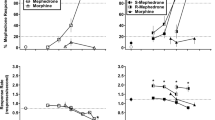
Abstract
Drug discrimination studies have proven useful for comparing and contrasting the behavioral effects of site-selectiveN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists. This study examined the effects of competitive and non-competitive NMDA antagonists in squirrel monkeys trained to discriminate 1 mg/kgd-CPPene [d-3-(2-carboxypiperazine-4-yl)-1-propenyl-1-phosphonic acid; SDZ EAA 494] from vehicle in a two-lever drug discrimination procedure. Results show thatd-CPPene and several other competitive NMDA antagonists (NPC 17742, CGS 19755, and CGP 37849) completely substituted ford-CPPene in a dose-dependent manner. In contrast, phencyclidine (PCP) and ketamine produced only partial substitution at doses that severely suppressed response rates. These results are consistent with results of earlier studies with rats and monkeys showing differences in the discriminative stimulus effects of competitive and PCP-like non-competitive NMDA antagonists. The data support the predictions (1) thatd-CPPene and the other competitive NMDA antagonists tested would have similar subjective effects in humans and (2) that some differences would be found in the subjective effects of competitive NMDA antagonists and PCP-like non-competitive antagonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebischer B, Frey P, Haerter HP, Herrling PL, Mueller W (1989) Synthesis and NMDA antagonistic properties of the enantiomers of 4-(3-phosphonopropyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acid (CPP) and of the unsaturated analogue (E)-4-(3-phosphonoprop-2-enyl) piperazine-2-carboxylic acid (CPP-ene). Helv Chim Acta 72:1043–1051
Balster RL (1990) Perception of drug effects. In: Berkley MA, Stebbins WC (eds) Comparative perception. Wiley, New York, pp 127–154
Balster RL (1991) Discriminative stimulus properties of phencyclidine and other NMDA antagonists. In: Glennon RA, Järbe TUC, Frankenheim J (eds) Drug discrimination: applications to drug abuse research (National Institute on Drug Abuse Research Monograph Series, vol 116) US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, pp 163–180
Beardsley PM, Balster RL, Salay JM (1987) Separation of the response rate and discriminative stimulus effects of phencyclidine: training dose as a factor in phencyclidine-saline discrimination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:159–165
Beardsley PM, Hayes BA, Balster RL (1990) The self-administration of MK-801 can depend upon drug-reinforcement history and its discriminative stimulus properties are phencyclidine-like in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:953–959
Bobelis DJ, Balster RL (1993) Pharmacological specificity of the discriminative stimulus properties of 2-amino-4,5-(1,2-cyclohexyl)-7-phosphonoheptanoic acid (NPC 12626), a competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:845–853
Brady KT, Balster RL (1981) Discriminative stimulus properties of phencyclidine and five analogues in the squirrel monkey. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 14:213–218
Brady KT, Balster RL (1982) Discriminative stimulus properties of ketamine stereoisomers in phencyclidine-treated rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:291–295
Brady KT, Balster RL, May EL (1982) Stereoisomers of N-allylnormetazocine: phencyclidine-like behavioral effects in squirrel monkeys and rats. Science 212:178–180
Browne RG, Weissman A (1981) Discriminative stimulus properties of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: mechanistic studies. J Clin Pharmacol 21:227S-234S
Chapman AG, Graham J, Meldrum BS (1990) Potent oral anticonvulsant action of CPP and CPPene in DBA/2 mice. Eur J Pharmacol 178:97–99
Chen M, Bullock R, Graham DI, Frey P, Lowe D, McCulloch J (1991) Evaluation of a competitive NMDA antagonist (d-CPPene) in feline focal cerebral ischemia. Ann Neurol 30:62–70
Fagg GE, Olpe HR, Pozza MF, Baud J, Steinmann M, Schmutz M, Portet C, Baumann P, Thedinga K, Bittiger H, Allgeier H, Heckendorn R, Angst C, Brundish D, Dingwall JG (1990) CGP 37849 and CGP 39551: novel and potent competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists with oral activity. Br J Pharmacol 99:791–797
Ferkany JW, Hamilton GS, Patch RJ, Huang Z, Borosky S, Bednar DL, Jones BE, Zubrowski R, Willetts J, Karbon EW (1993) Pharmacological profile of NPC 17742 [2R, 4R, 5S-(2-amino-4, 5-(1, 2-cyclohexyl)-7-phosphonoheptanoic acid)], a potent, selective and competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:256–264
France CP, Woods JH, Ornstein P (1989) The competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist CGS 19755 attenuates the rate-decreasing effects of NMDA in rhesus monkeys without producing ketamine-like discriminative stimulus effects. Eur J Pharmacol 159:133–139
France CP, Moerschbaecher JM, Woods JH (1991) MK-801 and related compounds in monkeys: discriminative stimulus effects and effects on a conditional discrimination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:727–734
Gold LH, Balster RL (1993) Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists in squirrel monkeys trained to discriminate the competitive NMDA receptor antagonist NPC 12626 from saline. Eur J Pharmacol 230:285–292
Goldstein A (1964) Biostatistics: an introductory text. MacMillan, New York
Kaplita PV, Ferkany JW (1990) Evidence for direct interactions between the NMDA and glycine recognition sites in brain. Eur J Pharmacol 188:175–179
