Abstract
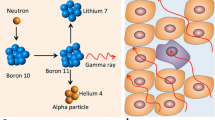
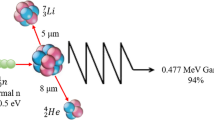
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is based on the nuclear reaction that occurs when a stable isotope, boron-10, is irradiated with low energy (0.025 eV) thermal neutrons (n th) to yield alpha (4He) particles and,7Li nuclei (10B+n th→[11B]→4He+7Li+2.79 MeV). The success of BNCT as a tumoricidal modality is dependent on the delivery of a sufficient quantity of10B andn th to individual cancer cells to sustain a lethal10B(n, α)7Li reaction. Boron delivery agents include a variety of compounds, such as the sulfhydryl containing polyhedral borane sodium borocaptate (Na2B12H11SH, [BSH]), boronoporphyrins, boronophenylalanine, carboranyl uridines (CBU), and boronated monoclonal antibodies (MAb). The present review will focus on three delivery systems that currently are under investigation in our laboratories, boronated monoclonal antibodies, carboranyl uridines, and boronophenylalanine. Methodology has been developed to heavily boronate MAb using a precision macromolecule, a “starburst” dendrimer, which can be linked to MAb by means of heterobifunctional reagents. Although the resulting immunoconjugates retain their in vitro immunoreactivity, they lose their in vivo tumor localizing properties and accumulate in the liver. In order to obviate this problem, work is now in progress to produce bispecific MAb, which can simultaneously recognize a tumor-associated antigen and a boronated macromolecule. Boron containing, nucleosides are potential vehicles for incorporating boron compounds into nucleic acids of neoplastic cells. For this purpose, carboranyl uridines have been synthesized with the boron moiety on either the pyrimidine base or on the carbohydrate component. Although such structures appear to be avidly taken up and retained by tumor cells in vitro, only the 5-carboranyl-nucleosides are converted biologically to the nucleotide. There is no evidence, however, that the latter are incorporated into nucleic acids. Other carboranyl nucleosides currently are being synthesized that may have better tumor localizing properties. The potential use of boronophenylalanine as a capture agent for the treatment of melanoma metastatic to the brain also is under investigation. A nude rat model has been developed using human melanoma cells that are stereotactically implanted into the brain. BNCT-treated animals have either had prolonged survival times or continue to live compared to control rats that invariably died of their tumors, thereby suggesting therapeutic efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam F., Barth R. F. and Soloway A. H. (1989) Boron containing immunoconjugates for neutron capture therapy of cancer and for immunocytochemistry.Antibody, Immunoconj. Radiopharm. 2, 145–163.
Alam F., Bapat V., Soloway A. H., Barth R. F., Mafune N. and Adams D. M. (1989) Boronated compounds for neutron capture therapy.Strahlenther. Onkol. 165, 121–123.
Asbury A. K., Ojeann R. G., Nielsen S. L. and Sweet W. H. (1972) Neuropathologic study of fourteen cases of malignant brain tumor treated by boron-10 slow neutron capture radiation.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 31, 278–303.
Barth R. F., Adams D. M., Soloway A. H., Mechetner E. B., Alam F., and Anisuzzaman A. K. M. (1991) Determination of boron in tissues and cells using direct-current plasma atomic emission spectroscopy.Analy. Chem. 63, 890–893.
Barth R. F., Soloway A. H., Adams D. M. and Alam F. (1992) Delivery of boron-10 for neutron capture theory by means of monoclonal antibody-starburst dendrimer immunoconjugates. inProgress in Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer (Allen B. W., Moore D. E., and Harrington B., eds.), Plenum, NY, pp. 265–268.
Barth R. F., Soloway A. H., Fairchild R. G. and Brugger R. M. (1992) Boron neutron capture therapy for cancer. Realities and prospects.Cancer 70, 2995–3007.
Bendayan M., Barth R. F., Gingras D., Londono I., Robinson P. T., Alam F., Adams D. M. and Mattiazzi L. (1989) Electron spectroscopic imaging for high resolution immunocytochemistry: use of boronated protein A.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37, 573–580.
