Abstract
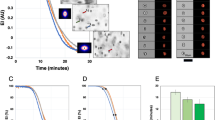
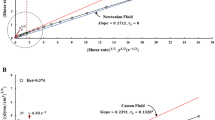
The suspension of hardened red blood cells (RBCs) differs from the suspension of normal RBCs with respect to their rheological behavior. The present study investigated the effect of deformability of RBCs on blood viscosity. RBC deformability and blood viscosity were measured with a recently developed slit-flow laser-diffractometer and the pressure-scanning capillary viscometer, respectively. At the same level of cell concentration, the viscosity of the hardened RBC suspension is higher than that of the normal RBCs suspension. An increase in cell percentage for hardened RBCs shows the significant increase in the level of blood viscosity compared to the normal RBCs. In addition, it was found that RBC deformability played an important role in reducing viscosity at low shear rates as well as high shear rates. These results present the evidence for the effect of RBC deformability on blood viscosity using newly developed methods, which can be used in early diagnosis of the cardiovascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EI:
-
elongation index
- h:
-
slit gap, [m]
- L:
-
slit length, [m]
- n:
-
number of samples
- P:
-
pressure, [kPa]
- δP:
-
pressure difference(=Pa- P)
- Q:
-
volume flow rate, [m3/s]
- V:
-
volume, [m3]
- t:
-
time, [s]
- w:
-
slit width, [m]
- X:
-
length of major axis of ellipse
- Y:
-
length of minor axis of ellipse
- ρ:
-
density, [kg/m3]
- η:
-
non-Newtonian viscosity, [Pa*s]
- γ:
-
shear rate, [s-1]
- τ:
-
shear stress, [Pa]
- A:
-
atmosphere
- avg:
-
averaged
- w:
-
wall
References
Baskurt, O. K. and Meiselman, H. J., 2003, “Blood Rheology and Hemodynamics,”Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, Vol. 29, pp. 435.
Bessis, M. and Mohandas, N., 1975, “A Differactometric Method for the Measurement of Cellular Deformability,”Blood Cells, Vol. 1, pp. 307–312.
Chien, S., Usami, S., Dellenback, R. J. and Gregersen, M.I., 1967, “Blood Viscosity: Influence of Erythrocyte Deformation,”Science, Vol. 157, pp. 827–829.
Chien, S., 1987, “Red Cell Deformability and its Relevance to Blood Flow,”Annu Rev Physiol., Vol.49, pp. 177–192.
Diamantopoulos, E. J., Kittas, C., Charitos, D., Grigoriadou, M., Ifanti, G. and Raptis, S. A., 2004, “Impaired Erythrocyte Deformability Precedes Vascular Changes in Experimental Diabetes Mel-litus,”Horm. Metab. Res. Vol. 36, pp. 142–147.
Dobbe, J. G. G., Hardeman, M. R., Streekstra, G. J., Strackee, J., Ince, C. and Grimbergen, C. A., 2002, “Analyzing Red Blood Cell-Deformability Distributions,”Blood Cells, Molecules, and Diseases, Vol. 28, pp. 373–384.
Dobbe, J. G. G., Hardeman, M. R., Streekstra, G. J., Strackee, C. and Grimbergen, C. A., 2004, “Validation and Application of an Automated Rheoscope for Measuring Red Blood Cell Deformability Distributions in Different Species,”Biorheology, Vol. 41, pp. 65–77.
Evans, E. A. and LaCelle, P. L., 1975, “Intrinsic Material Properties of Ery-throcyte Membrane Indicated by Mechanical Analysis of Deformation,”Blood, Vol. 45, pp. 29–43.
Guck, J., Ananthakrishnan, R. Mahmood, Moon, T. J., Cunningham, C. C. and Ka, J., 2001, “The Optical Stretcher: A Novel Laser Tool to Micromanipulate Cells,”Biophysical J., Vol. 81, pp. 767–784.
Hanss, M., 1983, “Erythrocyte Filterability Measurement by the Initial Flow Rate Method,”Biorheology, Vol. 20, pp. 199–211.
Hardeman, M. R., Goedhart, P. T., Dobbe, J. G. G. and Lettinga, K. P., 1994, “Laser-assisted Optical Rotational Cell Analyser (LORCA): A New Instrument for Measurement of Various Structural Hemorheological Parameters,”Clin. Hemorheol. Vol. 14, pp. 605–610.
Hiruma, H., Noguchi, C. T., Uyesaka, N., Schechter, A. N. and Rodgers, G. P., 1995, “Contributions of Sickle Hemoglobin Polymer and Sickle Cell Membranes to Impaired Filterability,”Am. J. Physio., Vol. 268, pp. H2003–2008.
Hochmuth, R. M. and Waugh, R., 1986, “Erythrocyte Membrane Elasticity and Viscosity,”Annu Rev Physiol., Vol. 49, pp. 209–219.
Jeffrey, D. J. and Acrivos, A., 1977, “The Rheological Properties of Suspensions of Rigid Particles,”AIChE J. Vol. 22, pp. 417–432.
Lowe, G., 1988.Clinical Blood Rheology, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Lux, S. E., 1979, “Dissecting the Red Cell Membrane Skeleton,”Nature, Vol. 281, pp. 426–429.
Macosko, C. W. 1993,Rheology: Principles, Measurements, and Applications, VCH, New York, pp. 237–258.
Mohandas, N. and Chasis, J. A., 1993, “Red Blood Cell Deformability, Membrane Material Properties and Shape: Regulation by Transmembrane, Skeletal and Cytosolic Proteins and Lipids,”Semin Hematol., Vol. 30, pp. 171–192.
Puniyani, R. R., Ajmani, R. and Kale, P. A., 1991, “Risk Factors Evaluation in Some Cardiovascular Diseases,”J. Biomed. Eng., Vol. 13, pp. 441–443.
Shin, S., Keum, D. Y. and Ku, Y. H., 2002. “Blood Viscosity Measurement Using a Pressure-Scanning Capillary Viscometer,”KSME Int. J., Vol. 16, pp. 1719–1724.
Shin, S., Ku, Y. H., Park, M. S., Moon, S. Y., Jang, J. H. and Suh, J. S., 2004a, “Laser-diffraction Slit Rheometer to Measure Red Blood Cell Deformability,”Rev. Sci. Instr., Vol. 75, pp. 559–561.
Shin, S., Lee, S. W. and Ku, Y. H., 2004b, “Measurements of Blood Viscosity using a Pressure-scanning Slit Viscometer,”KSME Int. J., Vol. 18, pp. 1036–1041.
Stoltz, J.-F., Singh, M. and Riha, P., 1999,Hemorheology in Practice, IOS Press, Amsterdam, Netherlands, pp. 67–72.
Testa, I., Manfrini, S., Gregorio, F., Refe, A., Bonfigli, A. R., Testa, R. and Piantanelli, L., 1995, “Red Blood Cell Deformability in Diabetic Retinopathy,”Biorheology, Vol. 32, pp. 389–395.
Wang, X., Zhao, H., Zhuang, F. Y. and Stoltz, J. F., 1999, “Measurement of Erythrocyte Deformability By two Laser Diffraction Methods,”Clinical Hemorheol and Microcirculation, Vol. 21, pp. 291–295.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, S., Ku, Y., Park, MS. et al. Deformability of red blood cells: A determinant of blood viscosity. J Mech Sci Technol 19, 216–223 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916121
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916121