Abstract
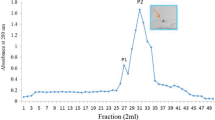
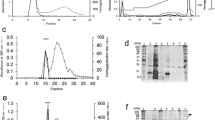
The galactose-binding lectin of human Placenta has been Purified to homogeneity by affinity chromatograPhy on asialo-fetuin column. The Protein, extractable from the tissue only with lactose is aPParently membrane-bound. Molecular weight determination of native Protein and subunit indicated a dimer of l3.4 kDa subunits. Inhibition of haemagglutination with various saccharides indicate that thiodigalactoside is the best inhibitor followed by lactose. However,P-nitroPhenyl-and 1-O-methyl derivatives of galactose showed that α-anomers inhibited slightly better than β-anomer. Modification of amino acid residues indicated involvement of arginine, lysine and histidine residues at the saccharidebinding site. Cysteine residue modificatioin also abolished haemagglutinating activity. Amino acid comPosition of the lectin is also Presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PHMB:
-
P-Hydroxymercuribenzoate
- DTNB:
-
dithionitrobenzene
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulPhate
- TNBS:
-
trinitrobenzene sulPhonic acid
- PBS:
-
PhosPhate buffered saline
- WGA:
-
wheatgerm agglutinin
- RCA1:
-
caster bean agglutinin
- WBA:
-
winged bean agglutinin
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electroPhoresis
- IgA:
-
immunoglobulin A
References
Andrews, R. (1965)Biochem. J.,96, 595.
Appukuttan, P. S., Surolia, A. and Bachhawat, B. K. (1977)Indian J. Biochem. BioPhys.,14, 382.
Appukuttan, P. S. and Basu, D. (1981)Anal. Biochem.,113, 253.
Ashwell, G. (1977)Mammalian Cell Membranes,4, 57.
Ashwell, G. and Harford, J. (1982)Annu. Rev. Biochem.,51, 531.
Atassi, M. Z. and Habeeb, A. F. S. A. (1972)Methods Enzymol.,25, 546.
Axen, R., Porath, J. and Ernback, S. (1967)Nature (London),214, l302.
Baenziger, J. U. and Kornfeld, S. (1974)J. Biol. Chem.,249, 7260, 7270.
Baenziger, J. U. and Maynard, Y. (1980)J. Biol. Chem.,255, 46l3.
Barondes, S. H. (1984)Science,223, 1259.
Bencze, W. L. and Schmid, K. (1957)Anal. Chem.,29, 1193.
Bloch, R. and Burger, M. M. (1974)Biochem. BioPhys. Res. Commun.,58, 13.
Bradford, M. M. (1976Anal. Biochem.,72, 248.
Butler, P. J. G., Harris, J. I., Hartley, B. S. and Leberman, R. (1969)Biochem. J.,112, 679.
Carding, S. R., Childs, R. A., ThorPe, R., Spitz and Feizi, T. (1985)Biochem. J.,228, 147.
Davis, B. D. (1964)Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.,121, 404.
de Waard, A., Hickman, S. and Kornfeld, S. (1976)J. Biol: Chem.,251, 7581.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A. and Smith, F. (1965)Anal. Chem.,28, 350.
Ellman, G. L. (1959)Arch. Biochem. BioPhys.,82, 70.
Fields, R. (1972)Methods Enzymol.,25, 464.
Habeeb, A. F. S. A. (1972)Methods Enzymol.,25, 457.
Hirabayashi, T. and Kasai, K. I. (1984)Biochem. BioPhys. Res. Commun.,122, 938.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970)Nature (London),227, 680.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J. (1951)J. Biol. Chem.,193, 265.
Miles, E. W. (1977)Methods Enzymol.,47, 431.
Riordian, J. F. and Vallee, B. L. (1972)Methods Enzymol.,25, 449, 500.
Roque-Barreira, M. C. and CamPos-Neto, A. (1985)J. Immunol.,13, 1740.
Savige, W. E. and Fontana, A. (1977)Methods Enzymol.,47, 442.
Smith, E. L. (1977)Methods Enzymol.,47, 156.
SPiro, R. G. (1966)Methods Enzymol.,8, 26.
Sureshkumar, G., APPukuttan, P. S. and Basu, D. (1982)J. Biosci.,4, 257.
Surolia, A., Prakash, N., Bishayee, S. and Bachhawat, B. K. (1973)Indian J. Biochem. BioPhys.,10, 145.
Takahashi, K. (1968)J. Biol. Chem.,243, 6171.
Thorpe, P. E., Detre, S. I., Foxwell, B. M. J., Brown, A. N. F., Skilleter, D. N., Wilson, G., Forrester, J. A. and Stripe, F. (1985)Eur. J. Biochem.,147, 197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nambiar, M.P., Basu, D. & Appukuttan, P.S. Physicochemical ProPerties and binding-site amino acid residues of galactoside-binding Protein of human Placenta. J. Biosci. 11, 331–338 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704683
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704683