Bennett B. D., Mumford-Zisk J., Barth R. F., Soloway A. H. and Morison G. H. (1993) Probing boronated nucleoside utilization by glioma cells using ion microscopy, inAdvances in Neutron Capture Therapy, (Soloway A. H., Barth R. F., and Carpenter D. E., eds.), Plenum, NY, pp. 423–428.
Clendenon N. R., Barth R. F., Gordon W. A., Goodman J. H., Alam F., Staubus A. E., Boesel C. P., Yates A. J., Moeschberger M. L., Fairchild R. G., and Kalef-Ezra J. A. (1990) Boron neutron capture therapy of a rat glioma.Neurosurgery 26, 47–55.
Coderre J. A., Joel D. D., Micca, P. L., Nawrocky M. M. and Slatkin D. N. (1992) Control of intracerebral gliosarcomas in rats by boron neutron capture therapy with p-boronophenylalanine.Radiation Res. 129, 290–296.
Entzian W., Soloway A. H., Raju R., Sweet W. H. and Brownell G. L. (1966) Effect of neutron capture irradiation upon malignant brain tumors in mice.Acta Radiol. 5, 95–100.
Fairchild R. F. and Bond V. P. (1985) Current status of10B-neutron capture therapy: enhancement of tumor dose via beam filtration and dose rate, and the effects of these parameters on minimum boron content: a theoretical evaluation.Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 11, 831–840.
Fairchild R. G., Bond V. P. and Woodhead A. (1989) Workshop summary of moderators’ reports, inClinical Aspects of Neutron Capture Therapy, Plenum, NY, pp. 261, 262.
Farr L. E., Sweet W. H., Robertson W. H., Foster J. S., Locksley H. B., Sutherland D. L., Mendelsohn M. L. and Stickley E. E. (1954) Neutron capture therapy with boron in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme.Am. J. Roentgenol. 71, 279–291.
Farr L. E., Haymaker W., Konikowski T. and Lippincott S. W. (1962) Effects of α-particles randomly induced in the brain in the neutron-capture treatment of intracranial neoplasms.Int. J. Neurol. 3, 564–575.
Glover G. H., Pauley J. M. and Bradshaw K. M. (1992) Boron-11 imaging with a three-dimensional reconstruction method.J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 2, 47–52.
Goudgaon N. M. and Schinazi R. F. (1994) Development of boron-containing pyrimidine and nucleoside analogues for neutron capture therapy. Current topics in medicinal chemistry, in press.
Hatanaka, H., Amano, K., Kamano S., and Sano K. (1986) Clinical experience of boron neutron capture therapy between 1968 and 1985, inNeutron Capture Therapy, (Hatanaka H., ed.), Nishimura Co., Ltd., Niigata, Japan, pp. 447–449.
Hatanaka H., Sano K., and Yasukochi H. (1992) Clinical results of boron neutron capture therapy, inProgress in Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer (Hatanaka H., ed.), Nishimura Co., Ltd., Niigata, Japan, pp. 561–568.
Joel D. D., Fairchild R. G., Laissue J. A., Saraf S. K., Kalef-Ezra J. A., Slatkin D. N. (1990) Boron neutron capture therapy of intracerebral rat gliosarcomas.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 87, 9808–9812.
Johnson C. W., Barth R. F., and Adams D. (1987) Phenotypic diversity of murine B16 melanoma detected by anti-B16 monoclonal antibodies.Cancer Res. 47, 1111–1117.
Kahl S. B., Joel D. D., Nawrocky M. M., Micca P. L., Tran K. P., Finkel G. C., and Slatkin D. N. (1990) Uptake of anido-carboranylporphyrin by human glioma xenografts in athymic nude mice and by syngeneic ovarian carcinomas in immunocompetent mice.Proc. Natl. Sci. USA 87, 7265–7269.
Köhler G. and Milstein C. (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity.Nature 256, 495–497.
Köhler G. and Milstein C. (1976) Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion.Europ. J. Immunol. 6, 511–519.
Liu L., Barth R. F., Soloway A. H., Anisuzzaman A. K. M., Alam F., Tjarks W., Zhao X., and Morrison G. H. (1991) Cellular uptake and distribution of 2-O-(o-Carboranyl Uridine) (CBU)Proc. Amer. Assoc. Cancer Res. 32, 407.
Locher G. L. (1936) Biological effects and therapeutic possibilities of neutrons.Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium. Ther. 36, 1–13.
