Abstract
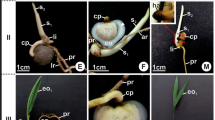
Thein vitro embryoids ofEschscholzia californica do not form normal plantlets in cultures. However, 6-benzylaminopurine and gibberellic acid, when added to the medium, partially alleviate this inhibition. Experiments involving decotylization, and culture of embryoids at different stages, indicated the cardinal role of cotyledons in plumular growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Zeid, A., Neumann, K. H.: Preliminary investigations on the influence of cotyledons on the development of cherry embryos (Priuns avium L.). — Z. Pflanzenphysiol.69: 299–305, 1973.
Ammieato, P. V.: Some effects of abscisic acid on the development of embryos from caraway colls in suspension cultures. — Amer. J. Bot.60: 22–23, 1973.
Aung, L. H.: The nature of root-promoting substance inLycopersicon esculentum seedlings. — Physiol. Plant.26: 306–309, 1972.
International Seed Testing Association: International rules of seed testing. Proc. Int. Seed Tost. Ass.31: 1–152, 1966.
Jensen, W. A.: Botanical Histochemistry. — W. H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco—London 1962.
Kamiaska, S.: Requirement of cotyledons for gibberellic acid induced hypocotyl elongation in lettuce seedlings. Isolation of the cotyledon factor active in enhancing the effect of gibberellio acid.— Plant Coll Physiol.14: 747–755, 1973.
Kavathekar, A. K.: Studies on Origin, Development and Dormancy of Embryoids inEschscholzia californica. — Ph. D. Thesis, Univ. Delhi, 1974.
Kavathekar, A. K., Ganapathy, P. S.: Embryoid differentiation inEschscholzia californica. — Curr. Soi.42: 671–673, 1973.
Kavathekar, A. K., Ganapathy, P. S., Johki, B. M.: Chilling indueos development of embryoids into plantlcts inEschscholzia. — Z. Pflanzenphysiol.81: 358–363, 1977.
Khan, A. A.: Primary, preventive and permissive roles of hormones in plant systems. — Bot. Rev.41: 391–420, 1975.
Konak, R. N., Nataraja, K.: Morphogenesis of isolated floral buds ofRanunculus scclcratus L.in vitro. — Acta bot. neerl.18: 680–699, 1969.
Nitsch J. P., Nitsch, C.: Haploid plants from pollen grains. — Science163: 85–87, 1969.
Steward, F. C.: Tho Croonian Lecture, 1969. From cultured cells to wholo plants: the induction and control of their growth and morphogenesis. — Proc. roy. Soe. London Ser. B175: 1–31, 1970.
Thevenot, C., Come, D.: Germination des embryons do pommier (Pyrus malus) dormants amputés d'une partie plus ou moins importante de lours cotyledons. — Compt. rend. Acad. Sci. (Paris) Sér. D272: 1240–1243, 1973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavathekar, A.K., Ganapathy, P.S. & Johri, B.M. In vitro Responses of Embryoids ofEschscholzia californica . Biol Plant 20, 98–106 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02923269
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02923269