Abstract
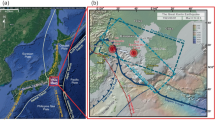
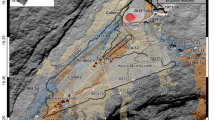
The cause for prolific seismicity in the Koyna region is a geological enigma. Attempts have been made to link occurrence of these earthquakes with tectonic strain as well as the nearby reservoirs. With a view to providing reliable seismological database for studying the earth structure and the earthquake process in the Koyna region, a state of the art digital seismic network was deployed for twenty months during 1996–97. We present preliminary results from this experiment covering an area of 60 × 80 km2 with twenty seismic stations. Hypocentral locations of more than 400 earthquakes confined to 11×25 km2 reveal fragmentation in the seismicity pattern — a NE — SW segment has a dip towards NW at approximately 45°, whilst the other two segments show a near vertical trend. These seismic segments have a close linkage with the Western Ghat escarpment and the Warna fault. Ninety per cent of the seismicity is confined within the depth range of 3–10 km. The depth distribution of earthquakes delimits the seismogenic zone with its base at 10 km indicating a transition from an unstable to stable frictional sliding regime. The lack of shallow seismicity between 0 and 3 km indicates a mature fault system with well-developed gouge zones, which inhibit shallow earthquake nucleation. Local earthquake travel time inversion for P- and S-waves show ≈ 2% higher velocity in the seismogenic crust (0–10 km) beneath the epicentral tract relative to a lower velocity (2–3%) in the adjoining region. The high P- and S-wave velocity in the seismogenic crust argues against the presence of high pressure fluid zones and suggests its possible linkage with denser lithology. The zone of high velocity has been traced to deeper depths (≈ 70 km) through teleseismic tomography. The results reveal segmented and matured seismogenic fault systems in the Koyna region where seismicity is possibly controlled by strain build up due to competent lithology in the seismic zone with a deep crustal root.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athavale R N and Mohan I 1976 Integrated geophysical studies in the Koyna Hydro-electric project area of Maharashtra state, India;Technical Report, NGRI
Burst J F 1969 Diagenesis of Gulf Coast clay sediments and its possible relation to petroleum;American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin 53 73–93
Chadha R K, Gupta H K (and 10 others) 1997 Delineation of active faults, nucleation process and pore pressure measurements at Koyna, (India);Pure Appl. Geophys. 150 552–562
Christensen I N 1989 Pore pressure, seismic velocities and crustal structure, in Pakiser L C and Mooney W D, Geophysical framework of the continental United States: Boulder, Colorado;The Geological Society of American Memoir 172 783–798
Dziewonski A M, Ekstrom G, Franzen J E and Woodhouse J H 1988 Global seismicity of 1980; Centroid moment tensor solutions for 515 earthquakes;Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 50 127–154
Eberhart-Phillips D, Stanley W D, Rodriguez B D and Lutter W J 1995 Surface seismic and electrical methods to detect fluid related to faulting;J. Geophys. Res. 100 12919–12936
Fertl W H 1976 Abnormal formation pressure (New York, Elsevier) 382
Geological Survey of India, 1968, A geological report on the Koyna earthquake of 11th Dec. 1967, Satara District, Maharastra State, Unpublished Report (GSI), p. 242
Gubin I E 1968 Seismic zoning of Indian peninsula;Bull. Int. Inst. Seism. Earthquake Engg. 5 109–139
Gubin I E 1969 Seismic zoning of the western margin of the Indian peninsula in Maharashtra state, UNESCO, serial no.l519/BMS.RD/SCE, Paris
Gupta H K, Narain H, Rastogi B K and Mohan I 1969 A study of the Koyna earthquake of Dec. 10, 1967;Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 70 1149–1162
Gupta H K 1992 Reservoir Induced Earthquakes (Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishers) p. 364
Iyer H M and Hirahara K 1993 Seismic Tomography: Theory and Practice, (Chapman and Hall) 319–360
