Abstract
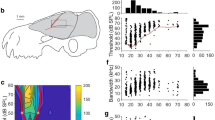
By using a combined closed and free-field stimulation system, binaurality and azimuth tuning of the neurons in the auditory cortex of the big brown bat,Eptesicus fuscus, were studied. A variety of azimuth-tuning functions were demonstrated for the binaural neurons. The large majority of EE (contralateral and ipsilateral excitatory) neurons exhibited azimuth selectivity with the best azimuths (BA) at contralateral 30°–40°, some at ipsilateral 20°-40° and preferred azimuth ranges (PAR, response amplitude ⩾75% of maximum) between 8° and 40°. Sound source azimuths strongly modulate spike counts with a mean modulation depth of 83.8% for EE neurons. EI (contralateral excitatory and ipsilateral inhibitory) neurons have simple azimuth tuning with BA located at contralateral 20°-40° and a broad PAR ranged from 30° to 55°. The present results suggest that azimuth-tuning characteristics of binaural neurons in the auditory cortex of the bat are of significance for acoustic behaviour.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bregman, A. S., Auditory scene analysis, The Perceptual Organization of Sound, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1990.
Schnupp, J. W. H., Mrsic-Flogel, T. D., King, A. J., Linear processing of spatial cues in primary auditory cortex, Nature, 2001, 414: 200.
Clarey, J, C., Barone, P., Imig, T. J., Physiology of thalamus and cortex, The Mammalian Auditory Pathway: Neurophysiology (eds. Popper, A. N., Fay, R. R.) New York: Springer, 1992, 232–334.
Middlebrooks, J. C., Xu, L., Eddins, A. C. et al., Codes for sound-source location in nontonotopic auditory cortex, J. Neurophysiol., 1998, 80: 863.
Brugge, J. F., Reale, R. A., Hind, J. E., The structure of spatial receptive fields of neurons in primary auditory cortex of the cat, J. Neurosci., 1996, 16: 4420.
Imig, T. J., Irons, W. A., Samson, F. A., Single-unit selectivity to azimuthal direction and sound pressure level of noise bursts in cat high-frequency primary auditory cortex, J. Neurophysiol., 1990, 63: 1448.
Middlebrooks, J. C., Pettigrew, J. D., Functional classes of neurons in primary auditory cortex of the cat distinguished by sensitivity to sound location, J. Neurosci., 1981, 1: 107.
Rajan, R., Aitkin, L. M., Irvine, D. R. F., Azimuthal sensitivity of neurons in primary auditory cortex of cats, Part I: Types of sensitivity and the effects of variations in stimulus parameters, J. Neurophysiol., 1990, 64: 872.
Ahissar, M., Ahissar, E., Bergman, H. et al., Encoding of sound-source location and movement activity of single neurons and interactions between adjacent neurons in the monkey auditory cortex, J. Neurophysiol., 1992, 67: 203.
Grinnell, A. D., Hearing in bats: An overview, Hearing by Bats (eds. Popper, A. N., Fay, R. R.), New York: Springer, 1995, 1–36.
Manabe, T., Suga, N., Ostwald, J., Aural representation in the Doppler-shifted-CF processing area of the auditory cortex of the mustache bat, Science, 1978, 200: 339.
Shen, J. X., Chen, Q. C., Jen, P. H. S., Binaural and frequency representation in the primary auditory cortex of the big brown bat,Eptesicus fuscus, J. Comp. Physiol. A, 1997, 181: 591.
Fuzessery, Z. M., Pollak, G. D., Neural mechanisms of sound localization in an echolocating bat, Science, 1996, 225: 725.
Jen, P. H. S., Chen, D. M., Directionality of sound pressure transformation at the pinna of echolocating bats, Hear. Res., 1988, 34: 101.
Samson, F. K., Barone, P., Clarey, J. C. et al., Effects of ear plugging on single-unit azimuth sensitivity in cat primary auditory cortex, 2. Azimuth tuning dependent upon binaural stimulation, J. Neurophysiol., 1994, 71: 2194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Chen, Q. Binaurality and azimuth tuning of neurons in the auditory cortex of the big brown bat. Chin. Sci. Bull. 47, 1024–1027 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907575
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907575