Abstract
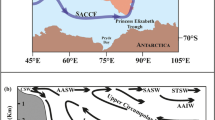
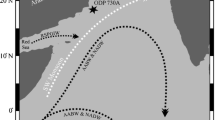
The species diversity indices, as defined by the number of species,S; Shannon-Wiener index,H(S) and Buzas-Gibson index,É, of DSDP sites 219, 220, 237 and 238 were measured to determine the benthic foraminiferal diversity patterns in the Indian Ocean deep sea sequences during the Neogene. The Time-Stability hypothesis could satisfactorily explain the observed diversity patterns. The general patterns of diversity suggest environmental stability during the Neogene. However, few small fluctuations in diversity during the Middle Miocene (c.14·8 Ma), Late Miocene (c.6·0 Ma) and Late Pliocene (c.2·0 Ma) may possibly be the effects of Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW) activity in this region. The benthic foraminiferal diversity in the tropical Indian Ocean is more than the high latitudinal areas with comparable depths.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basharin G P 1959 On a statistical estimate for the entropy of a sequence of independent random variables, in Artin N (ed.) Theory of probability and its applications, Vol. 4, Philadelph.,Indus. Appl. Math. Soc., 333—336
Berggren W A, Kent D V and Van Cauring J A 1985 Neogene geochronology and chronostratigraphy, in Geochronology and the record, Geological Society London, Special Paper, (ed.) N J Snelling pp. 211—260
Brian M V 1953 Species frequencies in random samples from animal populations;J. Anim. Ecol. 22 57–64
Brillouin L 1964 Scientific uncertainty and information (New York: Academic Press) pp. 164
Brookhaven National Laboratory 1969 Diversity and stability in ecological system; Brookhaven Symp. Biol.22 pp. 264
Buzas M A and Gibson T G 1969 Species diversity: Benthonic foraminifera in the Western North Atlantic; Science163 72–75
Caswell H 1978 Predator — mediated coexistence: A nonequilibrium model;Am. Nat. 112 127–154
Connell J H 1978 Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs;Science 199 1302–1310
Connell J H and Orias E 1964 The ecological regulation of species diversity;Am. Nat. 98 399–414
Connell J H and Slater R D 1977 Mechanism of succession in natural community, stability and organization;Am.Nat. 111 1119–1144
Davies T A, Luyedyk B P, Rodolfo K S, Kempe D R C, Leidy Rd, Horvath G J, Hyndman R D, Thierstein H R, Herb R C, Boltovskoy E and Doyle P 1974Initial Rep. Deep Sea Drill. Proj. 26 1–1129
Deevey E S 1969 Specific diversity in fossil assemblages, in diversity and stability in the ecological systems;Brookhaven Natl. Lab. Symp. Biol. 22 224–241
Dobzhansky T 1950 Evolution in the tropics;Am. Sci. 38 209–221
Dunbar M J 1960 The evolution of stability in marine environments. Natural selection at the level of the ecosystem;Am. Nat. 94 129–136
Fischer A G 1960 Latitudinal variation in organic diversity; Evolution14 64–81
Fisher R A, Corbett A S and Williams C B 1943 The relation between the number of species and number of individuals in random sample of animal population;J. Anim. Ecol. 12 42–58
Gibson L B 1966 Some unifying characteristics of species diversity;Cushman. Found. Foraminiferal. Res. Contrib.17 117–124
Gibson T G and Buzas M A 1973 Species diversity patterns in modern and miocene foraminifera of the eastern margin of North America;Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 84 217–238
Gupta A K 1987 Neogene deep water benthic foraminifera from the Northern Indian Ocean (DSDP Leg 22) Ph.D. Thesis, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi (Unpublished)
Gupta A K and Srinivasan M S 1990 Species diversity of Neogene deep sea benthic foraminifera from the Northern Indian Ocean DSDP sites 214 and 216A, in Fourth Int. Symp. on Benthic Foraminifera, Sendai, Japan, (Abstr.) p. 53
Hessler R R and Sanders H L 1967 Faunal diversity in the deep sea;Deep-Sea Res.,14 65–78
Huston M 1979 A general hypothesis of species diversity;Am. Nat. 113 81–101
Kaminski M A 1984 Evidence for control of abyssal agglutinated foraminiferal community structure by substrate disturbance: results from the HEBBLEA Area, in Deep Ocean Sediment Transport (eds) Nowell and Holister, p. 113–131
