Abstract
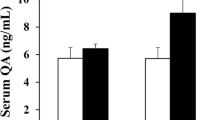
The aim of this paper was to determine whether prolonged drinking of lead acetate-containing water by adult rats, which imitates environmental exposure to lead (Pb), affects some morphological and biochemical properties of rat brain microvessels. We noted a significant increase of lead level in capillaries and synaptosomes obtained from brains of rats under chronic toxicity conditions. Intravenously injected horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was used to evaluate the functional state of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The results indicate that, systematically administered at low doses, lead induces BBB dysfunction. The changes, revealed in light microscopy and confirmed by electron microscopic studies, are typical for “leaky” microvessels, reported for variety of neuropathological conditions associated with BBB damage. Enhanced pinocytotic activity of the endothelial cells and the opening of interendothelial tight junctions, together with enormous phagocytizing action of the pericytes, are the most characteristic ultrastructural features noted. The presence of specific type of perivascular cells containing droplets of lipids in the cytoplasm, together with changes in phospholipid profile in brain capillaries, suggest that altered lipid composition of membranes may, at least in part, be responsible for changes in observed membrane permeability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bär T. (1987) Difference in mitochondrial content and cytochrome oxidase activity between pericytes and endothelial cells of rat brain capillaries, inStroke and Microcirculation (Cervos-Navarro, J. and Ferszt R. eds.), Raven, New York, pp. 27–33.
Bligh E. G. and Dyer W. J. (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification.Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 911–917.
Booth R. F. G. and Clark J. B. (1978) A rapid method for the preparation of relatively pure, metabolically competent synaptosomes from rat brain.Biochem. J. 176, 365–370.
Cory-Slechta D. A. and Wichowski D. V. (1991) Low level lead exposure increases sensitivity to the stimulus properties of dopamine D1 and D2 agonists.Brain Res. 553, 65–74.
Davies I. M., Elias R. W., and Grant L. D. (1993) Current issues in human lead exposure and regulation of lead.NeuroToxicology 14(2–3), 15–28.
Dąbrowska-Bouta B., Strużyńska L., and Rafałowska U. (1996) Does lead provoke the peroxidation porocess in rat brain synaptosomes?Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 29, 127–139.
Deane R. and Bradbury M. W. B. (1990) Transport of lead-203 at the blood-brain barrier during short cerebrovascular perfusion with saline in the rat.J. Neurochem. 54, 905–914.
Dermietzel R. and Krause D. (1991) Molecular anatomy of the blood-brain barrier as defined by immunocytochemistry, inInternational Review of Cytology. A Survey of Cell Biology, vol. 127 (Jeon K. W. and Friedlander M., eds.), Academic, San Diego, CA, pp. 57–109.
Deutsch C., Drown C., Rafałowska U., and Silver I. A. (1981) Synaptosomes from rat brain: morphology, compartmentation and transmembrane pH and electrical gradients.J. Neurochem. 36, 2063–2071.
Donaldson W. E. and Knowles S. O. (1993) Mini review. Is lead toxicosis a reflection of altered fatty acid composition of membranes?Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 104C,3, 377–379.
Donaldson W. E. and Leeming T. K. (1984) Dietary lead: effects on hepatic fatty acid composition in chicks.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 73, 119–123.
Gehrmann J., Matsumoto Y., and Kreutzberg G. W. (1995) Microglia: instrinsic immuno-effector cell of the brain.Brain Res. Rev. 20, 269–287.
Goldstein G. W., Asbury A. K., and Diamond, I. (1974) Pathogenesis of lead encephalopathy: Uptake of lead and reaction of brain capillaries.Arch. Neurol. 31, 382–389.
Goyer R. A. and Rhyne B. C. (1973) Pathological effects of lead.Internat. Rev. Exp. Pathol. 12, 1–77.
Grandjean P. (1993) International perspectives of lead exposure and lead toxicity.Neuro-Toxicology 14(2–3), 9–14.
Grant L. D., Kimmel C. A., West G. L., Martinez-Vargos Ch. M., and Howard J. L. (1980) Chronic low-level lead toxicity in the rat.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 56, 42–58.
Holtzman D., De Vries C., Ngunyen H., Olsen I., and Bensch V. (1984) Naturation of resistance to lead encephalopathy: Cellular and subcellular mechanisms.Neuro Toxicology 5, 97–124.
Khalil-Manesh F., Gonick H. C., Weiler E., and Saldanha L. (1991) Effect of dimercaptosuccinic acid on lead-induced hypertension, inHeavy Metals in the Environment (Farmer J. G., ed.), International Conference, Edinburgh.
Kochen J. A., Greener Y., and Hirano A. (1977) Relationship of blood and brain lead levels to morphologic changes in lead-induced chick embryo encephalopathy. II. Biochemical studies, inNeurotoxicology (Roizin L., Shiraki H., and Grčević N., eds.), pp. 309–311, Raven, New York.
