Abstract
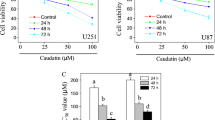
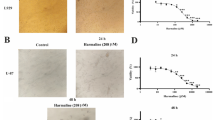
We have elucidated the pharmacological action of the anti-matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor BE16627B on glioma cells. The study was limited to the noncytotoxic dose range. The aim of the study was to investigate whether the cytotoxicity of BE16627B, an anti-MMP agent, is related to apoptosis in the human malignant glioma cell lines U87MG, U251MG, and U373MG. MTT assay was performed to detect the cytotoxic dose range. Agarose gel electrophoresis was performed with purified genomic DNA following exposure to 20 to 500 μM BE16627B for 24h, compared with 0 μM for the control group. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was employed to study nuclear fragmentation following exposure to 0, 20, and 500 μM of the agent for 24 h. An in situ endolabeling assay was performed to determine the index of apoptotic induction. MTT assay revealed that concentrations of 100 μM and above were cytotoxic. DNA laddering was demonstrated in agarose gel electrophoresis. TEM disclosed condensing and fragmentation of the chromatin. None of these changes were observed in the control group and the noncytotoxic dose group. The in situ endolabeling study disclosed that the apoptotic index was significantly elevated by cytotoxic doses of this agent (U373MG; control, 4.0%; 500 μM, 68.5%). These results indicated that cytotoxic concentrations of BE16627B induced apoptosis in human malignant glioma cell lines. In our previous report, this agent inhibited activity of MMP in noncytotoxic concentrations. Further study should be done to determine the pharmacological action of toxic BE16627B.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavenee WK, Furnari FB, Nagane M, et al (2000) Diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas. In: Kleihues P, Cayenee WK (eds) Pathology and genetics of the nervous system, IARC Press, Lyon, France, pp 10–21
Del Maestro R, Vaithlingham I, MacDonald W (1995) Degeneration of collagen type IV by C6 astrocytoma cells. J Neurooncol 24:75–81
Abe T, Mori T, Kohno K, et al (1994) Expression of 72 kDa type IV collagenase and invasion activity of human glioma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 12:296–304
Nakagawa T, Kubota T, Kabuto M, et al (1994) Production of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 by human brain tumors. J Neurosurg 81:69–77
Nakano A, Tani E, Miyazaki K, et al (1995) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in human gliomas. J Neurosurg 83:298–307
Rao J, Stack PA, Mohanan S, et al (1993) Elevated level of Mr 92 000 type IV collagenase in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 53:2208–2211
Yoshida D, Noha M, Watanabe K, et al (2001) Novel approach to analysis of in vitro tumor angiogenesis with a variable-pressure scanning electron microscope: suppression by matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor SI-27. Brain Tumor Pathol 18:89–100
Watanabe K, Yoshida D, Noha M, et al (2001) Suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and-9 mediated cell invasiveness by a novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, BE16627B on human glioma cell lines; in vitro study. J Neurooncol 52:1–9
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Wick W (2001) Molecular determinants of glioma cell migration and invasion. J Neurosurg 94:978–984
Shalinsky DR, Brekken J, Zou H, et al (1999) Broad antitumor and angiogenic activities of AG3340, a potent and selective MMP inhibitor undergoing advanced oncology clinical trials. Ann NY Acad Sci 30:236–270
Bernstein J, Laws E, Levine K, et al (1991) C6 glioma-astrocytoma cell and fetal astrocyte migration into artificial basement membrane: a permissive substrate for neural tumors but not fetal astrocytes. Neurosurgery 28:652–658
Pedersen P, Ness G, Engebraaten O, et al (1994) Heterogenous response to the growth factors [EGF, PDGF (bb), TGF-alpha, bFGF, IL-2] on glioma spheroid growth, migration and invasion. Int J Cancer 56:225–261
Heylen N, Vincent LM, Devos V, et al (2002) Fibroblasts capture cathepsin D secreted by breast cancer cells: possible role in the regulation of the invasive process. Int J Oncol 20:761–767
