Abstract
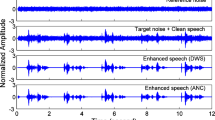
The electrolarynx provides a valuable means of verbal communication for people who cannot use their natural voice-production mechanism, but technology has changed very little since it was introduced in the 1950s. The presence of background noise degrades the resulting speech. In this study background noise was reduced by a new method, independent component analysis-based adaptive noise cancelling, which can remove noise components of the primary input signal based on statistical independence, by incorporating both second-order and higher-order statistics. The method shows better performance than the conventional least mean square algorithm. Acoustic analysis of the denoised electrolarynx speech revealed a significant reduction in the amount of background noise. Results from the perceptual evaluations indicated that the new filtering technique produced a noticeable improvement in the acceptability of the electrolarynx speech in a quiet environment (from 1.75 to 2.49, arbitrary units) or a noisy environment (from 0.59 to 1.82). In general, there was no significant improvement or degradation in intelligibility in the quiet environment (from 52.7 to 53.3). However, the processing did improve the intelligibility in a babble-noise environment (from 24.9 to 40.6). The improvement in acceptability and intelligibility may increase the communication ability of the user in daily situations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barney, H., Haworth, F., andDunn, H. (1959): ‘An experimental transistorized artificial larynx’,Bell Syst. Tech. J.,38, pp. 1337–1356
Bell, A., andSejnowski, T. (1995): ‘An information maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution’,Neur. Comput.,7, pp. 1129–1159
Cole, D., Sridharan, S., Moody, M., andGeva, S. (1997): ‘Application of noise reduction techniques for alaryngeal speech enhancement’, IEEE Region 10 Annual Conf. TENCON-Speech and Image Technologies for Computing and Telecommunications, 2, pp. 491–494
Douglas, S., andMeng, T. (1994a): ‘Stochastic gradient adaptation under general error criteria’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,42, pp. 1335–1351
Douglas, S., andMeng, T. (1994b): ‘Normalized data nonlinearities for LMS adaptation’,IEEE Trans. Signal Process.,42, pp. 1352–1365
Doyle, P., Swift, E., andHaaf, R. (1989): ‘Effects of listener sophistication on judgments of tracheoesophageal talker intelligibility’,J Commun. Dis.,22, pp. 105–113
Espy-Wilson, C., Chari, V., andHuang, C. (1996): ‘Enhancement of alaryngeal speech by adaptive filtering’, Spoken Language, ICSLP 96, Proc. Fourth Int. Conf., Philadelphia, PA, USA, OCT 3-6, pp. 764–767
Espy-Wilson, C., Chari, V., MacAuslan, J., Huang, C., andWalsh, M. (1998): ‘Enhancement of electrolaryngeal speech by adaptive filtering’,J. Speech. Lang. Hearing Res.,41, pp. 1253–1264
Hillman, R., Walsh, M., Wolf, G., Fisher, S., andHong, W. (1998): ‘Functional outcomes following treatment for advanced laryngeal cancer: Part 1, voice preservation in advanced laryngeal cancer. Part II, laryngectomy rehabilitation: the state-of-the-art in the VA system’,Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol.,107, pp. 1–27
Holley, S., Lerman, J., andRandolph, K. (1983): ‘A comparison of the intelligibility of esophageal, electrolarynx, and normal speech in quiet and in noise’,J. Commun. Disord.,16, pp. 143–155
King, P., Fowlks, E., andPierson, G. (1968): ‘Rehabilitation and adaptation of laryngectomy patients’,Am. J. Phys. Med.,47, pp. 192–203
Knox, A., andAnneberg, M. (1973): ‘The effects of training in comprehension of electrolaryngeal speech’,J. Commun. Dis.,6, pp. 110–120
Lauder, E. (1970): ‘The laryngectomee and the artificial larynx-A second look’,J. Speech Hearing Disorders,35, pp. 62–65
Lee, T. (1998): ‘Independent component analysis—theory and applications’ (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, 1998)
Norton, R., andBernstein, R. (1993): ‘Improved laboratory prototype electrolarynx (LAPEL): using inverse filtering of frequency response function of the human throat’,Ann. Biomed. Eng.,21, pp. 163–174
Park, H., Oh, S., andLee, S. (2001): ‘On adaptive noise cancelling based on independent component analysis’. 3rd Int. Conf. on Independent Component Analysis and Blind Signal Separation, December 9–12, San Diego, California, USA, pp. 394–399
Rabiner, L., andSchafer, R. (1978): ‘Digital processing of speech signals’ (Prentice-Hall, Inc., 1978)
Rothman, H. (1982): ‘Acoustic analysis of artificial electronic larynx speech’, inSeikey, A. (Ed.): ‘Electroacoustics analysis and enhancement of alaryngeal speech’ (Charles Thomas, Springfield, IL, 1982), pp. 95–118
Simon, H. (1991): ‘Adaptive filter theory’ (Englewood Cliffs, Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1991), pp. 377–385
Takahashi, H. (2000): ‘Voice generation system using an intra-mouth vibrator for the laryngectomee’, MS Thesis, The University of Tokyo, Japan
Weiss, M., Yeni-Komshian, G., andHeinz, J. (1979): ‘Acoustic and perceptual characteristics of speech produced with an electronic artificial larynx’,J. Acoust. Soc. Am.,65, pp. 1298–1308
Widrow, B., Glover, J., Mccool, J. et al. (1975): ‘Adaptive noise cancelling: principles and applications’,Proc. IEEE,63, pp. 1692–1716
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, H.J., Wan, M.X., Wang, S.P. et al. Enhancement of electrolarynx speech using adaptive noise cancelling based on independent component analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 41, 670–678 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02349975
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02349975