Summary
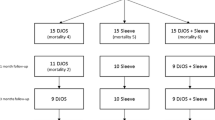
Many animal experiments have been studied on the choleretic effects of secretin. We intended to estimate secretin choleresis in human (15 patients) who had received PTCD or T-tube insertion into the common bile duct. Based upon these data of secretin and choleresis, secretin was administered to 11 patients with prolonged jaundice due to intrahepatic cholestasis in order to evaluate this as a new therapy for intrahepatic jaundice. As controls, eleven patients with intrahepatic cholestasis treated with steroid hormones and/or phenobarbital were used. In all cases with biliary drainage, secretin produced a remarkable choleretic effect with a high concentration of bicarbonate. In 9 out of 11 patients with intrahepatic cholestasis who were treated with secretin, levels of serum bilirubin decreased linearly and other liver function tests returned to the normal range. The mean values of T1/2 (number of days required for reduction by half) of serum bilirubin in 9 effective cases to secretin was 10.8 days. On the other hand, that in 11 effective cases treated with steroid hormones and/or phenobarbital was 23.2 days. These results suggest that secretin therapy may be an effective treatment for intrahepatic cholestasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stogiu G, Cavalli G: Some morphologic aspects and pathogenetic and therapeutic considerations in intrahepatic cholestasis. In: Gentilivi P, Teodori U, Gorini S, Popper H, eds. Intrahepatic Cholestasis. Raven Press, New York. 1975;153–164
Shaldon S, Sherlock S: Virus hepatitis with features of prolonged bile retention. Br Med J 1957;2:734–738
Fukumoto Y, Okita K, Oda M, et al: Marked hyperlipidemia and intrahepatic cholestasis. Acta Hepat Jap 1980;21:225–230 (in Jpn)
Desmet VJ: Morphologic and histological aspects of cholestasis. In: Popper H, Schaffner F, eds. Progress in Liver Diseases, volume 4. Grune & Stratton, New York. 1972;97–132
Johes RS, Geist RE, Hall AD: The choleretic effects of glucagon and secretin in the dog. Gastroenterology 1971;60:64–68
Wheeler HO, Mancusi-Ungaro PL: Role of bile ducts during secretin choleresis in dogs. Am J Phyiol 1966;210:1153–1159
William G, Hardison M, Norman JC: Electrolyte composition of the secretin flaction of bile from the perfused pig liver. Am J Physiol 1968;214:758–763
Forker EL: Two sites of bile formation as determined by mannitol and erythritol clearance in the guinea pig. J Clin Invest 1967;46:1189–1195
Forker EL: Hepatocellular uptake of insulin, sucrose and mannitol in rats. Am J Physiol 1970;219:1568–1573
Barnhard JL, Combes B: Erythritol and mannitol clearance with taurocholate and secretin-induced choleresis. Am J Physiol 1968;234:146–156
Strasberg SM, Ilson RG, Siminovitch KA, et al: Analysis of the components of bile flow in the rhesus monkey. Am J Physiol 1975;228:115–121
Galivan J: Stabilization of cholic acid uptake in primary cultures of hepatocytes. Archiv Bioch Biophy 1982;214:850–852
Klaassen CD, Watkins JB: Mechanisms of bile formation, hepatic uptake and biliary excretion. Pharmacol Rev 1984;36:1–67
Miner PB, Sutherland E, Simon FR: Regulation of hepatic sodium plus potassium-activated adenosine triphosphate activity by glucocorticoids in the rat. Gastroenterology 1980;79: 212–221
Stiehl A, Thalel MM, Admirand WH: The effects of phenobarbital on bile salts and bilirubin in patients with intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholestasis. N Engl J Med 1972;286:858–862
Salen TG, Shefer S: Effect of ulsodeoxycholic acid and cholesterol and bile acid metabolism. Gastroenterology 1986;91: 1007–1018
Dumont M, Erlinger S, Uchman S: Hypercholeresis induced by ursodeoxycholic acid and 7-ketolithocholic acid in the rat: Possible role of bicarbonate transport. Gastroenterology 1980;79:82–89
Romanski KW, Bochenek WJ: Effect of secretin, pancreozymin OP-CCK, and glucagon on bile flow and bile lipid secretion in rat. Gut 1983;24:803–806
Boyer JL, Bloomer JR: Canalicular bile secretion in man. Studies utilizing the biliary clearance of [14C] mannitol. J Clin Invest 1974;54:773–781
Russel TR, Searle GL, Jones RS: The choleretic mechanisms of sodium taurocholate, secretin and glucagon. Surgery 1975;77:498–504
Kaminski DL, Deshpande YG: Effect of theophylline on glucagon and secretin stimulated bile flow. Dig Dis Sci 1984;29:261–266
Thomen OÖ, Lasen JA: The effect of glucagon, dibtyrylic cyclic AMP and insulin on bile production in the intact rat and the perfused rat liver. Acta Pysiol Scand 1981;111:23–30
Igimi H, Carey MC: pH-solubility relations of chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids: Physical-chemical basis for dissmilar solution and membrane phenomena. J Lipid Res 1980;21:72–90
Ricci GL, Michiels R, Fevery J, et al: Enhancement by secretin of the apparently maximal hepatic transport of bilirubin in the rat. Hepatology 1984;4:651–657
Levine RA, Hall RC: Cyclic AMP in secretin choleresis. Evidence for a regulatory role in man and baboons but in dogs. Gastroenterology 1976;70:537–544
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukumoto, Y., Okita, K., Yasunaga, M. et al. A new therapeutic trial of secretin in the treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterol Jpn 24, 298–307 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774328
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774328