Abstract
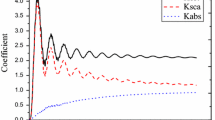
The data, measured by a three-wavelength Integrating Nephelometer over Lanzhou City during the winters of 2001/2002 and 2002/2003 respectively, have been analyzed for investigating the scattering properties of atmospheric aerosols and exploring their relationship and the status of air pollution. The aerosol particle volume distribution is inverted with the measured spectral scattering coefficients. The results show that the daily variation of the aerosol scattering coefficients is in a tri-peak shape. The average ratio of backscattering coefficient to total scattering coefficient at 550 nm is 0.158; there exists an excellent correlation between the scattering coefficients and the concentration of PM10. The average ratio of the concentration of PM10 to the scattering coefficients is 0.37 g m−2, which is contingent on the optical parameters of aerosol particles such as the size distribution, etc.; an algorithm is developed for inverting the volume distribution of aerosol particles by using the histogram and Monte-Carlo techniques, and the test results show that the inversion is reasonable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. L., and Coauthors, 1996: Performance characteristics of a high-sensitivity, three-wavelength, total scatter/backscatter nephelometer.J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol.,13(5), 967–986.
Bennett, B. G., J. G. Kretzschmar, G. G. Akland, and H. W. de Koning, 1985: Urban air pollution worldwide.Environmental Science and Technology,19, 298–304.
Charlson, R. J., H. Horvath, and R. F. Pueschel, 1967: The Direct Measurement of Atmospheric Light Scattering Coefficient for Studies of Visibility and Pollution.Atmospheric Envionment,1, 469–478.
Charlson, R. J., N. C. Ahlquist, and H. Horvath, 1968: On the Generality of Corre1ation of Atmospheric Aerosol Mass Concentration and Light Scatter.Atmospheric Envionment.,2, 455–464.
Chen Changhe, Huang Jianguo, Long Xuezhu, Wang Haixiao, Meng Jinfu, and Chen Zhenmei, 1992: Winter Boundary Layer Characteristics over a Valley City.Chinese Science Bulletin,37(6), 490–493.
Dockery, D., and A. Pope, 1996: Epidemiology of acute health effects: Summary of time-series studies.Particles in Our Air: Concentration and Health Effects., Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, 123–147.
Du Ping, 2002: Retrieval of the Optical Depth of Dust Aerosol Using Satellite Data. Ph. D. dissertation, Lanzhou University, 113pp.
Guan Hong, Lu Daren, and Wu Beiying, 1992: Retrieval of the Profile of Stratospheric Aerosols from the intensity of Skylight During Twilight Period.Scientia Atmospherica Sinica,16(2), 216–227. (in Chinese)
Guasta, M. D., and S. Marini, 2000: On the retrieval of urban aerosol mass concentration by a 532 and 1064 nm LIDAR.J. Aerosol Sci.,31(12), 1469–1488
Heintzenberg, J., H. Muller, H. Quenzel, and E. Tomalla, 1981: Information content of optical data with respect to aerosol properties: Numerical studies with a randomized minimizationsearchtechnique inversion algorithm.Appl. Opt.,20, 1308–1315.
Li Jie, and Mao Jietai, 1989: Inverse of the Property of Atmospheric Aerosols by Optical Remote Sensing.Acta Meteorologica Sinica,47(4), 450–456. (in Chinese)
Lu Daren, Zhou Xiuji, and Qiu Jinhuan, 1981: The principle and numerical experiment of remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol size distribution by combined solar extinction and forward scattering method.Science in China,12, 1516–1524. (in Chinese)
Middleton, W. E. K., l952:Vision Through the Atmosphere. University of Toronto Press, 250pp.
Qiu Jinhuan, and Nobuo Takeuchi, 2001: Effects of Aerosol vertical Inhomogeneity on the Upwelling Radiance and Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Reflectance.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,18(4), 539–553.
Qiu Jinhuan, Wang Hongqi, Zhou Xiuji, and Lu Daren, 1983: Experimental study of remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol size distribution by combined solar extinction and forward scattering method.Chinese J. Atmos. Sci.,7(1), 855–859. (in Chinese)
Schwartz, J., D. W. Dochery, and L. M. Neas, 1996: Is daily mortality associated specifically with fine particles?J. Air and Waste Management Association,46, 927–939.
Su Wenying, and Chen Changhe, 1997: The research of Parameterization Method of Determining the Aerosol Optical Absorption Characteristics.Scientia Atmospheric Sinica,21(1), 49–57.
Trijonis, J. C., 1990: Visibility: Existing and Historical Conditions-Causes and Effects. National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program Report,24, Vol. III, Superintendent of Documents, Government Printing Office, Washington, D. C., 24–85.
Waggoner, A. P., and R. E. Weiss, 1980: Comparison of Fine Particle Mass Concentration and Light Scattering Extinction in Ambient Aerosol.Atmospheric Environment,14, 623–626.
Wei Dongjiao, and Qiu Jinhuan, 1998: Determination of the imaginary part of the complex refractive index of atmospheric aerosol by remote sensing from broadband solar diffuse radiation.Chinese J. Atmos. Sci.,22(5), 677–685. (in Chinese)
White, W. H., 1986: On the Theoretical and Empirical Basis for Apportioning Extinction by Aerosols: A Critical Review.Atmospheric Environment,20, 1659–1672.
Wu Beiying, and Lu Daren, 1988: Retrieval of stratospheric background aerosol scattering coefficient from twilight measurements.Appl. Opt.,27, 4899–4906. (in Chinese)
Zhang Junhua, Liu Li, and Mao Jietai, 2000: Remote sensing of aerosol optical properties with multi-spectral sun photometer in the Damxung region, Tibetan Plateau.Chinese J. Atmos. Sci.,24(4), 549–558. (in Chinese)
Zhang Junhua, Mao Jietai, and Wang Meihua, 2002: Analysis of the Aerosol Extinction Characteristics in Different Areas of China.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,19(1), 136–152.
Zhang Yufen, and Chen Changhe, 1998: A Study on the Characteristics of Winter Temperature Stratification over Lanzhou City.Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),34(2), 104–110. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Bo, H., Changhe, C. et al. Scattering properties of atmospheric aerosols over Lanzhou City and applications using an integrating nephelometer. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 21, 848–856 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915587
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02915587