Abstract
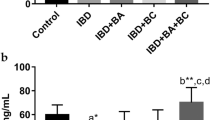
We had previously reported that the protective effect of taurine against indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury was due to its antioxidant effects, which inhibited lipid peroxidation and neutrophil activation. In this study, we examined the effect of taurine on reducing the inflammatory parameters of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), in rats. In order to induce IBD, ethanolic TNBS was given to rats intracolonically. Then they received 500 mg/kg/day of taurine orally and were sacrificed one week after IBD induction. While ulceration and inflammation of distal colon with formation of granuloma in the vehicle-treated IBD rats two days after administration of TNBS were observed, treatment with taurine ameliorated colonic damage and decreased the incidence of diarrhea and adhesion. Also, colon weight as an index of tissue edema, which was markedly increased in the IBD rats, became significantly lower after taurine treatment. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in the vehicle-treated IBD rats was substantially increased, compared with that of normal control. The taurine-treated animals significantly reduced MPO activity (35% lower) when compared with that of the vehicle-treated animals. Taurine treatment decreased both basal and formyl-methionyl leucyl phenylalanine-stimulated reactive oxygen generation from colonic tissue in the IBD rats. These results suggest that the administration of taurine reduce the inflammatory parameters in this IBD rat model by increasing defending capacity against oxidative damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Boughton-Smith, N. K., Wallace, J. L., Morris, G. P. and Whittle, B. J. R., The effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on eicosanoid formation in a chronic model of inflammatory bowel disease in the rat.Br. J. Pharmacol., 94, 65–72 (1988).
Buffinton, G. D. and Doe, W. F., Depleted mucosal antioxidant defences in inflammatory bowel disease.Free Rad. Biol. Med., 19, 911–918 (1995).
Fukuda, K., Hirai, Y., Yoshida, H., Hakajiman, T. and Usii, T., Free amino acid content of lymphocytes and granulocytes compared.Clin. Chem., 28, 1758–1761 (1982).
Green, T. R., Fellman, J. H., Eicher, A. L. and Pratt, K. J., Antioxidant role and subcellular location of hypotaurine and taurine in human neutrophils.Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1073, 91–97 (1991).
Gurujeyalakshmi, G., Iyer, S. N., Hollinger, M. A. and Giri, S. N., Procollagen gene expression is down-regulated by taurine and niacin at the transcriptional level in the bleomycin hamster model of lung fibrosis.J. Pharm. Exp. Ther., 277, 1152–1157 (1996).
Kim, C., Park, E., Quinn, M. R. and Schuller-Levis, G., The production of superoxide anion and nitric oxide by cultured murine leukocytes and the accumulation of TNF-α in the conditioned media is inhibited by taurine chloramine.Immunopharm., 34, 89–95 (1996).
Krawisz, J. E., Sharon, P. and Stenson, W. F., Quantitative assay for acute intestinal inflammation based on myeloperoxydase activity. Assessment of inflammation in rat and hamster models.Gastroenterology, 87, 1344–1350 (1984).
McLoughlin, D. M., Stapleton, P. P. and Bloomfield, F. J., Influence, of Taurine and a substituted taurine on the respiratory burst pathway in the inflammatory response.Biochem. Soc. Trans., 19, 73–78 (1991).
McKenzie, S. J., Baker, M. S., Buffinton, G. D. and Doe, W. F., Evidence of oxidant induced injury to epithelial cells during inflammatory bowel disease.J. Clin. Invest., 98, 136–141 (1996).
Morris, G. P., Beck, P. L., Herridge, W., Szewczuk, M. R. and Wallace, J. L., Hapten-induced model of chronic inflmmation and ulceration in the rat colon.Gastroenterology, 96, 759–803 (1989).
Murakami, M., Asagoe, K., Dekigai, H., Kusaka, S., Saita, H. and Kita, T., Products of neutrophil metabolism increase ammonia-induced gastric mucosal damage.Dig. Dis. Sci., 40, 268–273 (1995).
Nielsen, O. H., Berild, D. and Ahnfelt-Ronne, I.,In vitro superoxide production by peripheral neutrophils from patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Mediat. Inflam., 3, 161–164 (1994).
Pfeiffer, C. J. and Qiu, B. S., Effects of chronic nitric oxide synthase inhibition on TNBS-induced colitis in rats.J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 47, 827–832 (1995).
Quinn, M. R., Park, E. and Schuller-Levis, G., Taurine chloramine inhibits prostaglandin E2 production in activated Raw 264.7 cells by post-transcriptional effects on inducible cyclooxygenase expression.Immunol. Letters., 50, 185–188 (1996).
Sartor, R. B., Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: pathophysiological and clinical considerations.Gastroenterology, 106, 533–539 (1994).
Schuller-Levis, G., Quinn, M. R., Wright, C. and Park, E., Taurine protects against oxidant-induced lung injury: possible mechanism(s) of action, In Huxtable, R. (Ed.)Taurine in health and disease. Plenum Press, New York, pp. 31–39, 1994.
Sharon, P. and Stenson, W. F., Enhanced synthesis of leukotriene B4 by colonic mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease.Gastroenterology, 86, 453–460 (1984).
Simmonds, N. J., Allen, C. R., Stevens, T. R., Van Someren, R. N. M., Blake, D. R. and Rampton, D. S., Chemiluminescence assay of mucosal reactive oxygen metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease.Gastroenterology, 103, 186–196 (1992).
Son, M., Kim, H. K., Kim, W. B., Yang, J. and Kim, B. K., Protective effect of taurine on indomethacininduced gastric mucosal injury, In Huxtable, R. J., Azuma, J., Kuriyama, K., Nakagawa, M. and Baba, A. (Eds.).Taurine 2. Plenum Press, New York. pp. 147–155, 1996.
Stapleton, P. P., Molloy, A. M., Rogers, S. and Bloomfield, F. J., Neutrophil taurine in psoriasis.Ir. J. Med. Sci., 165, 173–176 (1996).
Tamai, H., Kachur, J. F., Grisham, M. B. and Gaginella, T. S., Scavenging effect of 5-aminosalicylic acid on neutrophil-derived oxidants: Possible contribution to the mechanism of action in inflammatory bowel disease.Biochem. Pharm., 41, 1001–1006 (1991).
Test, S. T., Lampert, M. P., Ossanna, P. J., Thoene, J. G. and Weiss, S. J., Generation of nitrogen-chlorine oxidants by human phagocytes.J. Clin. Invest., 74, 1341–1349 (1984).
Wang, Q., Giri, S. N., Hyde, D. M. and Nakashima, J. M., Effects of taurine on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in hamsters.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 190, 330–338 (1989).
Whittle, B. J. R., Temporal relationship between cyclooxygenase inhibition measured as prostacyclin biosynthesis and gastrointestinal damage induced by indomethacin in the rat.Gastroenterology, 80, 94–98 (1981).
Wright, C. E., Lin, T. T., Lin, Y. Y., Sturman, J. and Gaull, G., Taurine scavenges oxidized chlorine in biological systems.Prog. Clin. Biol. Res., 179, 113–123 (1985).
Yamada, T. and Grisham, M. B., Role of neutrophilderived oxidants in the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation.Klin. Wochenschift., 69, 988–944 (1991).
Yue, G., Sun, F. F., Dunn, C., Yin, K. and Wong, P. Y. K., The 21-aminosteroid tirilazad mesylate can ameliorate inflammatory bowel disease in rats.J. Pharm. Exp. Ther., 276, 265–270 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, M.W., Ko, J.I., Doh, H.M. et al. Protective effect of taurine on TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 21, 531–536 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975370
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975370