Summary
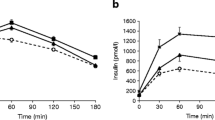
Alteration in insulin secretion and reduced peripheral sensitivity to the hormone have been reported in type II diabetes. In this paper, a comparison is made of basal glucose production (3H-6 glucose), insulin secretion and insulin sensitivityin vivo (hyperglycemic clamp) andin vitro (binding to circulating monocytes) in 24 patients with recently diagnosed type II diabetes, matched for age and fasting glycemia and divided into non-obese (14 subjects) and moderately obese (10 subjects), and in 9 non-obese controls. The non-obese diabetics were slightly hyperinsulinemic during fasting (10.8±1.0vs 4.8±0.8 µU/ml in controls, p < 0.0005), with a significant reduction in early and late insulin secretion (14.0±1.5vs 20.8 ± 2.0 µU/ml, p<0.01 and 24.8±3.3vs 34.7±2.14 µU/ml, p<0.025). The insulin sensitivity index MCR/I was significantly reduced (2.30±0.32vs 4.14±0.40, p<0.005). Endogenous glucose production was significantly increased (107±10.2vs 84±3.7 mg/m2 per min, p<0.025) and displayed a positive correlation with fasting glycemia (r=0.51, p<0.05). Insulin binding to monocytes was significantly lower than in controls (2.36±0.22%vs 4.06±0.32%, p<0.0005). Moderately obese diabetics also were significantly hyperinsulinemic in the fasting state (18.1±2.8 µU/ml, p<0.0005vs controls) but, typically, lacked the early secretory phase (20.6±3.6 µU/mlvs baseline, n.s.). A similar increase of hepatic glucose production (107±11.2 mg/m2 per min, p<0.025vs controls, n.s.vs non-obese diabetics) and decrease of peripheral sensitivity to insulin (MCR/I=1.78±0.31, p<0.0005vs controls, n.s.vs non-obese diabetics) was found in moderately obsese diabetics, as well as a significant reduction of insulin binding to insolated monocytes (2.62±0.4% p<0.01vs controls, n.s.vs non-obese diabetics). These results confirm that common defects of both non-obese and moderately obese type II diabetics are: lack of early phase of glucose induced insulin secretion, increase in hepatic glucose production and decrease of peripheral insulin sensitivity together with reduction of insulin binding to circulating monocytes. The hypothesis of a unique defect as a cause of hyperglycemia in type II diabetes in early clinical phase is not borne out by the results of this study. Moderate obesity, even if able to reduce insulin sensitivity, seems to be less important in determining hyperglycemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cherrington A. D., Williams P. E., Harris M. S.: Relationship between the plasma glucose level and glucose uptake in the conscious dog — Metabolism27, 787, 1978.
DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E.: The pathogenesis of non-insulin-dependent diabetes: an update — Medicine (Baltimore)61, 125, 1982.
DeFronzo R. A., Simonson D., Ferrannini E.: Hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance: a common feature of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus — Diabetologia23, 313, 1982.
DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R.: The glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance — Amer. J. Physiol.237, E214, 1979.
Dimitriadis G. D., Pehling G. B., Gerich J. E.: Abnormal glucose modulation of islet A- and B-cell responses to arginine in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes34, 541, 1985.
Doberne L., Greenfield M. S., Rosenthal M., Widstrom A., Reaven G.: Effect of variations in plasma glucose concentration on glucose utilization (M) and metabolic clearance (MCR) rates during insulin clamp studies in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes31, 396, 1982.
Donner C. C., Fraze E., Chen Y.-D. I., Reaven G. M.: Quantitation of insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes34, 831, 1985.
Fajans S. S., Floyd J. C. Jr., Taylor C. E., Pek S.: Heterogeneity of insulin responses in latent diabetes — Trans. Ass. Amer. Phycns87, 83, 1974.
Ginsberg H., Kimmerling G., Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M.: Demonstration of insulin resistance in untreated adult onset diabetic subjects with fasting hyperglycemia — J. clin. Invest.55, 454, 1975.
Halter J. B., Porte D. Jr., Best J. D., Pfeifer M. A.: Glucose regulation in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: interaction between pancreatic islet and the liver — Amer. J. Med.79, (Suppl. 2B), 6, 1985.
Himsworth H.P., Kerr R. B.: Insulin-sensitive and insulin-insensitive types of diabetes mellitus — Clin. Sci.4, 119, 1942.
Hosker J. P., Burnett M. A., Davies E. G., Harris E. A., Turner R. C.: Sulphonylurea therapy doubles B-cell response to glucose in type 2 diabetic patients — Diabetologia28, 809, 1985.
