Abstract
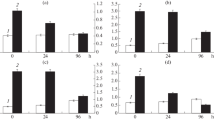
Corynebacterium sp. 3 B and three unidentified bacterial strains, all utilizing acetonitrile as a sole carbon and nitrogen source, were isolated from soil by the enrichment culture technique.Agrobacterium radiobacter 8/4/1, also capable of growing on acetonitrile as a sole C and N source, was obtained from a bromoxynil-metabolizing strainA. radiobacter 8/4 using the same method. Resting cells of strains BSA 1 and 3 B produced acetamide and acetic acid during incubation with acetonitrile, whileA. radiobacter 8/4/1 produced acetic acid only.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano Y., Fujishiro K., Tani Y., Yamada H.: Aliphatic nitrile hydratase fromArthrobacter sp. J-1. Purification and characterization.Agric. Biol. Chem. 46, 1165–1174 (1982).
DiGeronimo M.J., Antoine A.D.: Metabolism of acetonitrile and propionitrile byNocardia rhodochrous LL 100-21.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31, 900–906 (1976).
Harper D.B.: Microbial metabolism of aromatic nitriles. Enzymology of C-N cleavage byNocardia sp. (rhodochrous group) NCIB 11216.Biochem. J. 165, 309–319 (1977a).
Harper D.B.: Fungal degradation of aromatic nitriles. Enzymology of C-N cleavage byFusarium solani.Biochem. J. 167, 685–692 (1977b).
Jallageas J.C., Arnaud A., Galzy P.: Bioconversions of nitriles and their applications.Adv. Biochem. Eng. 14, 1–32 (1980).
Kobayashi M., Yanaka N., Nagasawa T., Yamada H.: Purification and characterization of a novel nitrilase ofRhodococcus rhodochrous K22 that acts on aliphatic nitriles.J. Bacteriol. 172, 4807–4815 (1990).
Mauger J., Nagasawa T., Yamada H.: Occurrence of a novel nitrilase, arylacetonitrilase, inAlcaligenes faecalis JM3.Arch. Microbiol. 155, 1–6 (1990).
Mayaux J.F., Cerbelaud E., Soubrier F., Faucher D., Petre D.: Purification, cloning and primary structure of an enantiomer-selective amidase fromBrevibacterium sp. strain R 312. Structural evidence for genetic coupling with nitrile hydratase.J. Bacteriol. 172, 6764–6773 (1990).
Nagasawa T., Yamada H.: Large-scale bioconversion of nitriles into useful amides and acids, pp. 277–318 in D.A. Abramowicz (Ed.):Biocatalysis. Van Nostrand Reinhold Catalysis Series, New York 1990.
Narayanasamy K., Shukla S., Parekh L.J.: Utilization of acrylonitrile by bacteria isolated from petrochemical waste waters.Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 28, 968–971 (1990).
Yamada H., Asano Y., Tani Y.: Microbial degradation of nitrile compounds. II. Microbial utilization of glutaronitrile.J. Ferment. Technol. 58, 495–500 (1980).
Yamamoto K., Komatsu K.: Purification and characterization of nitrilase responsible for the enantioselective hydrolysis fromAcinetobacter sp. AK 226.Agric. Biol. Chem. 55, 1459–1466 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínková, L., Hrůzová, J., Machek, F. et al. Isolation of acetonitrile-utilizing bacteria. Folia Microbiol 37, 372–376 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815665
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815665