Abstract
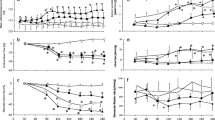
We investigated the interaction between nitric oxide and the renin angiotensin system in regulating isolated pulmonary arterial tension and pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) in renal hypertensive rats (RHR) made by complete ligation of left renal artery. Losartan induced a depressor response that was smaller in RHR than in normotensive rats (NR) (3.3 and 7.0 mmHg, respectively, at 3.0 mg/kg, p<0.05), and the response was significantly reduced by NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME). Angiotensin II elevated the PAP (7.6 and 10.8 mmHg at 0.1 μg/kg; 20.3 and 23.6 mmHg at 1.0 μg/kg, respectively) and contracted the isolated pulmonary artery (pD2: 8.79 and 8.71, respectively) from both NR and RHR with similar magnitude, and these effects were significantly enhanced by L-NAME in NR, but not in HRR. Acetylcholine lowered the PAP slightly less effectively in RHR than in NR (3.8 and 6.0 mmHg at 10 μg/kg, respectively) and relaxed the pulmonary artery precontracted with norepinephrine in both rats with similar magnitude (Emax: 60.8 and 63.6%, respectively), and the effect being completely abolished after pretreatment with L-NAME or removal of endothelial cells. These results suggest that nitric oxide interacts with renin angiotensin system to control the pulmonary vascular tension and pulmonary arterial circulation of RHR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
DeGraaf, G. L., Pals, D. T., Couch, S. J., and Lawson, J. A., Hormonal and cardiovascular effects of losartan (DuP753), an angiotensin receptor antagonist, in nonhuman primates.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 264, 6–10 (1993).
Gardes, J., Gonzalez, M. F., Alhenc Gelas, F., and Menard, J., Influence of sodium diet on L-NAME effects on renin release and renal vasoconstriction.Am. J. Physiol., 267, F798–804 (1994).
Guan, H., Cachofeiro, V., Pucci, M. L., Kaminski, P. M., Wolin, M. S., and Nasjletti, A., Nitric oxide and the depressor response to angiotensin blockade in hypertension.Hypertension, 27, 19–24 (1996).
Haber, E., Koerner, T., Page, L. B., Kliman, B., and Purnode, A., Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin 1 to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 29, 1349–1355 (1969).
Haberl, R. L., Decker, P. J., and Einhaupl, K. M., Angiotensin degradation products mediate endothelium-dependent dilation of the rabbit brain arterioles.Circ. Res., 68, 1621–1627 (1991).
Henderson, A. H., Vascular endothelium in ischemic heart disease: possible role for endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Cardiovasc.Drugs Ther., 3 (Suppl 1), 241–248 (1989).
Higashi, Y., Oshima, T., Ono, N., Hiraga, H., Yoshimura, M., Watanabe, M., Matsuura, H., Kambe, M., and Kajiyama, G., Intravenous administration of L-arginine inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme in humans.J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 80, 2198–2202 (1995).
Ignarro, L. J., Endothelium-derived nitric oxide: actions and properties.FASEB J., 3, 31–36 (1989).
Ito, S., Johnson, C. S., and Carretero, O. A., Modulation of angiotensin II-induced vasoconstriction by endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the isolated microperfused rabbit afferent arteriole.J. Clin. Invest. 87, 1656–1663 (1991).
Knowles, R. G., and Moncada, S., Nitric oxide as a signal in blood vessels. Trends.Biochem. Sci., 17, 399–402 (1992).
Lee, B. H., Shin, H. S., Huh, I. H., Ann, H. S., and Roh, J. K., Angiotensin II reactivity in systemic and pulmonary arterial system of acute renal hypertensive rats.Yakhak Hoeji, 37, 605–614 (1993a).
Lee, B. H., Shin, H. S., and Huh, I. H., Differential function of EDRF in systemic arterial and pulmonary arterial system of renal hypertensive rats.Korean J. Pharmacol, 29, 213–223 (1993b).
Lee, B. H. and Shin, H. S.,In vivo pharmacological evaluation of newly synthesized nonpeptidic AT1 receptor antagonists in rats.Arch. Pharm. Res., 17, 263–268 (1994).
Lee, B. H. and Shin, H. S., Interaction of nitric oxide and renin angiotensin system in renal hypertensive rats.Jpn. J. Pharmacol., 74, 83–90 (1997).
Moncada, S., Palmer, R. M., and Higgs, E. A., Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology.Pharmacol. Rev., 43, 109–142 (1991).
Ohishi, K., Carmines, P. K., Inscho, E. W., and Navar, L. G., EDRF-angiotensin II interactions in rat juxtamedullary afferent and efferent arterioles.Am. J. Physiol., 263, F900-F906 (1992).
Prince, R. C. and Gunce, D. E., Rising interesst in nitric oxide synthase.Trends. Biochem. Sci., 18, 35–36 (1993).
Rees, D. D., Palmer, R. M., Schulz, R., Hodson, H. F., and Moncada, S., Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthasein vitro andin vivo.Br. J. Pharmacol., 101, 746–752 (1990).
Ruilope, L. M., Lahera, V., Rodicio, J. L., and Romero, J. C., Participation of nitric oxide in the regulation of renal function: possible role in the genesis of arterial hypertension.J. Hypertens., 12, 625–631 (1994).
Scholz, H. and Kurtz, A., Involvement of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the pressure control of renin secretion from isolated perfused kidney.J. Clin. Invest., 91, 1088–1094 (1993).
Schricker, K., Hegyi, I., Hamann, M., Kaissling, B., and Kurtz, A., Tonic stimulation of renin gene expression by nitric oxide is counteracted by tonic inhibition through angiotensin II.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U. S. A., 92, 8006–8010 (1995).
Sudhir, K., MacGregor, J. S., Gupta, M., Barbant, S. D., Redberg, R., Yock, P. G., and Chatterjee, K., Effect of selective angiotesin II receptor antagonism and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition on the coronary vasculaturein vivo. Intravascular two-dimensional and Doppler ultrasound studies.Circulation, 87, 931–938 (1993).
Timmermans, P. B., Wong, P. C., Chiu, A. T., Herblin, W. F., Benfield, P., Carini, D. J., Lee, R. J., Wexler, R. R., Saye, J. A., and Smith, R. D., Angiotensin II receptors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists.Pharmacol. Rev., 45, 205–251 (1993).
Van de Voorde, J. and Leusen, I., Endothelium-dependent and independent relaxation of aortic rings from hypertensive rats.Am. J. Physiol., 250, H711-H717 (1986).
Vidal, M. J., Romero, J. C., and Vanhoutte, P. M., Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits renin release.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 149, 401–402 (1988).
Zhang, J., Pfaffendorf, M., Zhang, J. S., and van Zwieten, P. A., Influence of the vascular endothelium on angiotensin II-induced contractions in rabbit renal artery.Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol., 9, 25–29 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B.H., Shin, H.S. Interaction of nitric oxide and renin angiotensin system in pulmonary arterial circulation of RHR. Arch. Pharm. Res. 20, 389–395 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973928
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973928