Abstract
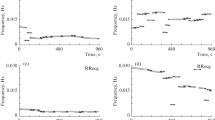
Measurements of respiratory impedance by means of the forced oscillation technique (FOT) are usually made using a loudspeaker as the excitation device. Its nonlinear nature can introduce artifacts that coincide with the frequencies applied to excite the respiratory system, limiting the accuracy of the impedance estimation. In this paper, this hypothesis is evaluated in the case of both a traditional estimator and the unbiased estimator proposed byDaróczy andHantos (1982). A simulated study under apnoea conditions in the pressure range 0.5–3.0 cmH2O peak-to-peak reveals that loudspeaker nonlinearities introduce a characteristic pattern of dispersion in both the resistance and reactance curves that can be significantly decreased (p≃0.03, signtest) by reducing the nonlinearities. A simulation of spontaneous breathing shows the same pattern, and is observed in the case of traditional as well as unbiased estimators. The dispersion is quantified by the mean absolute distance between the theoretical and simulated data and decreases with the reduction of nonlinearities when impedance is estimated with a traditional estimator (from 6.63 to 4.72% in real estimates and from 6.78 to 3.47% in imaginary estimates) as well as with an unbiased estimator (real estimates from 4.84 to 1.57% and 5.61 to 2.06% in imaginary estimates). Studies with normal subjects show the same dispersion pattern, which decreases if the generator nonlinearities are reduced. These results supply substantial evidence that reducing generator nonlinearities can contribute to the production of more reliable mechanical impedance FOT measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beydon, L., Malassiné, P., Lorino, A. M., andMariette, C. (1996): ‘Respiratory resistance by end-inspiratory occlusion and forced oscillations in intubated patients’,J. Appl. Physiol.,80, (4), pp. 1105–1111
Brochard, L., Pelle, G., Palmas, J., Brochard, P., Carre, A., Lorino, H., andHarf, A. (1987): ‘Density and frequency dependence of resistance in early airway obstruction’,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.,135, pp. 579–584
Cauberghs, M., andVan de Woestijne, K. P. (1991): ‘Errors in the estimation of respiratory impedance: use of a unbiased estimator’,Eur. Respir. Rev.,1, pp. 206–209
Colloms, M. (1991): ‘High performance loudspeakers’ (Pentech Press, London, 4th edition)
Daroczy, B., andHantos, Z. (1982): ‘An improved forced oscillatory estimation of respiratory impedance’,Int. J. Biomed. Comp.,13, pp. 221–235
Daroczy, B., Fabula, A., andHantos, Z. (1991): ‘Use of noninteger-multiple pseudorandom excitation to minimize nonlinear effects in impedance estimation’,Eur. Respir. Rev.,1, pp. 183–187
Delavault, E., Saumon, G., andGeorges, R. (1980): ‘Characterization and validation of forced oscillation technique’,Resp. Physiol.,40, pp. 119–136
Dubois, A. B., Brody, A. W., Lewis, D. H., andBurgess, Jr., B. F. (1956): ‘Oscillation mechanics of lungs and chest in man’,J. Appl. Physiol.,8, pp. 587–594
Duvivier, C., Peslin, R., Wendling, F., Felicio Da Silva, J., Gremillet, F., Gallina, C., andNavajas, D. (1990): ‘Mesure de l'impédance thoraco-pulmonaire par oscillations forcées: présentation d'un appareil’,Innov. Tech. Biol. Med.,11, pp. 381–399
Farré, R., Navajas, D., Peslin, R., Rotger, M., andDuvivier, C. (1989): ‘A correction procedure for the asymmetry of differential pressure transducers in respiratory impedance measurements’,IEEE Trans. Biom. Eng.,36, pp. 1137–1140
Farré, R., Rotger, M., andNavajas, D. (1991): ‘Time domain digital filter to improve the signal-to-noise ratio in respiratory impedance measurements’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 29, pp. 18–24
