Abstract
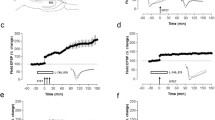
Effects of redox reagents on excitatory and inhibitory synaptic responses as well as on the bidirectional plasticity of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-propionic acid (AMPA) andN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated synaptic responses were studied in CA1 pyramidal neurons in rat hippocampal slices. The oxidizing agent 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB, 200 μM) did not affect AMPA, GABAA or GABAB receptor-mediated synaptic responses or the activation of presynaptic metabotropic receptors. However, DTNB irreversibly decreased (by approximately 50%) currents evoked by focal application of NMDA. DTNB also decreased the NMDA component of the EPSC. The reversal potential of NMDA currents and the Mg2+ block were not modified. In the presence of physiological concentrations of Mg2+ (1.3 mM), DTNB did not affect the NMDA receptor-dependent induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) or long-term depression (LTD) expressed by AMPA receptors. In contrast, DTNB fully prevented LTP and LTD induced and expressed by NMDA receptors. Plasticity of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses could be reinstated by the reducing agenttris-(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine (TCEP, 200 μM). These results suggest that persistent, bidirectional changes in synaptic currents mediated by NMDA receptors cannot be evoked when these receptors are in an oxidized state, whereas NMDA-dependent LTP and LTD are still expressed by AMPA receptors. Our observations raise the possibility of developing therapeutic agents that would prevent persistent excitotoxic enhancement of NMDA receptor-mediated events without blocking long-term modifications of AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic responses, thought to underlie memory processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Kimura H (1996) The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci 16:1066–1071
Aizenman E, Lipton S, Loring R (1989) Selective modulation of NMDA responses by reduction and oxidation. Neuron 2:1257–1263
Andiné P, Jacobson I, Hagberg H (1988) Calcium uptake evoked by electrical stimulation is enhanced postischemically and precedes delayed neuronal death in CA1 area of rat hippocampus, involvement of NMDA receptors. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:799–807
Aniksztejn L, Ben-Ari Y (1995) The expression of LTP by AMPA and/or NMDA receptors is determined by the extent of NMDA receptors activation during the tetanus. J Neurophysiol 74: 2349–2357
Andrade R (1991) Blockade of neurotransmitter-activated K+ conductance by QX-314 in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol 199:259–262
Ashwood T, Wheal H (1987) The expression ofN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated component during epileptiform synaptic activity in the hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol 91:815–822
Avoli M, Olivier A (1987) Bursting in human epileptogenic neocortex is depressed by anN-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist. Neurosci Lett 76:249–254
Asztely F, Wigstrom H, Gustaffson B (1992) The relative contribution of NMDA receptor channels in the expression of long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region. Eur J Neurosci 4:681–690
Barrantes E (1980) Modulation of acetylcholine receptor states by thiol modification. Biochemistry 19:2957–2965
Baskys A, Malenka RC (1991) Agonists at metabotropic glutamate metabotropic receptors presynaptically inhibit EPSC8 in neonatal rat hippocampus. J Physiol (Lond) 444:687–701
Bashir Z, Alford S, Davies S, Randall A, Collingridge G (1991) Long-term potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. Nature 349:367–380
Bear M, Malenka R (1994) Synaptic plasticity, LTP and LTD. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4:389–399
Ben-Ari Y, Represa A (1990) Brief seizure episode induces long-term potentiation and mossy fiber sprouting in the hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 13:312–318
Ben-Ari Y, Aniksztejn L, Bregestovski P (1992) Protein kinase C modulation of NMDA currents, an important link for LTP induction. Trends Neurosci 15:333–339
Bernard C, Hirsch J, Ben-Ari Y (1995) Non-involvement of the redox site of NMDA receptors in bidirectional synaptic plasticty in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 193:197–200
Bernard C, Wheal H (1995a) Simultaneous expression of long-term depression of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation of AMPA responses in the hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 7:1651–1655
Bernard C, Wheal H (1995b) Expression of EPSP/spike potentiation following low frequency and tetanic stimulation in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 15:6542–6551
Berretta N, Berton F, Bianchi R, Brunelli M, Capogna M, Francesconi W (1991) Long-term potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated EPSP in guinea-pig hippocampal slices. Eur J Neurosci 3:850–854
Collingridge G, Kehl S, McLennan H (1983) Excitatory amino acids transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of rat hippocampus. J Physiol (Lond) 334:33–46
Crunelli V, Forda S, Kelly J (1983) Blockade of amino-acid-induced depolarizations and inhibition of excitatory post-synaptic potentials in rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol (Lond) 341:627–640
Dohlman H, Thorner J, Caron M, Lefkowitz R (1991) Model of systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem 60:653–688
