Abstract
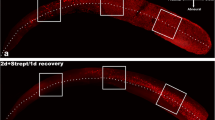
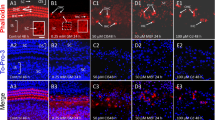
We reported that apoptosis occurred in the guinea pig vestibular hair cells after chronic aminoglycoside treatments. In the present study, we used in situ nick-end labeling to determine whether apoptosis was also induced by the acute effects of aminoglycosides in guinea pig ampullar cristae. In addition, we evaluated the effect of zinc supplements upon these ototoxic treatments. After a local application of streptomycin directly to the round window, we found labeled bodies in the vestibular hair cells. The zinc supplement increased the number of labeled bodies resulting in severe hair cell loss. These findings indicate that the acute effects of aminoglycosides also induce apoptosis of the vestibular hair cells, and that zinc enhances aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Consequently, we propose that an interaction with ion channels may play a key mechanism in the processes of apoptosis affecting the vestibular hair cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettger WJ, O'Dell BL (1981) A critical physiological role of zinc in the structure and function of biomembranes. Life Sci 28:1425–1428
Bicknell GR, Cohen GM (1995) Cleavage of DNA to large kilobase pair fragments occurs in some forms of necrosis as well as apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 207:40–47
Bright J, Khar A (1994) Apoptosis: programmed cell death in health and disease. Biosci Rep 14:67–81
Corcoran GB, Fix L, Jones DP, Moslen MT, Nicotera P, Oberhammer FA, Buttyan R (1994) Apoptosis: molecular control point in toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 148:169–181
Ernst A, Reuter GR, Zimmermann U, Zenner HP (1994) Acute gentamicin ototoxicity in cochlear outer hair cells of the guinea pig. Brain Res 636:153–156
Fredrickson CJ, Hernandez MD, McGinty JF (1989) Translocation of zinc may contribute to seizure-induced death of neurons. Brain Res 480:317–321
Garetz SL, Altschuler RA, Schachat J (1994) Attenuation of gentamicin ototoxicity by glutathione in the guinea pig in vivo. Hear Res 77:81–87
Garetz SL, Rhee DJ, Schachat J (1994) Sulfhydryl compounds and antioxidants inhibit cytotoxicity to outer hair cells of a gentamicin metabolite in vitro. Hear Res 77:75–80
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 149:493–501
Hawkins JE, Johnson LG (1981) Histopathology of cochlear and vestibular ototoxicity in laboratory animals. In: Lerner SA, Matz GJ, Hawkins JE (eds) Aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 175–195
Koh J, Suh SW, Gwang BJ, He YY, Hsu CY, Cho DW (1996) The role of zinc in selective neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia. Science 272:1014–1016
Li L, Nevill G, Forge A (1995) Two modes of hair cell loss from the vestibular sensory epithelia of the guinea pig inner ear. J Comp Neurol 355:405–417
McGowan AJ, Fernandes RS, Verhaegen S, Cotter TG (1994) Zinc inhibits UV radiation-induced apoptosis but fails to prevent subsequent cell death. Int J Radiat Biol 66:343–349
Nakagawa T, Yamane H, Shibata S, Nakai Y (in press) Gentamicin ototoxicity induced apoptosis of the vestibular hair cells of guinea pigs. Eur Arch Otorhinlaryngol
Priuska E, Schacht J (1995) The radical activities of gentamicin. Abstr Assoc Res Otolaryngol 18:79
Schacht J (1986) Molecular mechanisms of drug-induced hearing loss. Hear Res 22:297–304
Shambaugh GE Jr (1985) Zinc and prebycusis. Am J Otol 6: 146–147
Shambaugh GE Jr (1986) Zinc for tinnitus, imbalance, and hearing loss in the elderly. Am J Otol 7:476–477
Shambaugh GE Jr (1989) Zinc: the neglected nutrient. Am J Otol 10:156–160
Sunderman FW Jr (1995) The influence of zinc on apoptosis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 25:144–142
Telford WG, Franker PJ (1995) Preferential induction of apoptosis in mouse CD4+ CD8+ α β TCR10 CD3 ε10 thymocytes by zinc. J Cell Physiol 164:259–270
Ueda N, Shah SV (1992) Endonuclease-induced DNA damage and cell death in oxidant injury to renal tubular epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 90:2593–2597
Wersall J (1981) Structural damage to the organ of Corti and the vestibular epithelia caused by aminoglycoside antibiotics in the guinea pig. In: Lerner SA, Matz GJ, Hawkins JE (eds) Aminoglycoside ototoxicity. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 197–214
Williams SE, Zenner HP, Schacht J (1987) Three molecular steps of aminoglycoside ototoxicity demonstrated in outer hair cells. Hear Res 30:14–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagawa, T., Yamane, H., Shibata, S. et al. Cell death caused by the acute effects of aminoglycoside and zinc in the ampullary cristae of guinea pigs. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 254, 153–157 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02471281
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02471281