Abstract
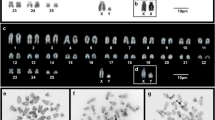
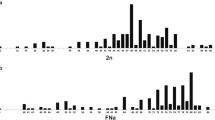
The banded karyotypes of 34 monkeys of known geographic origin and belonging to the Cercopithecus aethiops group of species (C. aethiops, C. pygerythrus, C. cynosurus, C. sabaeus) show that chromosome evolution in this group is highly conservative. All species have 2n =60 chromosomes with very similar chromosome banding. However, differences were found both within and between species. A polymorphism of the NOR area of the “marked” chromosome pairs was found in all taxa (9 of 34 animals). All individuals referred to C. sabaeus,from both West Africa and the Barbados, are characterized by having highly positive G- and C- banded terminal sequences on chromosomes 7,10,12, and 14. Outgroup comparisons with other primates and a parsimony analysis suggest that these terminal bands are derived and are probably good taxonomic and phylogenetic indicators. Moreover, chromosome 18 is variable both between and within species in G banding and in short-arm length. The existence of within-species variation in karyotypes suggests that karyological comparisons must be based on adequate samples that include specimens coming from all the major geographic populations of the species concerned.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton, E. H., and Zuckerman, S. (1950). The influence of geographic isolation on the skull of the green monkey (Cercopithecus aethiops sabaeus). I. A comparison between the teeth of the St. Kitts and the African green monkeys.Proc. Roy. Soc. B 137: 212–238.
Bobrow, M., and Madan, K. (1973). A comparison of chimpanzee and human chromosomes using Giemsa-11 and other chromosome banding techniques.Cytogenet. Cell. Genet. 12: 107–116.
Brown, D. (1982). Gene expression in eukaryotes.Science 211: 667–674.
Cassingena, R., Chany, C., Vignal, M., Suarez, H., Estrade, S., and Lazar, P. (1971). Use of monkey-mouse hybrid cells for the study of the cellular regulation of interferon production and action.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68: 580–584.
Chiarelli, B. (1963). Comparative morphometric analysis of the primate chromosomes. III. The chromosomes of generaHylobates, Colobus andPresbytis.Caryologia 16: 637–648.
Chiarelli, B. (1968). Chromosomal polymorphism in the species of the genusCercopithecus.Cytologia 33(1): 1–16.
Chu, E. H. Y., and Bender, M. A. (1962). Cytogenetics and evolution of primates.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 102: 253–266.
Comings, D. E. (1978). Mechanisms of chromosome banding and implication for chromosome structure.A. Rev. Genet. 12: 25–46.
Dandelot, P. (1959). Note sur la classification des Cercopithèques du groupeaethiops.Mammalia 23: 357–368.
de Grouchy, J., Finaz, C., and van Cong, N. (1977). Comparative banding and gene mapping in primate evolution. Evolution of chromosome 1 during fifty million years. In de la Chapelle, A., and Sorsa, M. (eds.),Chromosomes Today, Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, Vol. 6, pp. 183–190.
Dover, G. (1982). Molecular drive: A cohesive mode of species evolution.Nature (London) 299: 111–117.
Dutrillaux, B. (1979). Chromosomal evolution in primates: Tentative phylogeny fromMicrocebus murinus (prosimian) to man.Hum. Genet. 48: 251–314.
Dutrillaux, B., Viegas-Pequignot, E., Couturier, J., and Chauvier, G. (1978). Identity of euchromatic bands from man to Cercopithecidae (Cercopithecus aethiops, Cercopithecus sabaeus, Erythrocebus patas, andMiopithecus tatapoin).Hum. Genet. 45: 283–296.
Estop, A., Garver, J. J., and Pearson, P. L. (1978). Further studies on the comparative karyology of the African green and rhesus monkeys.Genetica 49(2/3): 131–138.
Finaz, C., Dubois, M.-F., Cochet, C., Vignal, M., and de Grouchy, J. (1976). Le caryotype du cercopithèque (Cercopithecus aethiops). Marquage et nomenclature.Ann. Genet. 19(3): 213–216.
Garver, J. J., Pearson, P. L., Estop, A., Dijksman, T. M., Wijnen, L. M. M., Westerveld, A., and Meera Khan, P. (1978). Gene assignments to the presumptive homologs of human chromosomes 1,6, 11, 12, and X in the Pongidae and Cercopithecoidea.Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 22: 564–569.
Giusto, J. P., and Margulis, L. (1981). Karyotypic fission theory and the evolution of Old World monkeys and apes.BioSystem. 13: 267–302.
Hill, W. C. O. (1966).Primates: Comparative Anatomy and Taxonomy, Vol. 6, Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh.
Ikeuchi, T. (1984). Inhibitory effects of ethidium bromide on mitotic chromosome condensation and its application to high-resolution chromosome banding.Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 38: 148–151.
Jones, K. W. (1977). Repetitive DNA and primate evolution. In Junis, Y. (ed.),Molecular Structure of Human Chromosomes, Academic Press, New York, pp. 295–326.
