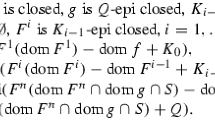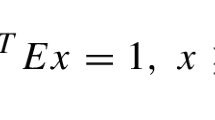Abstract
The classical Fermat-Weber problem is to minimize the sum of the distances from a point in a plane tok given points in the plane. This problem was generalized by Witzgall ton-dimensional space and to allow for a general norm, not necessarily symmetric; he found a dual for this problem. The authors generalize this result further by proving a duality theorem which includes as special cases a great variety of choices of norms in the terms of the Fermat-Weber sum. The theorem is proved by applying a general duality theorem of Rockafellar. As applications, a dual is found for the multi-facility location problem and a nonlinear dual is obtained for a linear programming problem with a priori bounds for the variables. When the norms concerned are continuously differentiable, formulas are obtained for retrieving the solution for each primal problem from the solution of its dual.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Bongartz, P.H. Calamai and A.R. Conn, A projection method forl p norm location-allocation problems,Mathematical Programming 66 (1994) 283–312.
T. Bonnesen and W. Fenchel,Theory of Convex Bodies (BCS Associates, Moscow, ID, 1987). [English translation ofTheorie der konvexen Körper, Ergebnisse der Mathematik und ihrer Grenzgebiete Band 3 (Springer, Berlin, 1934)].
P.H. Calamai and A.R. Conn, A stable algorithm for solving the multifacility location problem involving Euclidean distances,SIAM Journal of Scientific and Statistical Computing 1 (1980) 512–526
P.H. Calamai and A.R. Conn, A projected Newton method forl p norm location problems,Mathematical Programming 38 (1987) 75–109.
A. Dax, On regularized least norm problems,SIAM Journal of Optimization 2 (1992) 602–618.
A. Dax, On minimum norm solutions,Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 76 (1993) 183–193.
A. Dax, The relationship between theorems of the alternative, least norm problems, steepest descent directions, and degeneracy: a review,Annals of Operations Research 46 (1993) 11–60.
A. Dax, A further look at theorems of the alternative, Technical Report, Hydrological Service of Israel (1994) 1–26.
H. Juel and R.F. Love, On the dual of the linearly constrained multi-facility location problem with arbitrary norms,Transportation Science 15 (1981) 329–337.
H. Juel and R.F. Love, Duality in constrained location problems,Operations Research Letters 6 (1987) 281–284.
H. Juel and R.F. Love, The dual of a generalized minimax location problem,Annals of Operations Research 40 (1992) 261–264.
R.F. Love, The dual of a hyperbolie approximation to the generalized constrained multi-facility location-problem withl p distances,Management Science 21 (1974) 22–33.
M.L. Overton, A quadratically convergent method for minimizing a sum of Euclidean norms,Mathematical Programming 27 (1983) 34–63.
R. Schneider,Convex Bodies: The Brunn-Minkowski Theory (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1993).
V.P. Sreedharan, Solution of overdetermined linear equations which minimize error in an abstract norm,Numerical Mathematics 13 (1969) 146–151.
V.P. Sreedharan, Least squares algorithms for finding solutions of overdetermined linear equations which minimize error in an abstract norm,Numerical Mathematics 17 (1971) 387–401.
V.P. Sreedharan, Least squares algorithms for finding solutions of overdetermined linear equations which minimize error in a smooth strictly convex norm,Journal of Approximation Theory 8 (1973) 46–61.
V.P. Sreedharan, An algorithm for non-negative norm minimal solutions,Numerical Functional Analysis and Optimization 9 (1987) 193–232.
J. Stoer and C. Witzgall,Convexity and Optimization in finite dimensions I (Springer, Berlin, 1970).
C. Witzgall, Optimal location of a central facility, mathematical models and concepts, National Bureau of Standards Report 8388 (Washington, DC, 1964).
W.H. Yang, On generalized Hölder inequality,Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods and Applications 16 (1991) 489–498.
W.H. Yang, A duality theorem for plastic torsion,International Journal of Solids and Structures 27 (1991) 1981–1989.
W.H. Yang, Large deformation of structures by sequential limit analysis,International Journal of Solids and Structures 30 (1993) 1001–1013.
W.H. Yang, Solving linear programs by calculus, article in preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaplan, W., Yang, W.H. Duality theorem for a generalized Fermat-Weber problem. Mathematical Programming 76, 285–297 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02614441
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02614441