Abstract
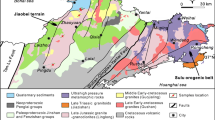
The study results of He and Ar isotopes from fluid inclusions in pyrites formed during mineralization stage of Jinding superlarge Pb-Zn deposit in west Yunnan, China are reported. The data show that the40Ar/36Ar and3He/4He ratios of fluid inclusions are respectively in the range of 301. 7–385. 7 and 0. 03–0.06Ra, suggesting the oreforming fluid is a kind of air saturated meteoric groundwater. On the basis of research on coupled relationships among He, Ar, S and Pb isotopes, the evolution history of ore-forming fluid of the deposit can be summarized as (i) air saturated meteogenic groundwater infiltrated down and was heated→ (ii) leached S, C and radiogenic He, Ar from the basinal strata → (iii) leached Pb and Zn from mantle-derived igneous rocks located in the bottom of the basin→ (iv) ore-forming fluid ascended and formed the deposit. Due to this process, the isotope signatures of crustal radiogenic He, atmospheric Ar (with partial radiogenic40Ar), crustal S and mantle-derived Pb remained in the ore-forming fluid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zartman, R. E., Wasserburg, G. J., Reynods, J. H., Helium, argon and carbon in some natural gases,J.Geophys, Res., 1961, 66:277.
Turner, G., Burnard, P. B., Ford, J. L., Tracing fluid sources and interaction,Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A, 1993, 344:127.
Baptiste, P. J., Fouquet, Y., Abundance and isotopic composition of helium in hydrothermal sulfides from the East Pacific Rise at l3N,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1996, 60:87.
Stuart, F. M., Burnard, P. G., Taylor, R. P. et al., Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralisation, South Korea,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1995, 59:4663.
Simmons, S. F., Sawkins, F. J., Schlutter, D. J., Mantle-derived helium in two Peruvian hydrothermal ore deposits,Nature, 1987, 329:429.
Turner, G., Burgess, R., Bannon, M., Volatile-rich mantle fluids inferred from inclusions in diamond and mantle xenoliths,Nature, 1990, 344:635.
Turner, G., Stuart, F., Helium/heat ratios and deposition temperatures of sulfides from the ocean floor,Nature, 1992, 357:581.
Stuart, F. M., Turner, G., Duckworth, R. C. et al., Helium isotopes as tracers of trapped hydrothermal fluids in oceanfloor sulfides,Geology, 1994, 22:823.
Zhu, S.Q., Tan, G.J., Chen, S.F. etal., Jinding superlarge Pb-Zn deposit, A30-04Project Report of Chinese State Climbing Plan, 1995.
Craig, H., Lupton, J. E., Primordial neon, helium and hydrogen in oceanic basalts,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1976, 31: 369.
Marty, B., Jambon, A., Sano, Y., Helium isotope and CO2 in volcanic gases of Japan,Chem. Geol., 1989, 76:25.
Lupton, J. E., Terrestrial inert gases: isotopic tracer studies and clues to primordial components in the mantle,Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 1983, 11:371.
Zhang, Q. Z., The Pb isotopic composition is a source of Jinding superlarge Pb-Zn deposit,Geology and Exploration (in Chinese), 1993, (5): 21.
Matthews, A., Fouillac, C., Hill, R. et al., Mantle-derived volatiles in continental crust: the Massif Central of France,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1987, 85:117.
Turner, G., Stuart, F., Helium/heat ratios and deposition temperatures of sulfides from the ocean floor,Nature, 1992, 357:581.
Hilton, D. R., Hammerschmidt, K., Teufel, S. et al., Helium isotope characteristics of Andean geothermal fluid and lavas,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1993, 120:265.
Shen, W.,Stable Isotope Geology (in Chinese), Beijing: Atomic Energy Press of China, 1987
Faure, G.,Principles of Isotope Geology, New Yorks: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project supported by A30 Project of the National Climbing Program of China and University of Manchester.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, R., Turner, G., Burnard, P.G. et al. Helium and argon isotopic geochemistry of Jinding superlarge Pb-Zn deposit. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 41, 442–448 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932698
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02932698