Abstract
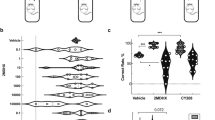
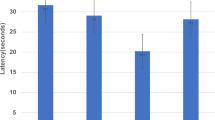
The Y-maze was used to examine the effects of purines acting at A1 and A2 adenosine receptors upon spontaneous alternation, a model of working memory, in mice. In support of previous work, scopolamine produced a loss of spontaneous alternation behaviour to the 0.5 chance level. The A1 receptor selective agonist N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) did not change spontaneous alternation behaviour alone, but it prevented the decrease of spontaneous alternation scores produced by scopolamine. The A1 receptor selective antagonist 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine (CPX) blocked the effect of CPA in combination with scopolamine but had no effect alone. The A2 receptor selective agonist (N6-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(2-methylphenyl)ethyl]adenosine (DPMA), and the A2 receptor selective antagonist 3,7-dimethyl-1-propargylxanthine (DMPX) had no effect of alternation behaviour alone and did not modify the effect of scopolamine. The results indicate the ability of A1 but not A2 receptor activation to modify working memory deficits induced by scopolamine, but suggest that endogenous adenosine does not normally participate in working memory processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlijanian MK, Takemori AE (1985) Effects of R-PIA and caffeine on nociception and morphine-produced analgesia, tolerance and dependence in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 112:171–179
Anisman H (1975) Dissociation of disinhibitory effects of scopolamine: strain and task factors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3:613–618
Barraco RA, Coffin VL, Altman HJ, Phillis JW (1983) Central effects of adenosine analogs on locomotor activity in mice and antagonism of caffeine. Brain Res 272:392–395
Barraco RA, Swanson TH, Phillis JW, Berman RF (1984) Anticonvulsant effects of adenosine analogues on amygdalakindled seizures in rats. Neurosci Lett 46:317–322
Barraco RA, Martens KA, Parizon M, Normile HJ (1993) Adenosine A2a receptors in the nucleus accumbens mediate locomotor depression. Brain Res Bull 31:397–404
Baumgold J, Nikodijevic O, Jacobson KA (1992) Penetration of adenosine antagonists into mouse brain as determined by ex vivo binding. Biochem Pharmacol 43:889–894
Beninger RJ, Jhamandas K, Boegman RJ, El-Defrawy SR (1986) Effect of scopolamine and unilateral lesions of the forebrain on T-maze spatial discrimination and alternation in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:1353–1360
Bruns RF, Fergus JH, Badger EW, Bristol JA, Santay LA, Hartman JD, Hays SJ Huang CC (1987) Binding of the A1-selective adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine to rat brain membranes. Arch Pharmacol 335:59–63
Coffin VL, Spealman, RD (1985) Modulation of the behavioural effects of clordiazepoxide by methylxanthines and analogues of adenosine in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235:724–728
Coffin VL Spealman RD (1987) Behavioural and cardiovascular effects of analogues of adenosine in cynomolgus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:76–83
Crawley JN, Patel J, Marangos PJ (1981) Behavioural characterization of two long lasting adenosine analogues: sedative properties and interaction with diazepam. Life Sci. 29:2623–2630
Dauge V, Derrien M, Blanchard JC, Roques BP (1992) The selective CCK-B antagonist BC264 injected into the anterolateral part of the nucleus accumbens, reduces the spontaneous alternation behaviour of rats. Neuropharmacology 31:67–75
Dennis WJ (1939) Spontaneous alternation in rats as an indicator of the persistence of stimulus traces. J Comp Psychol 28:305–312
Douglas RJ Isaacson RL (1966) Spontaneous alternation and scopolamine. Psychonom Sci 4:283–284
Drachman DA (1977) Memory and cognitive function in man: does the cholinergic system have a specific role? Neurology 27:783–790
Dragunow M (1988) Purinergic mechanisms in epilepsy. Prog Neurobiol 31:85–108
Drew WG, Miller LL Baugh EL (1973) Effects of THC, LSD-25 and scopolamine on continuous, spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze. Psychopharmacology 32:171–182