Koek W, Woods JH, Jacobson AE, Rice KC (1987) Phencyclidine (PCP)-like discriminative stimulus effects of metaphit and of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate in pigeons: generality across different training doses of PCP. Psychopharmacology 93:437–442
Koek W, Woods JH, Colpaert FC (1990)N-Methyl-d-aspartate antagonism and phencyclidine-like activity: a drug discrimination analysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:1017–1025
Koek W, Colpaert FC, Vignon J (1993) Effects of phencyclidine-type drugs in rats discriminating fentanyl from saline: pharmacological and behavioral characterization of intermediate levels of drug lever selection. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:746–756
Lehmann J, Schneider J, McPherson S, Murphy DE, Bernard P, Tsai C, Bennett DA, Pastor G, Steel DJ, Boehm C, Cheney DL, Liebman JM, Williams M, Wood PL (1987) CPP, a selectiveN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA)-type receptor antagonist: characterization in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:737–746
Lodge D, Johnson KM (1990) Noncompetitive excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11:81–86
Lodge D, Jones M, Fletcher E (1989) Noncompetitive antagonists ofN-methyl-d-aspartate. In: Watkins JC, Collingridge GL (eds) The NMDA receptor. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 37–51
Mansbach RS, Balster RL (1991) Pharmacological specificity of the phencyclidine discriminative stimulus in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:971–975
Mansbach RS, Willetts J, Jortani SA, Balster RL (1991) NMDA antagonists: lack of antipunishment effect in squirrel monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:977–981
Meldrum B (1987) Excitatory amino acid antagonists as potential therapeutic agents. In: Jenner P (ed) Neurotoxins and their pharmacological implications. Raven Press, New York, pp 33–53
Monaghan DT, Olverman HJ, Nguyen L, Watkins JC, Cotman CW (1988) Two classes ofN-methyl-d-aspartate recognition sites: differential distribution and differential regulation by glycine. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85:9836–9840
Näsström J, Böö É, Ståhlberg M, Berge OG (1993) Tissue distribution of two NMDA receptor antagonists, [3H]CGS 19755 and [3H]MK-801, after intrathecal injection in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:9–15
Olverman HJ, Watkins JC (1989) NMDA agonists and competitive antagonists. In: Watkins JC, Collingridge GL (eds) The NMDA receptor. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 19–36
Park CK, McCulloch J, Kang JK, Choi CR (1992) Efficacy ofd-CPPene, a competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neurosci Lett 147:41–44
Patel S, Chapman AG, Graham JL, Meldrum BS, Frey P (1990) Anticonvulsant activity of the NMDA antagonists, D(-)4-(3-phosphonopropyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acid (d-CPP) andd(-)(E)-4-(3-phosphonoprop-2-enyl) piperazine-2-carboxylic acid (d-CPPene) in a rodent and a primate model of reflex epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 7:3–10
Schmutz M, Portet C, Jeker A, Klebs K, Vassout A, Allgeier H, Heckendorn R, Fagg GE, Olpe HR, van Riezen H (1990) The competitive NMDA receptor antagonists CGP 37849 and CGP 39551 are potent, orally-active anticonvulsants in rodents. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 342:61–66
Turski L, Schwarz M, Turski WA, Klockgether T, Sontag KH, Collins JF (1987) Muscle relaxant action of excitatory amino acid antagonists. Neurosci Lett 53:321–326
Watkins JC (1989) The NMDA receptor complex: origins and development. In: Watkins JC, Collingridge GL (eds) The NMDA receptor. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 1–17
Wiley JL, Balster RL (1992) Preclinical evaluation of N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonists for antianxiety effects: a review. In: Kamenka JM, Domino EF (eds) Multiple sigma and PCP receptor ligands: mechanisms for neuromodulation and neuroprotection? NPP Books, Ann Arbor, Mich, pp 801–815
Wiley JL, Balster RL (1993) NMDA antagonists: a novel class of anxiolytics? In: Hamon M, Oilat H, Thiébot M-H (eds.) Anxiety: neurobiological, clinical and therapeutic aspects, John Libbey Eurotext, Montrouge, France, pp 177–184
Willetts J, Balster RL (1988) Phencyclidine-like discriminative stimulus properties of MK-801 in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 146:167–169
Willetts J, Balster RL (1989) Effects of competitive and noncompetitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists in rats trained to discriminate NMDA from saline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:627–633
Willetts J, Bobelis DJ, Balster RL (1989) Drug discrimination based on the competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist, NPC 12626. Psychopharmacology 99:458–462
Willetts J, Clissold DB, Hartman TL, Brandsgaard RR, Hamilton GS, Ferkany JW (1993) Behavioral pharmacology of NPC 17742, a competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:1055–1062
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiley, J.L., Balster, R.L. Effects of competitive and non-competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists in squirrel monkeys trained to discriminated-CPPene (SDZ EAA 494) from vehicle. Psychopharmacology 116, 266–272 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245327
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245327