Krigman M. R., Mushak P., and Bouldin T. W. (1977) An appraisal of rodent models of lead encephalopathy, inNeurotoxicology (Roizin L., Shiraki H., and Grčević N., eds.), pp. 299–302, Raven, New York.
Lawton L. J. and Donaldson W. E. (1991) Lead-induced tissue fatty acid alterations and lipid peroxidation.Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 28, 83–97.
Lowry O. H., Rosebrough N. J., Farr A. L., and Randall R. J. (1951) Protein measurements with Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Mato M., Aikawa E., Mato T. K., and Kurihara K. (1986) Tridimensional observation of fluorescent granular perithelial (FGP) cells in rat cerebral blood vessels.Anat. Res. 215, 413–419.
McMurche E. J. and Raison J. K. (1979) Membrane lipid fluidity and its effects on the activation energy of membrane-associated enzymes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 554, 364–374.
Mršulja B. B., Mršulja B. J., Fujimoto T., Klatzo I., and Spatz M. (1976). Isolation of brain capillaries: a simplified technique.Brain Res. 110, 361–365.
Nag S. and Harik S. I. (1987) Cerebrovascular permeability to horseradish peroxidase in hypertensive rats: effects of unilateral locus ceruleus lesion.Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 73, 247–253.
Nagy Z., Peters H., and Huttner J. (1984) Fracture faces of cell junctions in cerebral endothelium during normal and hyperosmotic conditions.Lab. Invest. 50, 313–322.
Nakazawa T., Nishikawa M., Aikawa E., and Mato M. (1994) Localization of lipids and lipoprotein in perivascular FGP cells of rat cerebellar cortex.Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 27, 323–330.
Needleman H. L. (1980)Low Level Lead Exposure. The Clinical Implications of Current Research. Raven, New York.
O'Tuama L. A., Kim C. S., Gatzy J. T., Krigman M. R., and Mushak P. (1976). The distribution of inorganic lead in guinea pig brain and neural barrier tissues in control and lead-poisoned animals.Toxicol. Applied Pharmacol. 36, 1–9.
Pentschew A. (1965) Morphology and morphogenesis of lead encephalopathy.Acta Neuropathol. 5, 133–160.
Pentschew A., and Garro F. (1966) Lead encephalomyelopathy of the suckling rat and its implications on the porphyrinopathic nervous diseases.Acta Neuropathol. 6, 266–278.
Rafałowska U., Erecińska M., and Wilson D. W. (1980) Energy metabolism in rat brain synaptosomes from nembutal-anesthetized and nonanesthetized animals.J. Neurochem. 34, 1380–1386.
Reese T. S., and Karnovsky M. J. (1967) Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase.J. Cell. Biol. 34, 207–215.
Rouser G., Fleischer S., and Yamamoto A. (1970) Two dimensional thin layer chromatographic separation of polar lipid and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots.Lipids 5, 494–496.
Silbergeld E. K. and Hruska E. (1980) Neurochemical investigations of low level lead exposure, inLow Level Lead Exposure. The Clinical Implication of Current Research (Needleman H. L., ed.), pp. 135–157, Raven, New York.
Sternberger N. H. and Sternberger L. A. (1987) Blood-brain barrier protein recognized by monoclonal antibody.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 8169–8173.
Sundströ R., Müntzing K., Kalimo H., and Sourander P. (1985) Changes in the integrity of the blood-brain barrier in suckling rats with low dose lead encephalopathy.Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 68, 1–9.
Thomas J. A., Dallenbach F. D., and Thomas M. (1973) The distribution of radioactive lead (210Pb) in the cerebellum of developing rats.J. Pathol. 109, 45–50.
Toews A. D., Kolber A., Hayward J., Krigman M. R., and Morell P. (1978) Experimental lead encephalopathy in the suckling rat: concentration of lead in cellular fractions enriched in brain capillaries.Brain Res. 147, 131–138.
Van Deurs B. (1976) Observations on the blood-brain barrier in hypertensive rats with particular reference to phagocytic pericytes.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 56, 65–77.
Walski M. and Borowicz J. (1995) Brain phagocytes and the microglia of the cerebral cortex of rats following an incident of total ischaemia.J. Brain Res. 36, 55–66.
Walski M. and Chomicz L. (1996) Ultrastructural evaluation of brain phagocytes in the period of survival after clinical death.Eur. J. Haematol. 57, 21–27.
Winder C., Carmichael N. G., and Lewis P. D. (1982) Effects of chronic low level lead exposure on brain development and function.Trends Neurosci. 6, 207–209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strużyńska, L., Walski, M., Gadamski, R. et al. Lead-induced abnormalities in blood-brain barrier permeability in experimental chronic toxicity. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 31, 207–224 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815125
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02815125