Dunbar GL, Rylett RJ, Schmidt BM, Sinclair RC, Williams LR (1993) Hippocampal choline acetyltransferase activity correlates with spatial learning in aged rats. Brain Res 604:266–272
Dunwiddie TV, Worth T (1982) Sedative and anticonvulsant effects of adenosine analogs in mouse and rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 220:70–76
Durcan MJ, Morgan PF (1989) NECA-induced hypomotility in mice: evidence for a predominantly central site of action. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32:487–490
Egger GJ, Livesey PJ, Dawson RG (1973) Ontogenetic aspects of central cholinergic involvement in spontaneous alternation behaviour. Dev Psychobiol 6:289–299
Glanzer M (1953) Stimulus satiation: an explanation of spontaneous alternation and related phenomena. Psychol Rev 60:257–268
Glasky AJ, Melchior CL, Pirzadeh B, Heydari N, Ritzmann RF (1994) Effect of AIT-082, a purine analog, on working memory in normal and aged mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 47:325–329
Grette Lydon R (1994) Cholinergic neurones and memory: and overview and historical perspective. In: Stone TW (ed) CNS neurotransmitters and neuromodulators, vol. 1: acetylcholine. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Chapter 14
Griebel G, Misslin R, Vogel E (1991a) Behavioural effects of selective A2 adenosine receptor antagonists, CGS 21197 and CGS 22706, in mice. NeuroReport 2:139–140
Griebel G, Saffroy-Spittler M, Misslin R, Remmy D, Vogel E, Bourguignon J-J (1991b) Comparison of the behavioural effects of an adenosine A1/A2 receptor antagonist CGS 15943A, and an A1-selective antagonist, DPCPX. Psychopharmacology 103:541–544
Hall JL, Gonder-Frederick LA, Chewning WW, Silveira J, Gold PE (1989) Glucose enhancement of memory in young and aged humans. Neuropsychology 27:1129–1138
Holmgren M, Hednar T, Nordberg G, Mellstrand T (1983) Antinociceptive effects in the rat of an adenosine analogue N6-phenylisopropyladenosine. J Pharm Pharmacol 35:679
Holtzman SG (1991) CGS 15943, a nonxanthine adenosine receptor antagonist: effects on locomotor activity of nontolerant and caffeine-tolerant rats. Life Sci 49:1563–1570
Itoh J, Ukai M, Kameyama T (1993) Dynorphin A(1–13) markedly improves scopolamine-induced impairment of spontaneous alternation performance in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 236:341–345
Jacobson KA, Nikodijevic O, de la Cruz D, Daly JW (1991) APEC, an A2-selective adenosine agonist, is a more potent locomotor depressant than N6-cyclohexyladenosine. Nucleosides Nucleotides 10:1211–1212
Janusz CA, Berman RF (1992) The A2-selective adenosine analog CGS 21680, depresses locomotor activity but does not block amygdala kindled seizures in rats. Neurosci Lett 141:247–250
Janusz CA, Berman RF (1993) Adenosinergic modulation of the EEG and locomotor effects of the A2 agonist, CGS 21680 Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:913–919
Kokkinidis L, Anisman H (1976) Interaction between cholinergic and catecholaminergic agents in a spontaneous alternation task. Psychopharmacology 48:261–265
Lohse MJ, Klotz KN, Lindenborn-Fotinos J, Reddington M, Schwab U, Olsson RA (1987) 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX) — a selective high affinity antagonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors. Arch Pharmacol 336:204–210
Manning CA, Hall JL, Gold PE (1990) Memory enhancement by glucose in aged humans. Psychol Sci 1:307–311
Martin GE, Rossi DJ, Jarvis MF (1993) Adenosine agonists reduce conditioned avoidance responding in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:951–958
Nikodijevic O, Sparges R, Daly JW, Jacobson KA (1991) Behavioural effects of A1 and A2-selective adenosine agonists and antagonists: evidence for synergism and antagonism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259:286–294
Normile HJ, Barraco RA (1991) N6-cyclopentyladenosine impairs passive avoidance retention by selective action at A1 receptors. Brain Res Bull 27:101–104
Ohno M, Yamamoto T, Watanabe S (1994) Blockade of hippocampal M1 muscarinic receptors impairs working memory performance of rats. Brain Res 650:260–266
Palmour RM, Lipowski CJ, Simon CK, Ervin FR (1989) Adenosine analogues inhibit fighting in isolated male mice. Life Sci 44:1293–1299