Matalka K. Z., Bailey M. Q., Barth R. F., Staubus A. E., Soloway A. H., Moeschberger M. L., et al. (1993) Boron neutron capture therapy of intracerebral melanoma using boronphenylalanine as a capture agent.Cancer Res. 53, 3308–3313.
Matsumoto T., Aoki O., and Aizawa O. (1991) Phantom experiment in calculation for in vivo boron analysis by prompt gamma ray spectroscopy.Phys. Med. Biol. 36, 329–338.
Mishima Y., Ichibashi M., Honda C., Shiono M., Nakagawa T., Obara H., Shirakawa J., Hiratsuka J., Kanda K. Kobayashi T., Nozaki T., Aizawa O., Sato T., Karashima H., Yoshino K., and Fukuda H. (1982) Specific killing effect10B-para-borono-phenylalanine in thermal neutron capture therapy of malignant melanoma:in vitro radiobiological evaluation.J. Invest. Dermatol. 78, 215–218.
Mishima Y., Ichihashi M., Honda C., Shiona M., Nakagawa T., Obara H., Shirakawa J., Hiratsuka J, Kanda K., Kobayashi T., Nozaki T., Aizawa O., Sato T., Karashima H., Yoshino K., and Fukuda H. (1972) Advances in the control of human cutaneous primary and metastatic melanoma by thermal neutron capture therapy, inProgress in Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer. (Allen, B. J., Moore, D. E., and Harrington, B. V., eds.), Plenum, New York, pp. 577–583.
Saris S. C., Solares G. R., Wazer D. E., Cano G., Kerley S. E., Joyce M. A., Adelman L. S., Harling O. K., Madoc-Jone H., and Zamenhof R. G. (1992) Boron neutron capture therapy for murine malignant gliomas.Cancer Res. 52, 4672–4677.
Schinazi R. F. and Prusoff W. H. (1978) Synthesis and properties of boron and silicon substituted uracil or 2′-deoxyuridine.Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 4981–4984.
Solares G., Zamenhof R., and Cano G. (1993) Microdosimetry of neutron capture therapy Monte Carlo simulation and actually cell histology, inAdvances in Neutron Capture Therapy (Soloway A. H., Barth R. J., and Carpenter D. E., eds.), Plenum, pp. 213–216.
Soloway A. H., Hatanaka H., and Davis M. A. (1967) Penetration of brain and brain tumor. VII. Tumor-binding sulfhydryl boron compounds.J. Med. Chem. 10, 714–717.
Spielvogel B., Sood A., Powell W., Tomasz J., Porter K., and Shaw G. (1993) Chemical and enzymatic incorporation of boron into DNA, inAdvances in Neutron Capture Therapy (Soloway A. H., Barth R. F., and Carpenter D. E. eds.), Plenum, pp. 389–394.
Tjarks W., Anisuzzaman A. K. M., Liu L., Soloway A. H., Barth R. F., Perkins D. J., et al. (1992) Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of boronated urindine and glucose derivatives for boron neutron capture therapy.J. Med. Chem. 35, 1628–1633.
Tolpin E. I., Wellum G. R., Dohan F. C., Jr., Kornblith P. L., and Zamenhof R. G. (1975) Boron neutron capture therapy of cerebral gliomas, II. Utilization of the blood-brain barrier and tumor-specific antigens for the selective concentration of boron in gliomas.Oncology (Basel) 32, 223–247.
Wang C-K. C., Blue T. E., and Gahbauer R. (1989) A design study of an accelerator-based epithermal neutron source for boron neutron capture therapy.Strahlenther. Onkol. 165, 75–78.
Wheeler F. J. and Nigg D. W. (1992) Three dimensional radiation dose distribution analysis for boron neutron capture therapy.Nuclear Sci. Eng. 110, 16–31.
Yamamoto Y., Seko T., Nakamivea H., Nemoto H., Hojo H., Mukai N., and Hashimoto Y. (1992) Synthesis of carboranes containing nucleoside bases. An unexpectedly high cytostatic and cytocidal toxicity towards cancer cells.J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 157–158 (January 15).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barth, R.F., Soloway, A.H. Boron neutron capture therapy of primary and metastatic brain tumors. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 21, 139–154 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815348
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815348