Kelkar Y N 1968 Earthquakes experienced by Maharashtra in the past three hundred years, Kesari (Marathi Language Daily), Jan. 7, p. 7, Pune
Krishna V G, Kaila K L and Reddy P R 1989 Synthetic seismogram modeling of crustal seismic record sections from the Koyna DSS Profiles in Western India. In:Properties and process of the Earths Lower crust; Am. Geophys. Union Geophys. Monogr. 51 IUGG 6, 143–157
Langston C A 1981 Source inversion of seismic waveform: The Koyna India earthquake of Sept. 13, 1967;Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 71 1–24
Langston C A and Franco-Spera M 1985 Modeling of Koyna, India, aftershock of 12th Dec. 1967;Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 75 651–660
Lee W H K and Raleigh C B 1969 Fault plane solution of the Koyna (India) earthquake;Nature 223 172–173
Lee W H K and Valdes C M 1985 HYPO71PC: A personal computer version of the HYPO71 earthquake location program;U. S. Geol. Surv. Open-File Report 85-749 p. 43
Lees J M 1990 Tomographic P-wave velocity images of the Loma Prieta earthquake asperity;Geophys. Res. Lett. 17 1433–1436
Lees J M and Nicholson C E 1993 Three dimensional tomography of the 1992 southern California earthquake sequence: constraints on dynamic earthquake rupture?Geology 21 387–390
Levorsen A I 1954Geology of petroleum (San Francisco: W H Freeman) p. 703
Mahadevan T M 1994 Deep continental structure of India: A review;Geol. Soc. India Mem. 28 p. 569
Mandai P, Rastogi B K and Sarma C S P 1998 Source parameters of Koyna earthquakes, India;Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 88 833–842
Marone C 1998 Laboratory derived friction laws and their application to seismic faulting;Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 26 663–696
Marone C and Scholz C H 1988 The depth of seismic faulting and the upper transition from stable to unstable slip regimes;Geophys. Res. Lett. 15 621–624
Miller C K and Furlong K P 1988 Thermal-mechanical controls on seismicity depth distribution in the San Andreas fault zone;Geophys. Res. Lett. 15 1429–1432
Pascoe E H 1964 A manual of the Geology of India and Burma; (Calcutta: Govt. of India Press)
Peshwa V V 1991 Geological studies of Chandoli dam site area Warna Valley, Sangli Dist. Maharashtra State, Studies based on remote sensing techniques; Unpublished report to Maharashtra Engg. Res. Inst., Nasik, Dept. of Geology, Pune Univ., p. 45
Raleigh C B 1971 Earthquake control at Rangely, Colorado: EOS Transactions of the American Geophysical Union,52 p. 344
Scholz C H 1998 Earthquakes and friction Laws;Nature 391 37–42
Snow D T 1982 Hydrology of induced seismicity and tectonism: Case history of Kariba and Koyna;Geol. Soc. Am. Spl. Paper 189 317–360
Talwani P, Kumar Swamy S V and Sawalwade C B 1996 The revaluation of seismicity data in the Koyna-Warna Area, 1963–1995;Univ. of South Carolina, Tech. Rep. p. 343
Talwani P 1997 Seismotectonics of the Koyna-Warna Area, India;Pure. Appl. Geophys. 150 511–550
Valdiya K S 1984 Aspects of Tectonics: Focus on South-Central Asia, (New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill)
Widdowson M and Cox K G 1996 Uplift and erosional history of the Deccan Traps, India: Evidence from laterites and drainage patterns of the Western Ghats and Konkan Coast;Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 137 57–68
Zhao D, Hasegawa A and Horiuchi S 1992 Tomographic imaging ofP- and S-wave velocity structure beneath northeastern Japan;J. Geophys. Res. 97 19909–19928
Zhao D and Kanamori H 1995 The 1994 Northridge earthquake: 3-D crustal structure in the rupture zone and its relation to the aftershock locations and mechanisms;Geophys. Res. Lett. 22 763–766
Zhao D, Kanamori H, Negishi H and Wiens D 1996 Tomography of source area of the Kobe earthquake: Evidence for fluids at the hypocenter?;Science 274 1891–1894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, S.S., Singh, S.K., Sarma, P.V.S.S.R. et al. What triggers Koyna region earthquakes? Preliminary results from seismic tomography digital array. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet Sci.) 108, 1–14 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840820
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02840820