Summary
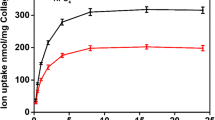
Several phosphoprotein preparations (phosvitin, rat incisor and fetal calf molar dentin phosphoproteins) all inhibit apatite growth/replication from pre-existing crystal seeds in metastable solutions. Two stages of the crystal growth process were inhibited by these phosphoproteins. First, an initial lag period was induced, probably associated with seed surface phenomena. This period was prolonged indefinitely when a combination of phosphoprotein precoated seeds was used together with soluble phosphoproteins in the crystal growth reaction. Second, the phosphoproteins prolonged that stage of the reaction where octacalcium phosphate is the predominant mineral phase present prior to its conversion to the final apatite product. Pretreatment of the phosphoproteins with calcium diminished their inhibitory activity to seeded crystal growth as well as towards de novo apatite formation in synthetic extracellular fluids. The presence of collagen diminished the inhibitory activity of the phosphoproteins towards de novo precipitation but had no effect on phosphoprotein-modulated apatite crystal growth in the seeded systems. These results suggest a potential regulatory role for phosphoproteins in dentin mineralization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schour, I., Massler, M.: The teeth. In E.J. Farris, J.Q. Griffith (eds.): The Rat in Laboratory Investigation, pp. 104–165. J.B. Lippincott Co., Philadelphia, 1942
Veis, A., Perry, A.: The phosphoprotein of dentin matrix, Biochemistry6:2409–2416, 1967
Veis, A., Spector, A.R., Zamoscianyk, H.: The isolation of an EDTA soluble phosphoprotein from mineralizing dentin, Biochim. Biophys. Acta257:404–413, 1972
Butler, W.T., Finch, J.E., Jr., DeSteno, C.V.: Chemical character of proteins in rat incisors, Biochim. Biophys. Acta257:161–171, 1972
Lee, S.L., Veis, A., Glonek, T.: Dentin phosphoprotein: an extracellular calcium binding protein, Biochemistry16:2971–2979, 1977
DeSteno, C.V., Feagin, F., Butler, W.T.: Mineralization of dentin, bone and tendonin vitro, Calcif. Tissue Res.17:161–163, 1975
Nawrot, C.F., Campbell, D.J., Schroeder, J.K., Van Valkenbourg, M.: Dentin phosphoprotein-induced formation of hydroxylapatite duringin vitro synthesis of amorphous calcium phosphate, Biochemistry15:3445–3449, 1976
Termine, J.D., Conn, K.M.: Inhibition of apatite formation by phosphorylated metabolites and macromolecules, Calcif. Tissue Res.22:149–157, 1976
Bernardi, G.: Chromatography of proteins on hydroxyapatite, Methods Enzymol22:325–339, 1971
Moreno, E.C., Varughese, K., Hay, D.I.: Effect of human salivary proteins on the precipitation kinetics of calcium phosphate, Calcif. Tissue Int.28:7–16, 1979
Termine, J.D., Eanes, E.D.: Calcium phosphate deposition from balanced salt solutions, Calcif. Tissue Res.15:81–84, 1974
Eanes, E.D.: The influence of fluoride on the seeded growth of apatite from stable supersaturated solutions at pH 7.4, J. Dent. Res.59:144–150, 1980
Williams, B.R., Gelman, R.A., Poppke, D.C., Piez, K.A.: Collagen fibril formation: optimalin vitro conditions and preliminary kinetic results, J. Biol. Chem.253:6578–6585, 1978
Termine, J.D., Torchia, D.A., Conn, K.M.: Enamel matrix: structural proteins. In M.U. Nylen, J.D. Termine (eds.): Proceedings, Third International Symposium on Tooth Enamel, pp. 773–778. J. Dent. Res.58B (AADR), Washington, D.C., 1979
Eanes, E.D.: The interaction of supersaturated calcium phosphate solutions with apatitic substrates, Calcif. Tissue Res.20:75–89, 1976
Weinstock, M., Leblond, C.P.: Radioautographic visualization of the deposition of a phosphoprotein at the mineralization front in the dentin of the rat incisor, J. Cell Biol.56:838–845, 1973
Grizzuti, K., Perlmann, G.E.: Binding of magnesium and calcium ions to the phosphoglycoprotein phosvitin, Biochemistry12:4399–4403, 1973
Glimcher, M.J.: Phosphopeptides of enamel matrix. In M.U. Nylen, J.D. Termine (eds.): Proceedings, Third International Symposium on Tooth Enamel, pp. 790–806. J. Dent. Res.58B (AADR), Washington, D.C. 1979
Schlueter, R.J., Veis, A.: The macromolecular organization of dentin matrix collagen. II. Periodate degradation and carbohydrate cross-linking, Biochemistry3:1657–1665, 1964
Carmichael, D.J., Veis, A., Wang, E.T.: Dentin matrix collagen: evidence for a covalently linked phosphoprotein attachment, Calcif. Tissue Res.7:331–334, 1971
Curley-Joseph, J., Veis, A.: The nature of the covalent complexes of phosphoproteins with collagen in the bovine dentin matrix, J. Dent. Res.58:1625–1633, 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Termine, J.D., Eanes, E.D. & Conn, K.M. Phosphoprotein modulation of apatite crystallization. Calcif Tissue Int 31, 247–251 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407188
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407188