Farré, R., Rotger, M., andNavajas, D. (1997): ‘Estimation of random errors in respiratory resistance and reactance measured by the forced oscillation technique’,Eur. Respir. J.,10, pp. 685–689
Farré, R., Ferrer, M., Rotger, M., Torres, A., andNavajas, D. (1998): ‘Respiratory mechanics in ventilated COPD patients: forced oscillation versus occlusion techniques’,Eur. Respir. J.,12, pp. 170–176
Franken, H. J., Clément, J., andVan de Woestijne, K. P. (1983): ‘Systematic and random errors in the determination of respiratory impedance by means of the forced oscillation technique: a theoretical study’,IEEE Trans. Biom. Eng.,30, pp. 642–651
Glison, T. H. (1985): ‘Introduction to system analysis’ (McGraw Hill, New York, United States)
Lebecque, P., andStanescu, D. (1997): ‘Respiratory resistance by the forced oscillation technique in asthmatic children and cystic fibrosis patients’,Eur. Respir. J.,10, pp. 891–895
Lorino, H., Mariette, C., Karouia, M., andLorino, A. M. (1993): ‘Influence of signal processing on estimation of respiratory impedance’,J. Appl. Physiol.,74, pp. 215–223
Lorino, A. M., Beydon, L., Mariette, C., Dahan, E., andLorino, H. (1996): ‘A new correction technique for measuring respiratory impedance through an endotracheal tube’,Eur. Respir. J.,9, pp. 1079–1086
Melo, P. L., Werneck, M. M., andGiannella-Neto, A. (1998): ‘Linear servocontroled pressure generator for forced oscillations measurements’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,36, pp. 11–16
Michaelson, E. D., Grassman, E. D., andPeters, W. R. (1975): ‘Pulmonary mechanics by spectral analysis of forced random noise’,J. Clin. Invest.,56, pp. 1210–1230
Navajas, D., Farré, R., Rotger, M., andPeslin, R. (1988): ‘A new estimator to minimize the error due to breathing in the measurement of respiratory impedance’,IEEE Trans.,BME 35, pp. 1001–1005
Navajas, D., Farré, R., Canet, J., Rotger, M., andSanchis, J. (1990): ‘Respiratory input impedance in anesthetized paralyzed patients’,J. Appl. Physiol.,69, pp. 1372–1379
Navajas, D., Farré, R., andArmengol, J. (1991): ‘Optimizing respiratory impedance measurements at low frequencies in spontaneously breathing subjects’,Eur. Respir. Rev.,1, pp. 202–205
Peslin, R., andFredberg, J. J. (1986): ‘Oscillation mechanics of the respiratory system’ in ‘Handbook of physiology’ (Am. Physiol. Soc., Bethesda, Maryland), vol. 3, part 1, sect. 3
Rotger, M., Peslin, R., Farré, R., andDuvivier, C. (1991): ‘Influence of amplitude, phases and frequency content of pseudorandom pressure input on impedance data and their variability’,Eur. Respir. Rev.,1, pp. 178–182
Schoukens, J., Pintelon, R., Ouderaa, E., andRenneboog, J. (1988): ‘Survey of excitation signals for FFT based signal analysers’,IEEE Trans. Instr. Meas.,37, pp. 342–352
Williams, S. P., Fullton, J. M., Tsai, M. J., Pimmel, R. L., andCollier, M. (1979): ‘Respiratory impedance and derived parameters in young children by forced random noise’,J. Appl. Physiol.,47, pp. 169–174
Willim, G., Tomalak, W., Stankiewick, J., Kurzawa, R., Pogorzelski, A., Mazurek, H., Haluszka, J., andPham, Q. T. (1997): ‘Forced oscillations technique in evaluating state of the respiratory system in chilren with chronic lung diseases’Eur. Resp. J.,10, p. 328
Wouters, E. F. M. (1991): ‘Data interpretation of total respiratory impedance measurement in clinical practice’,Eur. Respir. Rev.,1, pp. 216–217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Melo, P.L., Werneck, M.M. & Giannella-Neto, A. Effect of generator nonlinearities on the accuracy of respiratory impedance measurements by forced oscillation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 38, 102–108 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344697
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344697