Abstract
In the Cardiac Surgical Intensive Care Unit (CICU) of the University of Alabama Hospital in Birmingham, Alabama, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) is regulated by computer (H-P 21 MX) controlled infusion of vasodilating agents and has been performed in 1100 hypertensive patients following open heart surgery.
The MAP controller was developed based on investigation of the dynamics of the physiological responses of hypertensive patients to trimethaphan camsylate (Arfonad) and sodium nitroprusside (Nipride). Representative responses were selected for investigation by digital simulation of a computer programmed version of a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller algorithm. The PID controller parameters were tuned to elicit a response with acceptable settling time and minimal overshoot during the time course of the simulated MAP.
Eight IMED 929 (IMED Corporation, San Diego, CA) digitally controlled infusion pumps interfaced with our computer based CICU system are used to regulate the blood pressure of patients following cardiac surgery. A microprocessor based blood pressure controller employing this algorithm has been developed and is being evaluated.
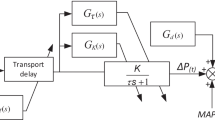
For system design, analysis, and evaluation, the essential aspects of the arterial blood pressure (MAP) and its response to nitroprusside has been modeled. The arterial pressure is considered the sum of nonstationary stochastic background activity and a change due to the nitroprusside (characterized by a transfer function). The model was applied to the simulation of a clinically used controller and has provided insight into responses observed in the treatment of patients. The model is presently being used for computer-aided design and evaluation of an adaptive controller.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cowley, A. W., J. P. Miller, and A. C. Guyton. Open-loop analysis of the renin-angiotensin system in the dog.Circ. Res. 28:568–581, 1971.
Davies, W. D. T.System Identification for Self-Adaptive Control. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1970.
Schultz, W. C. and V. C. Rideout. Control system performance measures: Past, present, and future.IRE Trans. Auto. Control. Vol. AC-6: 22–35, 1961.
Sheppard, L. C. Correlation analysis of arterial blood pressure responses to vasoactive drugs with particular reference to clinical surveillance of the post surgical patient. PhD. thesis, University of London, 1976.
Sheppard, L. C. and N. T. Kouchoukos. Automation of measurements and interventions in the systematic care of postoperative cardiac surgical patients.Med. Instrum. 11:296–301, 1977.
Sheppard, L. C. and B. McA. Sayers. Dynamic analysis of the blood pressure response to hypotensive agents studied in post surgical patients.Comput. Biomed. Res. 10:237–246, 1977.
Sheppard, L. C., J. F. Shotts, N. F. Roberson, F. D. Wallace, and N. T. Kouchoukos. Computer controlled infusion of vasoactive drugs in post cardiac surgical patients. IEEE/1979 Frontiers of Engineering in Health Care (IEEE CH1440-7), pp. 280–284, 1979.
Slate, J. B. Model-based design of a controller for infusing sodium nitroprusside during post surgical hypertension. Ph.D. thesis, University of Wisconsin-Madison, 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheppard, L.C. Computer control of the infusion of vasoactive drugs. Ann Biomed Eng 8, 431–444 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02363444
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02363444