: 439–449.
Wasaki, J., Yamamura, T., Shinano, T., and Osaki, M. 2003. Secreted acid phosphatase is expressed in cluster roots of lupin in response to phosphorus deficiency.Plant and Soil 248: 129–136.
Werner, D. 2005. Production and biological nitrogen fixation of tropical legumes. In:Nitrogen Fixation in Agriculture, Forestry, Ecology and the Environment. Springer, Dordrecht. pp. 1–13.
Xiao, K., Katagi, H., Harrison, M., and Wang, Z.Y. 2006. Improved phosphorus acquisition and biomass production in Arabidopsis by transgenic expression of a purple acid phosphatase gene fromM. truncatula.Plant Science 170: 191–202.
Yadav, R.S. and Tarafdar, J.C. 2003. Phytase and phosphatase producing fungi in arid and semi-arid soils and their efficiency in hydrolyzing different organic P compounds.Soil Biology and Biochemistry 35: 1–7.
Yan, X., Liao, H., Trull, M.C., Beebe, S.E., and Lynch, J.P. 2001. Induction of a major leaf acid phosphatase does not confer adaptation to low phosphorus availability in common bean.Plant Physiology 125: 1901–1911.
Yun, S.J. and Kaeppler, S.M. 2002. Induction of maize acid phosphatase activities under phosphorus starvation.Plant and Soil 237: 109–115.
Zimmermann, P., Zardi, G., Lehmann, M., Zeder, C., Amrhein, N., Frossard, E., and Bucher, M. 2003. Engineering the root-soil interface via targeted expression of a synthetic phytase gene in trichoblasts.Plant Biotechnology Journal 1: 353–360.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kouas, S., Louche, J., Debez, A. et al. Effect of phosphorus deficiency on acid phosphatase and phytase activities in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Symbiosis 47, 141–149 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179974
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179974