Jones, K. W. (1979). Related satellite DNA in man and higher primates. In Chiarelli, B., Koen, A. L., and Ardito, G. (eds.),Comparative Karyology of Primates, Mouton, The Hague, Paris, New York, pp. 61–71.
Ledbetter, D. H. (1981). Nor-bearing Y chromosome in a primate,Hylobates syndactylus.Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 29: 250–252.
Lejeune, J. (1982). Les chromosomes et l’espece.Pontif. Acad. Sci. (Scripta Varia) 50: 163–170.
Lejeune, J., Dutrillaux, B., Rethor, M. O., and Prieur, M. (1973). Comparison de la structure fine de chromatidesd’Homo sapiens et dePan troglodytes.Chromosoma 43: 423–444.
Marks, J. (1985). C-banding variability in the common chimpanzee,Pan troglodytes.J. hum. Evol. 14: 669–675.
Napier, J. R., and Napier, P. H. (1985).The Natural History of the Primates, British Museum (Natural History), London.
Ohno, S. (1970).Evolution by Gene Duplication. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Paris Conference (1975). Standardization in human cytogenetics.Cytogenet. Cell Genet. (Suppl.). 15: 201–238.
Ponsà, M., Estop, A. M., Miro, R., Rubio, A., and Egozcue, J. (1980). Banding patterns of the chromosomes ofMiopithecus talapoin compared toMacaca mulatto andCercopithecus aethiops.Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 28: 41–46.
Ponsà, M., MirÒ, R., Estop, A. M., and Egozcue, J. (1981). Banding patterns of the chromosomes ofErythocebus patas (Schreber, 1977) compared to other primate species.Genetica 56: 39–45.
Reumer, W. F., and de Boer, L. E. M. (1980). Standardization ofAotus chromosome nomenclature, with descriptions of the 2n = 49–50 karyotype and that of a new hybrid.J. hum. Evol. 9: 461–482.
Schwarz, E. (1926). Die Meerkatzen derCercopithecus aethiops Gruppe.Z. SÄugetierk. 1: 28–47.
Small, M., Stanyon, R., Smith, D., and Sineo, L. (1985). High resolution karyotype ofMacaca mulatto.Am. J. Primatol. 9(1): 63–67.
Soulie, J., and de Grouchy, J. (1981). A cytogenetic survey of 110 baboons (Papio cynocephalus).Am. J. phys. Anthrop. 56: 107–113.
Stanyon, R. (1983). A test of the karyotypic fissioning theory of primate evolution.BioSystem. 16: 57–63.
Stanyon, R., and Chiarelli, B. (1982). Phytogeny of the Hominoidea: The chromosome evidence.J. hum. Evol. 11: 493–504.
Stanyon, R., and Sineo, L. (1983). Citotassonomia e filogenesi del genereCercopithecus.Antropol. Contem. 6(3): 237–252.
Stanyon, R., Ardito, G., Lamberti, L., and Bigatti, P. (1983). The banded karyotypes ofMacaca fuscata compared withCercocebus aterrimus.Folia primatol. 41: 137–146.
Stanyon, R., Chiarelli, B., Gottlieb, K., and Patton, W. H. (1986). The phylogenetic and taxonomic position ofPan paniscus: A chromosomal perspective.Am. J. phys. Anthrop. 69: 489–498.
Staton, D. (1967). A preliminary analysis of karyotypic evolution in catarrhines.Mamm. Chr. Newslett. 8: 220–224.
Staton, D. (1970).Cercopithecus and centric fission.Mamm. Chr. Newslett. 11: 75–76.
Soulie, J., and de Grouchy, J. (1981). A cytogenetic survey of 110 baboons (Papio cynocephalus).Am. J. phys. Anthrop. 56: 107–113.
Stock, A. D., and Hsu, T. C. (1973). Evolutionary conservatism of genetic material. A comparative analysis of chromosome banding between Rhesus Macaque (2n = 42) and African green monkey (2n = 60).Chromosome 43: 211–224.
Tappen, N. (1960). Problems of distribution and adaptation of the African monkeys.Curr. Anthropol. 10: 91–126.
Thorington, R. W., and Groves, C. P. (1970). An annotated classification ot the Cercopithecoidea. In Napier, J. R., and Napier, P. H. (eds.).Old World Monkeys, Academic Press, New York, pp. 629–647.
Wilson, A. C., White, T. J., Carlson, S. S., and Cherry, L. M. (1977). Molecular evolution and cytogenetic evolution. In Sparkes, R. W., Comings, D. E., and Fox, C. F. (eds.),Human Molecular Cytogenetics, Academic Press, New York, pp. 375–393.
Yunis, J., Sawyer, J., and Dunham, K. (1980). The striking resemblance of high resolution G banded chromosomes of man and chimpanzee.Science 208: 1145–1148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sineo, L., Stanyon, R. & Chiarelli, B. Chromosomes of thecercopithecus aethiops species group:C. aethiops (Linnaeus, 1758),C. cynosurus (Scopoli, 1786),C. pygerythrus (Cuvier, 1821), andC. sabaeus (Linnaeus, 1766). Int JPrimatol 7, 569–582 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736662
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02736662