Abstract
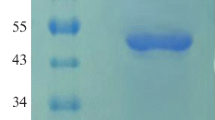
The extracellular activity ofAspergillus niger phytase at the end of the growth phase was 132 nkat/mL in a laboratory bioreactor. The purified enzyme has molar mass approximately 100 kDa, pH optimum at 5.0, temperature optimum at 55°C and high pH and temperature stability. TheK m for dodecasodium phytate, calcium phytate and 4-nitrophenyl phosphate are 0.44, 0.45 and 1.38 mmol/L, respectively. The enzyme is noncompetively inhibited by inorganic monophosphate (K i=2.85 mmol/L) and by Cu2+, Zn2+, Hg2+, Sn2+, Cd2+ ions and strongly by F− ones; it is activated by Ca2+, Mg2+ and Mn2+ ions. The substrate specificity of phytase is broad with the highest affinity to calcium phytate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976).
Laemmli U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriofage T4.Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Miller G.L.: Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar.Anal. Chem. 31, 426–428 (1959).
Newman K.: Phytase: The enzyme, its origin and characteristics: Impact and potential for increasing phosphorus availability, pp. 169–177 inBiotechnology in the Feed Industry, Proc. Alltech's 7th Ann. Symp. (T.P. Lyons, Ed.), Alltech Technical Publications. Nicholasville (Kentucky) 1991.
Powar V.K., Jagannathan V.: Purification and properties of phytate-specific phosphatase fromBacillus subtilis.J. Bacteriol. 151, 1102–1108 (1982).
Shieh T.R., Ware J.H.: Survey of microorganisms for the production of extracellular phytase.Appl. Microbiol. 16, 1348–1351 (1968).
Shimizu M.: Purification and characterization of phytase and acid phosphatase produced byAspergillus oryzae K1.Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 57, 1364–1365 (1993).
Simell M., Turunen M., Piironen J., Vaara T.: Feed and food applications of phytase. Lecture at3rd Meet. Industrial Applications of Enzyme, Barcelona (Spain) 1989.
Skowronski T.: Some properties of partially purified phytase fromAspergillus niger.Acta Microbiol. Polon. 27, 41–48 (1978).
Smith B.W., Roe J.H.: A photometric method for the determination of α-amylase in blood and urine, with the use of starchiodine color.J. Biol. Chem. 179, 53–59 (1949).
Ullah A.H.J.:Aspergillus ficuum phytase: Partial primary structure, substrate selectivity, and kinetic characterization.Prep. Biochem. 18, 459–471 (1988).
Ullah A.H.J., Gibson D.M.: Extracellular phytase (EC 3.1.3.8) fromAspergillus ficuum NRRL 3135: Purification and characterization.Prep. Biochem. 17, 63–91 (1987).
Volfová O., Dvořáková J., Hanzlíková A., Jandera A.: Phytase fromAspergillus niger.Folia Microbiol. 39, 479–482 (1994).
Watanabe R.S., Olsen S.R.: Test of an ascorbic method for determining phosphorus in water and NaHCO3 extracts from soil.Soil. Sci. Soc. Ann. Proc. 29, 667–678 (1965).
Yamada K., Minoda, Y., Yamamoto, S.: Chemical and physicochemical properties of phytase fromAspergillus tetteus.Agric. Biol. Chem. 36, 2097–2103 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dvořáková, J., Volfová, O. & Kopecký, J. Characterization of phytase produced byAspergillus niger . Folia Microbiol 42, 349–352 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816948
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816948