Furuhashi M, Ando M, Bielinska M, Pixley M, Shikone T, Hsueh A, Boime I (1994) Mutagenesis of cysteine residues in the human gonadotropin alpha subunit. Roles of individual disulfide bonds in secretion, assembly, and biological activity. J Biol Chem 269:25543–25548
Gozlan H, Diabira D, Chinestra P, Ben-Ari Y (1994) Anoxic LTP is mediated by the redox modulatory site of the NMDA receptor. J Neurophysiol 72:3017–3022
Gozlan H, Khazipov R, Ben-Ari Y (1995a) Multiple forms of long-term potentiations and multiple regulatory sites ofN-methyl-d-aspartate receptors: role of the redox site. J Neurobiol 26:360–369
Gozlan H, Khazipov R, Diabira R, Ben-Ari Y (1995b) In CA1 hippocampal neurons, the redox state of NMDA receptors determines LTP expressed by NMDA but not AMPA receptors. J Neurophysiol 73:2612–2617
Gozlan H, Ben-Ari Y (1995) NMDA receptor redox sites: are they targets for selective neuronal protection? Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:368–374
Hammond C, Crépel V, Gozlan H, Ben-Ari Y (1994) Anoxic LTP sheds light on the multiple facets of NMDA receptors. Trends Neurosci 17:497–503
Köhr G, Eckardt S, Luddens H, Monyer H, Seeburg P (1994) NMDA receptors channels: subunit-specific potentiation by reducing agents. Neuron 12:1031–1040
Kombian S, Malenka R (1994) Simultaneous LTP of non-NMDA-and LTD of NMDA-receptor-mediated responses in the nucleus accumbens. Nature 368:242–246
Levy D, Sucher N, Lipton S (1990) Redox modulation of NMDA receptor-mediated toxicity in mammalian central neurons. Neurosci Lett 110:291–296
Li H, Hsu P, Sachais B, Krause J, Leeman S, Boyd N (1996) Identification of the site in the substance P (NK-1) receptor for modulation of peptide binding in sulfhydryl reagents. J Biol Chem 271:1950–1956
Lipton S, Rosenberg P (1994) Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders. N Engl J Med 330: 613–622
Luhman H, Mudrick-Donnon L, Mittmann T, Heinemann U (1995) Ischaemic-induced long-term hyperexcitability in rat neocortex. Eur J Neurosci 7:180–191
McNamara J (1994) Cellular and molecular basis of epilepsy. J Neurosci 14:3413–3425
McBain C, Mayer M (1994)N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor structure and function. Physiol Rev 74:723–760
Mody I, Stanton P, Heinemann U (1988) Activation ofN-methyl-d-aspartate receptors parallels changes in cellular and synaptic properties of dentate gyrus granule cells after kindling. J Neurophysiol 59:1033–1054
Nowak L, Bregetovski P, Ascher P, Herbet A, Prochiantz A (1984) Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature 307:462–465
Otani S, Ben-Ari Y (1993) Biochemical correlates of long-term potentiation in hippocampal synapses. Int Rev Neurobiol 35: 1–41
Pan Z, Bahring R, Grantyn R, Lipton S (1995) Differential modulation by sulhydryl redox agents and glutathione of GABA-and glycine-evoked currents in rat retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 15:1384–1391
Quesada O, Hirsch J, Ben-Ari Y, Bernard C (1996) Redox site of NMDA receptors can modulate epileptiform activity in hippocampal slices from kainic acid-treated rats. Neurosci Lett 212: 171–174
Reynolds I, Rush E, Aizenman E (1990) Reduction of NMDA receptors with dithiothreitol increases MK-801 binding and NMDA-induced Calcium in fluxes. Eur J Pharmacol 101: 178–182
Ruiz-Gomez A, Fernandez-Shaw C, Morato E, Marvizon J, Vasquez J, Valdivieso F, Mayor E (1991) Sulfhydril groups modulate the allosteric interaction between glycine binding sites at the inhibitory glycine receptor. J Neurochem 56:1690–1697
Schmid G, Bonanno G, Raiteri M (1996) Functional evidence for two native GABAA receptor subtypes in adult rat hippocampus and cerebellum. Neuroscience 73:697–704
Selig D, Hjelmstad G, Herron C, Nicoll R, Malenka R (1996) In-dependent mechanisms for long-term depression of AMPA and NMDA responses. Neuron 15:417–426
Spruston N, Jonas P, Sakmann B (1995) Dendritic glutamate receptor channels in rat hippocampal CA3 and CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Physiol (Lond) 482:325–352
Sullivan J, Traynelis S, Chen V, Escobar W, Heinemann S, Lipton A (1994) Identification of two cysteine residues that are required for redox modulation of the NMDA subtype of glutamate receptor. Neuron 13:929–936
Tang L, Aizenman E (1993) The modulation ofN-methyl-d-aspartate receptors by redox and alkylating reagents in rat cortical neurones in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 465:303–323
Tauck DL (1992) Redox modulation of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic activity in the hippocampus. Neuroreport 3:781–784
Tauck D, Ashbeck A (1990) Glycine synergistically potentiates the enhancement of LTP induced by a sulfhydryl reducing agent. Brain Res 519:129–132
Xiao M, Karpefors M, Niu Y, Wigstrom H (1995) The complementary nature of long-term depression and potentiation revealed by dual component excitatory postsynaptic potentials in hippocampal slices from young rats. Neuroscience 68:625–635
Xiao M, Wigstrom H, Gustafsson B (1994) Long-term depression in the hippocampal CA1 region is associated with equal changes in AMPA and NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses. Eur J Neurosci 6:1055–1057
Xie X, Berger T, Barrionuevo G (1992) Isolated NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses express both LTP and LTD. J Neurophysiol 67:1009–1013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernard, C., Hirsch, J.C., Khazipov, R. et al. Redox modulation of synaptic responses and plasticity in rat CA1 hippocampal neurons. Exp Brain Res 113, 343–352 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02450332
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02450332