Abstract
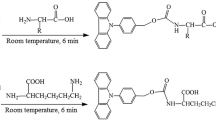
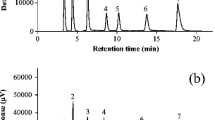
This study was performed in order to validate an effective high performance liquid chromatograpy (HPLC) method to determine L-carnitine in biological samples such as plasma, milk and muscle in cows. An L-carnitine derivative for fluorescence absorption was synthesized with 1-aminoanthracene (16 mg/mL in acetone) and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDAC; 160 mg/mL in 0.01 M NaH2PO4 buffer) as a precolumn fluorescent derivative reagent. γ-Butyrobetaine HCI was used as an internal standard. A reversed-phase column with fluorescence detection at the excitation and emission wavelengths of 248 and 418 nm were used. The mobile phase consisted of 30% acetonitrile with 0.1 M ammonium acetate in water (pH 3.5) adjusted with acetic acid and delivered at a flow rate of 1.5 mL/ min. The L-carnitine concentration in plasma, milk and muscle samples of cows after oral feeding with 24 g L-carnitine/day for 2 months was then determined. All biological samples were deproteinated by barium hydroxide and zinc sulfate heptahydrate before the derivative reaction. Blank cow plasma was dialyzed using cellulose membrane for standard calibration. The calibration curve showed good linearity (r2 >0.999) over the concentration range of 50 to 5000 ng/mL The precision and accuracy were also satisfactory with less than 15% intra- and inter-day coefficiency of variations. The peaks of L-carnitine and internal standard in HPLC chromatography were successfully separated in plasma, milk and muscle samples of cows. The current derivatization method of L-carnitine for fluorescence detection was simple and adequately sensitive and could be applied to determine L-carnitine in biological samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brass E. P., Pharmacokinetic considerations for the therapeutic use of carnitine in hemodialysis patients.Clin. Ther., 17, 176–185 (1995).
Bremer J., Carnitine: Metabolism and functions.Physiol. Rev., 63, 1420–80 (1983).
Campos Y., Huertas R., Bautista J., Gutierrez E., Aparicio M., Lorenzo G., Segura D., Villanueva M., Cabello A., Alesso L., and Arenas J., Muscle carnitine deficiency and liquid storage in patients with mitochondrial myopaty.Muscle Nerve, 16, 778–781 (1993).
Di Donato, S., Disorders of lipid metabolism affecting skeletal muscle: Carnitine deficiency syndromes, defects in the catabolic pathway, and Chanarin disease. In: Engel AG, Franzini-Armstrong C, editors. Myology, 2nd ed., New York: McGraw Hill, 1587–1609 (1994).
Kamimori, H., Hamashima, Y., and Konishi, M., Determination of carnitine and saturated-acyl group carnitines in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection.Anal Biochem., 218, 417–424 (1994).
Kuroda, N., Ohyama, Y., Nakashima, K., Nakashima, K., and Akiyama, S., HPLC determination of carnitine and acylcar- nitines in human plasma by means of fluorescence labeling using 2-(4-hydrazinocarbonylphenyl)-4,5-diphenylimidazole.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 44, 1525–1529 (1996).
Longo, A., Bruno, G., Curti, S., Mancinelli, A., and Miotto, G., Determination of L-carnitine, acetyl-L-carnitine and propionyl- L-carnitine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization with 1- aminoanthracen.J. Chromatography B., 686, 129–139 (1996).
Marzo, A. and Curti, S., L-carnitine moiety assay: an up-to-date reappraisal covering the commonest methods for various applications.J. Chromatography B., 702, 1–20 (1997).
Minker, P. E. and Hoppel, C. L, Quantification of carnitine and specific acylcarnitines by high-performance liquid chroma-tography: application to normal human urine and urine from patients with methylmalonic aciduria, isovaleric acidemia or medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency.J. Chromatography B., 613, 203–221 (1993).
O’connell, S. E. and Zurzola, F. J., A rapid quantitative determination of acetaminophen in plasma.J. Phanv. Sci., 71,1291–1294 (1982).
Siliprandi, N., Sartorelli, L, Ciman, M., and Di Lisa, F., Carnitine: Metabolism and clinical chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta., 183, 3–12 (1989).
Takeyama, N., Matsuo, N., Takagi, D., and Tanaka, T., Determination of overt carnitine palmitoyltransferase by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography.J. Chromatography B., 491, 69–76 (1989).
Yoshida, T., Aetake, A., Yamaguchi, H., Nimura, N., and Kinoshita, T., Determination of carnitine by high-performance liquid chromatography using 9-anthryldiazomethane.J. Chromatography A, 445,175–182 (1988).
Van Kempen Theo, A. T. G. and Odle, J., Quantification of carnitine esters by high-performance liquid chromatography: Effect of feeding medium-chain triglycérides on the plasma carnitine ester profile.J Chromatography: Biomédical Applications, 584,157–165 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, QR., Ren, S., Park, MJ. et al. Determination of highly soluble L-Carnitine in biological samples by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescent derivatization. Arch Pharm Res 30, 1041–1046 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02993974
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02993974