Parada-Turska J, Turski WA (1990) Excitatory amino acid antagonists and memory: effect of drugs acting at NMDA receptors in learning and memory tasks. Neuropharmacology 29:1111–1116
Post C (1984) Anti-nociceptive effects in mice after intrathecal injections of NECA. Neurosci Lett 51:325–330
Sarter M, Bodewitz G, Stephens DN (1988) Attenuation of scopolamine induced impairment of spontaneous alternation behaviour by antagonist but not inverse agonist and agonist b-carbolines. Psychopharmacology 94:491–495
Schingnitz G, Kufner-Muhl U, Ensinger H, Lehr E, Kuhn FJ (1991) Selective A1-antagonists for treatment of cognitive deficits. Nucleosides Nucleotides 10:1067–1076
Snyder SH, Katins JS, Annau Z, Bruns RF, Daly JW (1981) Adenosine receptors and the actions of the methylxanthines. Proc Natl Acad Sci 78:3260–3264
Spealman RD, Coffin VL (1986) Behavioural effects of adenosine analogues in squirrel monkeys: relation to adenosine A2 receptors. Psychopharmacology 90:419–421
Spencer DG, Lal H (1983) Effects of anticholinergic drugs on learning and memory. Drug Dev Res 3:489–502
Spencer DG, Pontecorvo MJ, Heise GA (1985) Central cholinergic inolvement in working memory: effects of scopolamine on continuous nonmatching and discrimination performance in the rat. Behav Neurosci 99:1049–1065
Squire LR (1969) Effect of pre-trial and post-trial administration of cholinergic and anticholinergic drugs on spontaneous alternation. J Comp Physiol Psychol 74:41–45
Stone TW, Simmonds HA (1991) Purines: basic and clinical aspects. Kluwer Press, Dordrecht
Stone WS Walser B, Gold SD, Gold PE (1991) Scopolamine and morphine induced impairments of spontaneous alternation performance in mice: reversal with glucose and with cholinergic and adrenergic agonists. Behav Neurosci 105:264–271
Stone WS, Rudd RJ, Gold PE (1992) Glucose attenuation of scopolamine and age induced deficits in spontaneous alternation behaviour and regional brain [3H]-2-deoxyglucose uptake in mice. Psychobiology 20:270–279
Swonger AK, Rech RH (1972) Serotonergic and cholinergic involvement in habituation of activity and spontaneous alternation of rats in a Y maze. J Comp Physiol Psychol 81:509–522
Tobe A, Egawa M, Nagai R (1983) Effect of MCI-2016 on the scopolamine induced deficit of spontaneous alternation behaviour in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 33:775–784
Troster AI, Beatty WW, Staton RD, Rorabaugh AG (1989) Effect of scopolamine on anterograde and remote memory in humans. Psychobiology 17:17–18
Walker DL Gold PE (1991) Effect of the novel NMDA antagonist NPC 12626 on long-term potentiation, learning and memory. Brain Res 549:213–221
Walker DL, Gold PE (1992) Impairment of spontaneous alternation performance by an NMDA antagonist: attenuation with non-NMDA treatments. Behav Neural Biol 58:69–71
Warburton DM, Heise GA (1972) Effects of scopolamine on spatial double alternation in rats. J Comp Hhysiol Psychol 81:523–532
Williams M, Braunwalder A, Erickson TE (1986) Evaluation of the binding of the A1-selective adenosine radioligand, cyclopentyladenosine to rat brain tissue. Arch Pharmacol 332:179–183
Willig F, Van de Velde D, Laurent J, M'Harzi M, Delacour J (1992) The Roman strains of rats as a psychogenetic tool for pharmacological investigation of working memory: example with RU 41656. Psychopharmacology 107:415–424
Winsky L, Harvey JA (1986) Retardation of associative learning in the rabbit by an adenosine analogue as measured by classical conditioning of the nictitating membrane response. J Neurosci 6:2684
Yarbrough GG, McGuffin-Clineschmidt TC (1981) In vivo behavioural assessment of CNS purinergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 76:137–144
Zarrindast MR, Bijan S (1994) Effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists on acquisition of passive avoidance learning. Eur J Pharmacol 256:233–239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hooper, N., Fraser, C. & Stone, T.W. Effects of purine analogues on spontaneous alternation in mice. Psychopharmacology 123, 250–257 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246579
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246579