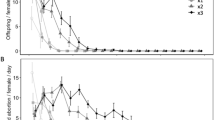
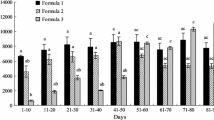
Abstract
The nutritional value forAmblyseius swirskii Athias-Henriot, of eggs or crawlers ofCoccus hesperidum L.,Saissetia oleae (Olivier),S. coffeae (Walker),Pseudococcus citriculus Green, andP. longispinus Targ.-Tozz, even with the addition of honeydew, was low; only a few young reached adulthood and the oviposition rate was negligible. However, addition of honeydew toTetranychus cinnabarinus Boisd. enhanced the oviposition rate ofAmblyseius swirskii. Honeydew was a favourite food forA. swirskii, whereas the eggs and crawlers tested were not eagerly attacked and consumed. Females and males fed honeydew ofSaissetia oleae mated readily and the females were inseminated, but fecundity was negligible.
Résumé
La valeur nutritive des aliments suivants a été faible même lorsqu'à du miellat ont été additionnés: des œufs ou des larves nouvelles nées deCoccus hesperidum L.,Saissetia oleae (Olivier),S. coffeae (Walker),Pseudococcus citriculus Green etP. longispinus Targ.-Tozz.; seulement une faible proportion est arrivée au stade adulte, le taux d'oviposition de ceux-ci étant négligeable. Cependant la ponte deAmblyseius swirskii a été accrue lorsque du miellat fut ajouté àTetranychus cinnabarinus Boisd. Le miellat est un aliment préféré deA. swirskii, tandis que les œufs et larves nouvelles nées des espèces testées ne sont pas attaqués ni dévorés avec appétit. Des femelles et des mâles élevés sur du miellat s'accouplent facilement, les femelles sont fécondées, mais la quantité d'œufs pondue reste négligeable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blommers, L.—1974. Preliminary studies on two predators [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] of the spider miteTetranychus neocaledonicus André [Acarina: Tetranychidae].—Z. Angew. Entomol., 75, 315–321.
Chant, D. A. &Fleschner, C. A.—1960. Some observations on the ecology of phytoseiid mites in California.—Entomophaga 5, 131–139.
Dosse, G.—1959. Über den Kopulationsvorgang bei Raubmilben aus der GattungTyphlodromus [Acar., Phytoseiidae].—Pflanzenschutzber., 22, 125–133.
Huffaker, C. B. &Kenneth, C. E.—1956. Experimental studies on predation: predation and cyclamen mite populations on strawberries in California.—Hilgardia, 26, 191–222.
McMurtry, J. A.—1963. Diaspidine scale insects as prey for certain phytoseiid mites, In: Advances in Acarology.—Comstock Publ. Assoc., Ithaca, N.Y., 151–154.
McMurtry, J. A. &Johnson, H. G.—1965. Some factors influencing the abundance of the predaceous miteAmblyseius hibisci in Southern California.—Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 58, 49–56.
McMurtry, J. A. &Scriven, G. T.—1964a Biology of the predaceous mite [Typholodromus rickeri Acarina: Phytoseiidae].—Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 57, 362–367.
——1964b. Studies on the feeding, reproduction, and development ofAmblyseius hibisci [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on various food substances—Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 57, 649–655.
——1965. Life history studies ofAmblyseius limonicus, with comparative observations onAmblyseius hibisci [Acarina: Phytoseiidae].—Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 58, 106–111.
Muma, M. H.—1955.Phytoseiidae [Acarina] associated with citrus in Florida.—Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am., 48, 262–272.
——1969.Typhlodromalus peregrinus (Muma) [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on Florida citrus.—Proc. 2nd Int. Congr. Acarology, 1968, 135–148.
——1971. Food habits ofPhytoseiidae [Acarina: Mesostigmata] including common species on Florida citrus.—Fla. Entomol., 54, 21–34.
Poe, S. L. &Enns, W.R.—1970. Effects of inbreeding on closed populations of predaceous mites [Acarina: Phytoseiidae].—Can. Entomol., 102, 1222–1229.
Porath, A. &Swirski, E.—1965. A survey of phytoseiid mites [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on citrus with a description of one new species.—Israel J. Agric. Res., 15, 87–100.
Rasmy, A. H. &Elbanhawy, E. M.—1975. Biology and predatory efficiency of two phytoseiid mites as affected by long-term pollen feeding—Entomophaga, 20, 93–95.
Swirski, E., Amital, S. &Dorzia, N.—1967a. Laboratory studies on the feeding, development and reproduction of the predaceous mitesAmblyseius rubini Swirski & Amitai andAmblyseius swirskii Athias [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on various kinds of food substances.—Israel J. Agric. Res., 17, 101–119.
——1967b. Laboratory studies on the feeding, development and oviposition of the predaceous miteTyphlodromus athiasae P. & S. [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on various kinds of food substances. —Israel J. Agric. Res., 17, 213–218.
——1970. Laboratory studies on the feeding habits, post-embryonic survival and oviposition of the predaceous mitesAmblyseius chilenensis Dosse andAmblyseius hibisci Chant [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on various kinds of food substances.—Entomophaga, 15, 93–106.
Swirski, E. &Dorzia, N.—1968. Studies on the feeding, development and oviposition of the predaceous miteAmblyseius limonicus Garman & McGregor [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on various kinds of food substances.—Israel J. Agric. Res., 18, 71–75.
——1969. Laboratory studies on the feeding, development and fecundity of the predaceous miteTyphlodromus occidentalis Nesbitt [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on various kinds of food substances. —Israel J. Agric. Res., 19, 143–145.
Swirski, E., Ragusa, S., van Emden, H. &Wysoki, M.—1973. Description of immature stages of 3 predaceous mites belonging to the genusAmblyseius Berlese [Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae].—Israel J. Entomol., 8, 69–87.
Wysoki, M. &Swirski, E.—1971. Studies on overwintering of the predaceous mites of the generaAmblyseius Berlese,Typhlodromus Scheuten andIphiseius Berlese [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] in Israel. In: Entomological Essays to Commemorate the Retirement of Professor Yasumatsu.—Hokuryukan Publ. Co., Tokyo, 255–292.
Yousef, A. Abd-El-Tawab &Shehata, K.K.—1971. Mites associated with pome fruit trees in the U.A.R.—Z. Angew. Entomol., 67, 360–370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution from the Agricultural Research Organization, The Volcani Center, Bet Dagan, Israel, 1976 Series, No. 196-E.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ragusa, S., Swirski, E. Feeding habits, post-embryonic and adult survival, mating, virility and fecundity of the predacious miteAmblyseius swirskii [Acarina: Phytoseiidae] on some coccids and mealybugs. Entomophaga 22, 383–392 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02373263
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02373263