Issekutz B. Jr., Allen M., Borkow I.: Estimation of glucose turnover in the dog with glucose-2-T and glucose-U-14C — Amer. J. Physiol.222, 710, 1972.
Katz J., Dunn A.: Glucose-2-T as a tracer for glucose metabolism — Biochemistry (Wash.)6, 1, 1967.
Klotz M. I.: Numbers of receptor sites from Scatchard graph: facts and fantasies — Science217, 1247, 1982.
Kolterman O. G., Gray R. S., Griffin J., Burstein P., Insel J., Scarlett J. A., Olefsky J. M.: Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — J. clin. Invest.68, 957, 1981.
Kolterman O. G., Olefsky J. M.: The impact of sulfonylurea treatment upon the mechanisms responsible for the insulin resistance in type II diabetes — Diabetes Care7 (Suppl. 1), 81, 1984.
Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M.: Insulin binding in diabetes. Relationship with plasma insulin levels and insulin sensitivity — Diabetes26, 680, 1977.
Pagano G., Cassader M., Bozzo C., Lenti G.: Study of the relationship between insulin receptors and human adipocytes: an approach to the diabetic problem. In:Crepaldi G., Lefebvre P. J., Alberti K. G. M. M. (Eds): Diabetes, obesity and hyperlipidemias. Academic Press, London-New York-San Francisco, 1978; p. 215.
Pagano G., Cassader M., Bozzo C., Masciola P., Trovati M., Lenti G.: Insulin resistance in human obesity:in vivo studies by ‘insulin clamping’ andin vitro by insulin binding and biological activity on isolated adipocytes. In:Enzi G., Crepaldi G., Pozza G., Renold A. E. (Eds): Obesity: pathogenesis and treatment. Academic Press, London-New York, 1981; p. 175.
Pagano G., Lombardi A., Pisu E., Bozzo C., Masciola P., Ferraris G. M., Bruno A.: Hyperglycaemic clamp and insulin binding to isolated monocytes before and after glibenclamide treatment of mild type II diabetics — Hormone metabol. Res.16, 215, 1984.
Raskin P.: Islet-cell abnormalities in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Amer. J. Med.79 (Suppl. 2B), 2, 1985.
Reaven G. M.: Insulin secretion and insulin action in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes Care7 (Suppl. 1), 17, 1984.
Reaven G. M.: Relationship between defects in insulin secretion and insulin action in the pathogenesis of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In:Belfiore F. (Ed.): Frontiers in diabetes, Vol. 4. S. Karger, Basel-New York, 1984; p. 55–68.
Reaven G. M., Bernstein R., Davis B., Olefsky J. M.: Nonketotic diabetes mellitus: insulin deficiency or insulin resistance? — Amer. J. Med.60, 80, 1976.
Reaven G. M., Olefsky J. M.: Relationship between heterogeneity of insulin responses and insulin resistance in normal subjects and patients with chemical diabetes — Diabetologia13, 201, 1977.
Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E.: Mechanism and significance of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes30, 990, 1981.
Scatchard G.: The attraction of proteins for small molecules and ions — Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.51, 660, 1949.
Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R.: A model of the kinetics of insulin in man — J. clin. Invest.53, 1481, 1974.
Simonson D. C., Ferrannini E., Bevilacqua S., Smith D., Barrett E., Carlson R., DeFronzo R. A.: Mechanism of improvement in glucose metabolism after chronic glyburide therapy — Diabetes33, 832, 1984.
Skyler J. S.: Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a clinical strategy — Diabetes Care7 (Suppl. 1), 118, 1984.
Steele R., Well J. S., DeBodo R. C., Altszuler N.: Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method — Amer. J. Physiol.187, 15, 1956.
Truglia J. A., Livingstone J. N., Lockwood D. M.: Insulin resistance: receptor and postbinding defects in human obesity and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Amer. J. Med.79 (Suppl. 2B), 13, 1985.
Ward W. K., Beard J. C., Halter J. B., Pfeifer M. A., Porte D. Jr.: Pathophysiology of insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus — Diabetes Care7, 491, 1984.
Weder H. G., Schildknecht J., Lutz A. L., Kesselring P.: Determination of binding parameters from Scatchard plots — Europ. J. Biochem.42, 475, 1974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant fromConsiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, P.F. Medicina Preventiva, SP4,Malattie Degenerative, N. 84.02449.56.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pisu, E., Lombardi, A., De Benedictis, D. et al. Insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity defects are a common feature of mild, clinically homogeneous, recently diagnosed type II (Non-insulin-dependent) diabetics. Acta diabet. lat 23, 215–225 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624707
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02624707