Abstract
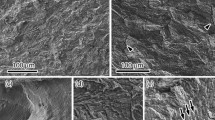
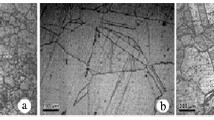
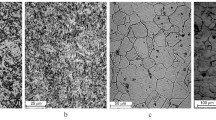
A study has been made of the effects of prior hydrogen attack damage on fatigue crack propagation behavior in commercial pressure vessel steels. Quenched and tempered Mn-Mo-Ni steel (ASTM A533B Class 2) and normalized and tempered 2.25Cr-1Mo steel (ASTM A387 Class 2 Grade 22) were exposed to gaseous hydrogen atmospheres for up to 1480 hours at hydrogen pressures of 12.4 to 17.2 MPa and temperatures of 550° to 600°C and tested in fatigue. Mild degrees of hydrogen damage, characterized by limited methane bubble formation with no appreciable decarburization, were found to increase growth rates slightly at near-threshold stress intensities. Severe degrees of hydrogen damage, characterized by extensive intergranular bubble formation and decarburization with associated large reductions in strength and toughness, were found to have no further influence on near-threshold growth rates. The minor influence of prior hydrogen damage on fatigue crack extension, even for cases of severe attack, is attributed to result from two mutually competitive mechanisms, namely, the creation of methane-filled voids on prior austenite grain boundaries, whichincreases growth rates, and the enhancement in crack closure from decarburization-induced softening and rough cavitated intergranular fracture surfaces, whichdecreases growth rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. Canonico, G. C. Robinson, and W. R. Martin: “Pressure Vessels for Coal Conversion Systems,” Report No. ORNL/TM-5685, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, Sept. 1978.
W. Lochmann:Proc. 4th Annual Conf. on Materials for Coal Conversion and Utilization, Gaithersberg, MD, Dept. of Energy, Washington, DC, 1979, pp. 1–31.
T. E. Scott: inApplication of 2 1/4 Cr-1Mo Steel for Thick-Wall Pressure Vessels, ASTM STP 755, Amer. Soc. Test. Matls., Philadelphia, PA, 1982, pp. 7–25.
R.W. Swindeman, R. D. Thomas, R. K. Hanstad, and C.J. Long: “Assessment of Need for an Advanced High Strength Chromium-Molybdenum Steel for Construction of Third Generation Gasifier Pressure Vessels,” Report No. ORNL/TM-8873, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 1983.
R.M. Horn, R.J. Kar, V. F. Zackay, and E. R. Parker:J. Mat. for Energ. Syst., 1979, vol. 1, pp. 77–92.
G. D. Nasman and W. P. Webb: inAdvanced Materials for Pressure Vessel Service with Hydrogen at High Temperatures and Pressures, M. Semchyshen, ed., ASME Vol. MPC-18, Amer. Soc. Mech. Eng., New York, NY, 1982, pp. 1–23.
R. O. Ritchie, E. R. Parker, P. N. Spencer, and J. A. Todd:J. Mat. for Energ. Syst., 1984, vol. 6, pp. 151–62.
T. George, E. R. Parker, and R. O. Ritchie:Mater. Sci. and Technol., 1985, vol. 1, pp. 198–208.
Anon: Steels for Hydrogen Service at Temperatures and Pressures in Petroleum Refineries and Petrochemical Plants, API Publication 941, 1977.
L.C. Weiner:Corrosion, 1961, vol. 17, pp. 137–43.
R.E. Allen, R. J. Janson, P.C. Rosenthal, and F.H. Vitovec:Proc. API, 1962, vol. 42, pp. 452–62.
D.A. Westphal and F. J. Worzala: inHydrogen in Metals, I.M. Bernstein and A. W. Thompson, eds., Amer. Soc. for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1974, pp. 78–79.
G. H. Geiger and O. P. Angeles: inA Study of the Effects of High Temperature and High Pressure Hydrogen on Low Alloy Steels, API Publication 945, New York, NY, 1975.
P.G. Shewmon:Metall. Trans. A, 1976, vol. 7A, pp. 279–86.