Kennett J P 1977 Cenozoic evolution of Antarctic glaciation, the Circum-Antarctic Ocean and their impact on global paleoceanography:J. Geophys. Res. 82 3843–3860
Kiester A R 1971 Species diversity of North American amphibians and reptiles;Syst. Zool. 20 127–137
Klopfer P H 1959 Environmental determinates of faunal diversity;Am. Nat. 93 337–342
Lagoe M B 1976 Species diversity of deep sea benthic foraminifera from the Central Arctic Ocean:Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 87 1678–1683
Margalef R 1957 La teoria de la informacion en ecologia,R. Acad. Cienc. Artes Barcelona Mem. 32 373–449
Margalef R 1963 On certain unifying principle in ecology;Am. Nat. 97 357–374
Margalef R 1969 Diversity and stability: A practical proposal and a model of interdependence;Brookhaven Symp. Biol. 22 25–37
Moore P D 1983 Ecological diversity and stress;Nature (London) 306 17
Osman R W 1977 The establishment and development of marine epifaunal community;Ecol. Monogr. 47 37–63
Paine R T 1966 Food web complexity and species diversity;Am. Nat. 100 65–75
Pianka E R 1966 Latitudinal gradients in species diversity: A review of concepts;Am. Nat. 100 33–46
Pielou E C 1966 The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections;J. Theor. Biol. 13 131–144
Preston F W 1948 The commonness and rarity of species;Ecology 29 254–283
Preston F W 1962 The canonical distribution of commonness and rarity, pt. I and pt. II;Ecology,43 185–215, 410—432
Rex M A 1981 Community structure in the deep sea benthos;Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 12 331–353
Rex M A 1983 Geographic patterns of species diversity in the deep sea benthos; in The Sea, (ed.) Gilbert T Rowe 8 453-472
Sanders H L 1968 Marine benthic diversity: A comparative study;Am. Nat. 102 243–282
Sanders H L 1969 Benthic marine diversity and the stability-time hypothesis, in diversity and stability in ecological system: Brookhaven Natl.Lab Symposia in Biology 22 71–81
Sen Gupta B K and Kilbourne R T 1974 Diversity of benthic foraminifera On the Georgia continental shelf;Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 85 969–972
Shannon C E and Wiener W 1949 The mathematical theory of communication, Univ. of Illinois Press, Urbana III, pp. 125
Simpson E H 1949 Measurement of diversity;Nature (London) 163 688
Simpson G G 1964 Species diversity of North American recent mammals;Syst. Zool. 13 57–73
Slobodkin L B and Sanders H L 1969 On the contribution of environmental predictability to species diversity, in diversity and stability in ecological systems;Brookhaven Natl. Lab. Symp. Biol. 22 82–95
Sousa W P 1979 Disturbance in marine intertidal boulder fields: The nonequilibrium maintenance of species diversity;Ecology 60 1225–1239
Srinivasan M S 1988 Late cenozoic sequences of Andaman-Nicobar Islands: Their regional significance and correlation;Indian J. Geol. 60 11–34
Srinivasan M S and Kennett J P 1981 Neogene planktonic foraminiferal biostratigraphy and evolution: Equatorial to Subantarctic, South Pacific;Mar. Micropal. 6 493–533
Srinivasan M S, Rai A K and Gupta A K 1992 Neogene benthic foraminiferal biostratigraphy of the Indian Ocean deep sea sequences, inProc. of 79th Indian Science Congress, Baroda, (Abstr.) Sect. VII, p. 19—20
Valentine J W 1966 Numerical analysis of marine molluscan ranges on the extra-tropical northeastern Pacific shelf;Limnol. Oceanogr. 11 198–211
Vincent E, Killingley J S and Berger W H 1985 Miocene carbon and oxygen isotope stratigraphy of the tropical Indian Ocean, in The Miocene (ed.) J P Kennett;Geol. Soc. Am. Mem., USA163 103–130
Williams C B 1964 Patterns in the balance of nature and related problems in quantitative ecology, (New York: Academic Press) pp. 324
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, A.K., Srinivasan, M.S. Neogene deep sea benthic foraminiferal diversity in the Indian Ocean: Paleoceanographic implications. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 101, 299–316 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878139
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878139