Liotta L, Steeg P, Steler-Stevenson W (1991) Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 64:327–336
Daiz VM, Planaguma J, Thomson TM, et al (2002) Tissue plasminogen activator is required for the growth, invasion, and angiogenesis of pancreatic tumor cells. Gastroenterology 122:806–819
Del Rosso M, Fibbi G, Pucci M, et al (2002) Multiple pathways of cell invasion are regulated by multiple families of serine proteinases. Clin Exp Metastasis 19:193–207
Kashida H, Kawamata H, Ichikawa K, et al (2001) Intracytoplasmic localization of cathepsin D reflects the invasive potential of gastric carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 36:809–815
Murray GI (2001) Matrix metalloproteinase: a multifunctional group of molecules. J Pathol 195:135–137
Yamamoto M, Mohanam S, Sawaya R, et al (1996) Differential expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase and its correlation with gelatinase activation in human malignant brain tumors in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res 56:384–392
Hornebeck W, Emonard H, Monboisse JC, et al (2002) Matrix-directed regulation of pericellular proteolysis and tumor progression. Semin Cancer Biol 12:231–241
Fillmore HL, VanMeter TE, Broaddus WC (2001) Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase (MT-MMPs): expression and function during glioma invasion. J Neurooncol 53:187–202
Yana I, Seiki M (2002) MT-MMPs play pivotal roles in cancer dissemination. Clin Exp Metastasis 19:209–215
Nagase H (1997) Activation mechanisms of matrix metalloproteinases. Biol Chem 378:151–160
Apodaca G, Ruthka J, Bouhana K, et al (1990) Expression of metalloproteinases and metalloproteinase inhibitors by fetal astrocytes and glioma cells. Cancer Res 50:2322–2329
Tonn J, Kerkau S, Bouterfa H, et al (1999) Effect of synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors on invasive capacity and proliferation of human malignant gliomas in vitro. Int J Cancer 80: 764–772
Naito K, Kambayashi N, Nakajima S, et al (1994) Inhibition of growth of human tumor cells in nude mice by a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Int J Cancer 58:730–735
Burke F, East N, Upton C, et al (1997) Interferon gamma induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a model of ovarian cancer: enhancement of effect by batimastat. Eur J Cancer 33:1114–1121
Amundson SA, Myers TG, Fornace AJ Jr (1998) Roles of p53 in growth arrest and apoptosis: putting on the brakes after genotoxic stress. Oncogene 17:3287–3299
Daniel C, Duffield J, Brunner T, et al (2001) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors cause cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in glomerular mesangial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:57–68
Mitsiades N, Poulaki V, Leone A, et al (1999) Fas-mediated apoptosis in Ewing’s sarcoma cell lines by metalloproteinase inhibitors. J Nat Cancer Inst 91:1678–1684
Nakamura Y, Sato K, Wakimoto N, et al (2001) A new matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor SI-27 induces apoptosis in several human myeloid leukemia cell lines and enhances sensitivity to TNF alpha-induced apoptosis. Leukemia 15:1217–1224
Noha M, Yoshida D, Watanabe K, et al (2000) Suppression of cell invasion on human malignant glioma cell lines by a novel matrix-metalloproteinase inhibitor SI-27: in vitro study. J Neurooncol 48:217–223
Yoshida D, Noha M, Watanabe K, et al (2002) SI-27, a novel inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases with antiangiogenic activity: detection with a variable-pressure scanning electron microscope. Neurosurgery 50:578–586
Laura A, Rudolph O, Lynn MM (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases in remodeling of the normal and neoplastic mammary gland. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 3:177–189
Riley SC, Webb CJ, Leask R, et al (2000) Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and apoptosis in tissue remodelling in the sheep placenta. J Repord Fertil 118:19–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, D., Watanabe, K., Takahashi, H. et al. Apoptotic induction by BE16627B on human malignant glioma cell lines by an anti-matrix metalloproteinase agent. Brain Tumor Pathol 20, 13–19 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478942
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478942