Summary
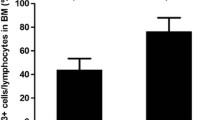
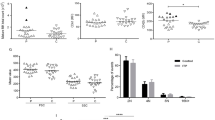
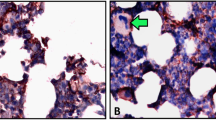
To investigate the effect of costimulatory factors in the pathogenesis of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (CITP), we examined the expression of CD80 on platelets and megakaryocytes in patients with CITP and the controls by FACS. By using CD80 monoclonal antibody (McAb) to inhibit interaction among cells which is mediated by costimulatory factors, we observed the effect of CD80 McAb on the growth and maturation of megakaryocytic progenitors of patients with CITPin vitro. The results showed the expression of CD80 on platelets and megakaryocytes in CITP group was significantly higher than that in controls (P<0.01). There was a significantly positive correlation between the expression of CD80 on platelets and serum PAIgG in CITP (r=0.86,P<0.05). The mean of various clone numbers (CFU-MK, BFU-MK and mCFU-MK) in CITP were all lower than those in controls (P<0.05). In megakaryocytes co-cultured with CD80 McAb, there was an increasing tendency of the number of CFU-MK and big CFU-MK (the number of megakaryocyte with GP IIIa positive was more than 20) and mediate CFU-MK (the number megakaryocyte with GP IIIa positive was 11–20). When the concentration of CD80 McAb was 10 μg/L, there was a significant difference in the number of megakaryocytic colony formation (CFU-MK, BFU-MK and mCFU-MK) between the group with CD80 McAb and that without it (P<0.05). These showed the abnormality of costimulatory factors had important effect in the pathogenesis of CITP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folzenlogen D, Hofer M F, Leung D Y Met al. Analysis of CD80 and CD86 expression on peripheral blood B lymphocytes reveals increased expression of CD86 in lupus patients. Clin Immunol Immunopathol, 1997, 83: 199
Verwilghen J, Lovis R, Boer M Det al. Expression of functional B7 and CTLA-4 on rheumatoid synovial T cells. J Immunol, 1994, 153:1378
Han Z C, Abgrall J F, Briere Jet al. Characterization and classification of human megakaryocyte colonies: Analysis based on the observation of platelet glycoproteins I b, II b, III a and II b/III a complex on cultured megakaryocytes and their progenitors in vitro cultures. Presented at the X X II congress of International Society of Hematology, Milan, Italy, Angust 28–September 2, 1988, P102.
John W, Youli M, Donna Cet al. Differences in serum cytokine levels in acute and chronic autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura: relationship to platelet phenotype and antiplatelet T-cell reactivity. Blood, 1996, 87: 4245
Early GS, Zhao W, Burns CM. Anti—CD40 ligand antibody treatment prevents the development of lupus—like nephritis in a subset of New Zealand black X New Zeal- and white mice. Response correlates with the absence of an anti—antibody response. J Immunol. 1996 Oct 1; 157(7):3159–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
CUI Guohui, female, born in 1963, Associate Professor
The project was supported by a grant for returned scholars from the Ministry of Education (No. 6-74).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guohui, C., Xiaoping, L. & Junxia, Y. The effect of costimulatory factors in the pathogenesis of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Current Medical Science 23, 352–355 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829415
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02829415