Summary
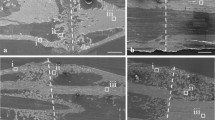
The study describes the SEM appearances of endosteal and periosteal surfaces of anorganic femoral diaphyses from 16-month-old normal and castrate male rats. Different types of surfaces could be recognized in both groups. Percentage areas occupied by each surface type were analyzed with a Ladd Data Analyzing Digitizer. Endosteal surfaces were composed of significantly more (P<0.05) incompletely mineralized, forming surface and significantly less (P<0.05) completely mineralized, resting surface in castrates than in controls. Both endosteal and periosteal surfaces from experimental bone demonstrated significantly more (P<0.05) osteoblast lucunae than did control surfaces, and vascular canal entrances were significantly wider (P<0.001) on castrate endosteal surfaces than on control endosteal surfaces. There was a greater proportion of small nodule forming surface/large nodule forming surface in castrate endosteal bone than in control, and a greater proportion prolonged resting surface/fibrous resting surface in control periosteal bone than in castrate. The results indicate that, when viewed in the SEM, anorganic endosteal and periosteal bone surfaces from femoral diaphyses of old castrate male rats demonstrate appearances characteristic of changes in bone turnover that occur with osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyde A, Hobdell MH (1968) A scanning electron microscope study of mammalian bone surfaces. J Dent Res 47:1006 (abst.)
Boyde A, Hobdell M (1968) Scanning electron microscopy of bone. Calcif Tissue Res 2: Suppl. 4-4B
Boyde A, Hobdell MH (1969) Scanning electron microscopy of primary membrane bone. Z Zellforsch 99:98–108
Boyde A, Hobdell MH (1969) Scanning electron microscopy of lamellar bone. Z Zellforsch 93:213–231
Jowsey JP, Kelley PJ, Riggs BL, Bianco AJ, Scholz DA, Gershon-Cohen J (1965) Quantitative microradiographic studies of normal and osteoporotic bone. J Bone Joint Surg A 47:785–806
Jones SJ, Boyde A (1970) Experimental studies on the interpretation of bone surfaces studied with the SEM. SEM/1970 IIT Research Institute, Chicago, IL 60616, pp 193–200
Dempster DW, Elder HY, Smith DA (1979) Scanning electron microscopy of rachitic rat bone. SEM/1979 IT SEM Inc., AMF O'Hare, IL 60666, pp 513–520
Wink CS, Felts WJL (1980) Effects of castration on the bone structure of male rats: a model of osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int 32:77–82
Jowsey J (1963) Microradiography of bone resorption. In R. F. Sognnaes (ed): Mechanisms of Hard Tissue Destruction, American Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, DC, pp 447–469
Harrison MR, Fraser R (1960) Bone structure and metabolism in calcium deficient rats. J Endocrinol21:197–205
Harris WH, Jackson RH, Jowsey J (1962) Thein vivo distribution of tetracyclines in canine bones. J Bone Joint Surg 44A:1308–1320
Frost HM, Villanueva AR (1960) Human osteoblastic activity. Henry Ford Hosp Med Bul 9:7–96
Adams P, Jowsey J (1967) Effect of calcium on cortisone induced osteoporosis: a preliminary communication. Endocrinology 81:735
Mills BG, Baretta LA (1969) Effect of parathyroid extract on bone collagen fractions. Clin Orthop 62:240–250
Nordin BEC (1965) The relation between dietary calcium and osteoporosis in different parts of the world. A report to the Nutritional Section of the World Health Organization. Privately printed, Glasgow
Garn SM, Rohmann CG, Wagner B: Bone loss as a general phenomenon in man. Fed Proc 26:1729
Garn SM, Rohmann CG, Wagner B, Davila GH: Dynamics of change at the endosteal surface of tubular bones. In G. D. Whedon, J. R. Cameron (eds): Proceedings of the Conference on Progress in Methods of Bone Mineral Measurements. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Garn SM, Rohmann CG, Wagner B, Davila GH, Ascoli W (1969) Population similarities in the onset and rate of adult endosteal bone loss. Clin Orthop 65:51–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wink, C.S. Scanning electron microscopy of castrate rat bone. Calcif Tissue Int 34, 547–552 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411302
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411302