Abstract
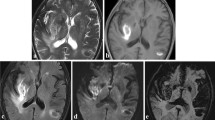
We reviewed a 7-year series of brain MRI examinations to determine the frequency and clinical significance of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system (SS). SS was defined by widespread bilateral signal loss at the surfaces of the cerebral or cerebellar hemispheres, the brain stem and the spinal cord on T2-weighted images. Clinical data comprised a neurological examination of identified patients and a review of their case notes. Among 8843 consecutive studies we identified 13 (0.15 %) patients with MRI evidence of SS. Only 2 had symptoms or signs characteristic of SS, such as cerebellar ataxia, hearing loss, myelopathy and dementia. Haemosiderin deposition was most widespread in both symptomatic individuals. A definite cause for SS was detected in 9 patients (69 %). None of them had a full clinical picture of SS. These data indicate SS per se to be much more frequent than may be assumed from the literature. It appears to become symptomatic only with extensive amounts of widespread iron deposition which develop preferentially with cryptic or unidentified causes of bleeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hughes JT, Oppenheimer DR (1969) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. A report on nine cases with autopsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 13:556–574
Koeppen AH, Dentinger MP (1988) Brain hemosiderin and superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47: 249–270
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA, Goldberg HI (1985) High-field MR imaging of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9: 972–975
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, Hackney DB, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1987) High-field spin-echo MR imaging of superficial and subependymal siderosis secondary to neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. Neuroradiology 29:339–342
Offenbacher H, Fazekas F, Reisecker F, Schmidt R, Payer F, Lechner H (1991) Superficial siderosis of the spinal cord: a rare cause of myelopathy diagnosed by MRI. Neurology 41:1987–1989
Stevens I, Petersen D, Grodd W, Poremba M, Dichgans J (1991) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. A 37-year follow-up of a case and review of the literature. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 241: 57–60
Willeit J, Aichner F, Felber S, Berek K, Deisenhammer F, Kiechl SG, Gerstenbrand F (1992) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: report of three cases and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci 111: 20–25
Daniele D, Bracchi M, Riva A, Duca S, Stura G, Bradac GB (1992) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: neuroradiological evaluation of two cases. Eur Neurol 32: 270–273
Bourgouin PM, Tampieri D, Melancon D, del Carpio R, Ethier R (1992) Superficial siderosis of the brain following unexplained subarachnoid hemorrhage: MRI diagnosis and clinical significance. Neuroradiology 34: 407–410
Bracchi M, Savoiardo M, Triulzi F, Daniele D, Grisoli M, Bradac GB, Agostinis C, Pelucchetti D, Scotti G (1993) Superficial siderosis of the CNS. MR diagnosis and clinical findings. AJNR 14: 227–236
de Souza NM, Cox CS, Hoare RD, Clarke CRA (1993) Cerebral siderosis: a complication of anticoagulant therapy? AJNR 14: 774–776
Janss AJ, Galetta SL, Freese A, Raps EC, Curtis MT, Grossman RI, Gomori JM, Duhaime AC (1993) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: magnetic resonance imaging and pathological correlation. J Neurosurg 79: 756–760
Stillhard G, Bont A, Huber-Gut D (1993) Haemosiderosis superficialis cerebri: seltene Ursache einer Ataxie und Hypakusis. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 123: 1027–1032
Kumar A, Aggarwal S, Willinsky R, TerBrugge KG (1993) Posterior fossa surgery: an unusual cause of superficial siderosis. Neurosurgery 32: 455–457
Kwartler JA, De La Cruz A, Lo WWM (1991) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 100: 249–250
Gell G (1983) AURA: routine documentation of medical texts. Methods Inf Med 22: 63–68
Pinkston JW, Ballinger WE, Lotz PR, Friedman WA (1983) Superficial siderosis: a cause of leptomeningeal enhancement on computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 1073–1076
Rosenthal P (1959) Siderose der Randzonen des Zentralnervensystems. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 178: 431–472
Oppenheimer DR, Griffith HB (1966) Persistent intracranial bleeding as a complication of hemispherectomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 29: 229–240
Iwanowski L, Olszewski J (1960) The effects of subarachnoid injections of iron containing substances on the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 19: 433–448
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Offenbacher, H., Fazekas, F., Schmidt, R. et al. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: MRI findings and clinical significance. Neuroradiology 38 (Suppl 1), S51–S56 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02278119
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02278119