Summary
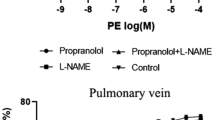
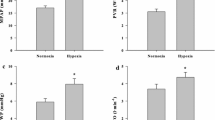
In this study, porcine pulmonary artery segments (intact or denuded) and bronchial segments (with or without epithelium) were tested in organ bath. Hypoxia caused a bronchial epithelium dependent relaxation of intact or denuded pulmonary artery preconstricted with phenylephrine. Constriction in intact pulmorary artery coated with epithelium denuded bronchus was observed during hypoxia. The bronchial epithelium-dependent relaxation could be inhibited by indomethacin but not be blocked by the following agents: atropine, propranolol, gossypol, methylene blue and chlorpheniramine. The results suggested tnat HPV was endothelium-dependent. Hypoxia could cause the production of an epithelium-derived relaxing factor (EpDRF), which acted directly on smooth muscle. The effect of EpDRF was not mediated by pulmonary endothelium, but might be rslated to aracnidonic acid cyclooxygenase pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morrison K Jet al. Epithelial modulation of airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol, 1990;258(6PT1):L254-L262
Wilkens J Het al. The effect of bronchial epithelium on bronchial contractility. Pneumologie, 1990;44 Supl 1:373–385
Manning P Iet al. The inhibitory influence of tracheal mucosa mounted in close proximity to canine trachealis. Eur J Pharmacol, 1990;178(1):85–90
Munakata Met al. Pharmacological differentiation of epithelium-derived relaxing factor from nitric oxide. J Appl Physiol, 1990;69(2):665–670
Vanhoutte P Met al. Epithelium derived relaxing factor(s) and bronchial reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 1989;83:855–861
Aizawa Het al. A possible role of airway epithelium in modulating hyperresponsiveness. Br J Pharmacol, 1988;93(1):139–145
Gao Yet al. Lowering PO2 induces epithelium dependent relaxation in isolated canine bronchi. Am J Physiol, 1989;257(26):Cl034–1037
Grustter C Aet al. Comparison of endothelium dependent relaxation in bovine intrapulmonary artery and vein by acetylcholine and A23187. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 1986;238:1055–1062
Stuart-Smith Ket al. Arachidonic acid evokes epithelium-dependent relaxation in canine airways. J Appl Physiol, 1988;65:2170–2180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei-han, W., Di-xun, W. The regulatory effect of substances released from porcine bronchial epithelial cells on hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Journal of Tongji Medical University 13, 84–87 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887921
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02887921