Abstract
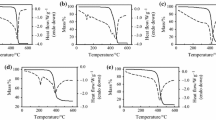
The thermogravimetry of a mixed polymer waste stream has been studied and the weight-loss behaviour of this heterogeneous mixture has been compared with results obtained from the weight-loss curves of some individual polymers. The results suggest that the behaviour of the mixture cannot be predicted by the simple additive behaviour of the individual polymers since interactions can occur which influence the degradation weight-loss profiles. The heterogeneous polymeric waste studied was that generated from the shredding of old discarded automobiles. The results of the study indicate that while it is possible to determine what is present in a sample, the relevance of the data to a very heterogeneous waste stream is questionable.
Zusammenfassung
Die Thermogravimetrie gemischter Polymerabfallströme wurde untersucht und das Gewichtsverlustverhalten dieser heterogenen Gemische mit den Resultaten der Gewichtsverlustkurven einiger reiner Polymere verglichen. Die Ergebnisse weisen darauf hin, daß das Verhalten des Gemisches nicht anhand eines einfachen additiven Verhaltens der Polymerkomponenten vorausgesagt werden kann, da Wechselwirkungen auftreten können, welche die Gewichtsverlustporofile der Zersetzungen beeinflussen. Der untersuchte heterogene Polymerabfall wurde durch Zerkleinerung von alten ausrangierten Automobilen gewonnen. Die Resultate der Untersuchung zeigen, daß es möglich ist, zu bestimmen, was in einer Probe enthalten ist, daß jedoch die Relevanz der Daten bei einem sehr heterogenen Abfallstrom fraglich ist.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Ratray, Resource Recycling, 5 (1993) 65.
T. R. Curlee and S. Das, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 5 (1991) 343.
J. W. Everett and J. J. Peirce, Resource, Conservation and Recycling, 6 (1992) 355.
F. Rodriguez, L. M. Vane, J.-J. Schreiter and P. Clark, ACS Symp. Series, 509 (1992) 99.
American Iron and Steel Institute. Special Report: “Recycling: State of the Art for Scrapped Automobiles Rept. #67110, 1992.
Plastics Institute of American, Secondary Reclamation of Plastic Waste, PIA Research Report Phase I: Development of Techniques for Preparation and Formulation, Technomic Publishing, 1987.
M. Day, J. Graham, R. Lachmansingh and E. Chen, Resource Conservation and Recycling, 9 (1993) 255.
E. Nieto, “Technical Support Document for Treatment Levels for Auto Shredder Waste” Final Report, State of California Department of Health Services, 1989.
M. Day, SAE Technical Paper 93-0562 March 1993.
S. J. Ainsworth, Chemical and Eng. News, 70 (1992) 34.
M. Day, J. D. Cooney and C. Klein, J. Thermal Anal., 40 (1993) 669.
R. J. Cvetanovic, D. L. Singleton and G. Paraskevopoulos, J. Phys. Chem., 83 (1979) 50.
V. Boyko, (Private Communications) 1993.
M. Day, J. D. Cooney and M. MacKinnon, “Recycling Mixed Plastic Waste Streams: II The role of impurities on Pyrolysis Processes” Proc. 22nd NATAS Conference, Sept. 1993, p. 556.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Issued as NRCC #37562