G. Sunderajan and P.G. Shewmon:ibid., 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 1761–65.
S. S. Vagarali and G. R. Odette:ibid., 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 2071–82.
G. R. Odette and S. S. Vagarali:ibid., 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 299–303.
J. Wanagel, T. Hakkarainer, and Che-Yu Li: inApplication of 2 1/4 Cr-1Mo Steel for Thick Wall Pressure Vessels, ASTM STP 755, Amer. Soc. Test. Matls., Philadelphia, PA, 1982, pp. 93–108.
P.G. Shewmon and Z.-S. Yu: inAdvanced Materials for Pressure Vessel Service with Hydrogen at High Temperatures and Pressures, M. Semchyshen, ed., ASME Vol. MPC-18, Amer. Soc. Mech. Eng., New York, NY, 1982, pp. 85–92.
D.W. Chung, J.A. Todd, J.K. Youngs, and E.R. Parker:ibid., M. Semchyshen, ed., ASME Vol. MPC-18, Amer. Soc. Mech. Eng., New York, NY, 1982, pp. 25–52.
W.E. Erwin: “The Mechanisms of Hydrogen Attack in 2 1/4 Cr-1Mo Steel,” Proc. 47th Midyear Refining Meeting, Session in Hydrogen Operations, API, New York, NY, 1982.
M. Natan and H. H. Johnson:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 963–71.
S.F. Clugston, J. R. Weertman, and P.G. Shewmon:ibid., 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 695–99.
G.H. Aronson and R.O. Ritchie:J. Test. Eval., 1979, vol. 7, pp. 208–15.
R.O. Ritchie:Int. Met. Rev., 1979, vol. 20, pp. 205–30.
V. B. Dutta, S. Suresh, and R.O. Ritchie:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1193–207.
R. J. Kar and J. A. Todd: inApplication of 2 1/4 Cr-1Mo Steel for Thick Wall Pressure Vessels, ASTM STP 755, Amer. Soc. Test. Matls., Philadelphia, PA, 1982, pp. 383–417.
R.O. Ritchie and J.F. Knott.Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 782–85.
K. Minakawa and A.J. McEvily:Scripta Met., 1981, vol. 15, pp. 633–36.
R.O. Ritchie, S. Suresh, and P. K. Liaw: inUltrasonic Fatigue, J.M. Wellset al., eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1982, pp. 443–60.
W. Elber:Eng. Fract. Mech., 1970, vol. 2, pp. 37–45.
A.T. Stewart:, 1980, vol. 13, pp. 463–78.
R.O. Ritchie, S. Suresh, and C.M. Moss:J. Eng. Matls. Tech., Trans. ASME Ser. H, 1980, vol. 102, pp. 293–99.
N. Walker and C.J. Beevers:Fat. Eng. Mat. Struct., 1979, vol. 1, pp. 135–48.
S. Suresh and R.O. Ritchie:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1627–31.
K. Endo, T. Okada, K. Komai, and M. Kiyota:Bull. JMSE, 1972, vol. 15, pp. 1316–23.
J.-L. Tzou, S. Suresh, and R.O. Ritchie:Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 105–16.
J.-L. Tzou, C.H. Hsueh, A.G. Evans, and R.O. Ritchie:ibid., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 117–27.
S. Suresh and R.O. Ritchie: inFatigue Crack Growth Threshold Concepts, D.L. Davidson and S. Suresh, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 227–61.
R.O. Ritchie:J. Eng. Matls. Tech., Trans. ASME Ser. H, 1977, vol. 99, pp. 195–204.
S. Suresh:Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 2375–85.
R.O. Ritchie and J.F. Knott:Acta Metall., 1973, vol. 21, pp. 639–48.
S. Suresh and R. O. Ritchie:Metal Sci., 1982, vol. 16, pp. 529–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Graduate Student in the Department of Materials Science and Mineral Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pendse, R.D., Ritchie, R.O. A study of fatigue crack propagation in prior hydrogen attacked pressure vessel steels. Metall Trans A 16, 1491–1501 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658681
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02658681