Abstract
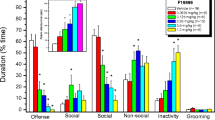
The effects were ascertained of two partial inverse agonists at benzodiazepine receptors (beta-CCE and FG 7142) on the incidence of timid (defensive-escape), aggressive, sociable and locomotor activities in both timid and aggressive singly-housed male mice, treated with drugs in paired interactions with untreated non-aggressive males. FG 7142 (5 mg/kg) and beta-CCE (8 mg/kg) increased defenses and escapes without producing other behavioral changes in timid mice. FG 7142 (20 mg/kg) and beta-CCE (1–8 mg/kg) moderately increased defenses and alert postures in aggressive mice and this effect was associated with marked reduction of aggressive behavior. FG 7142 (20 and 80 mg/kg) also decreased walking across cage in aggressive mice. It is concluded that beta-CCE and FG 7142 produced behavioral changes which could be interpreted as “anxiogenic”.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck CHM, Cooper SJ (1986a) The effect of the beta-carboline FG 7142 on the behaviour of male rats in a living cage: an ethological analysis of social and nonsocial behaviour. Psychopharmacology 89:203–207
Beck CHM, Cooper SJ (1986b) Beta-carboline FG 7142-reduced aggression in male rats: reversed by the benzodiazepine receptor antagonist, Ro 15-1788., Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:1645–1649
Crawley JN, Ninan PT, Pickar D, Chrousos GP, Linnoila M, Skolnick P, Paul SM (1985) Neuropharmacological antagonism of the beta-carboline-induced “anxiety” response in rhesus monkeys. J Neurosci 5:477–485
Dixon AK, Kaesermann HP (1987) Ethopharmacology of flight behaviour. In: Olivier B, Mos J, Brain PF (eds) Ethopharmacology of agonistic behaviour in animals and humans. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp 46–79
Dorow R, Horowski R, Paschelke G, Amin M, Braestrup C (1983) Severe anxiety induced by FG 7142, a beta-carboline ligand for benzodiazepine receptors. Lancet II:98–99
File SE, Baldwin HA (1987) Effects of beta-carbolines in animal models of anxiety. Brain Res Bull 19:293–299
File SE, Lister RG, Nutt DJ (1982) The anxiogenic action of benzodiazepine antagonists. Neuropharmacology 21:1033–1037
Grant EC, Mackintosh JH (1963) A comparison of the social postures of some common laboratory rodents. Behavior 21:246–259
Hansen S, Ferreira A, Selart MEJ (1985) Behavioural similarities between mother rats and benzodiazepine-treated non-maternal animals. Psychopharmacology 86:344–347
Insel TR, Ninan P, Aloi J, Jimerson DC, Skolnick P, Paul SM (1984) A benzodiazepine receptor-mediated model of anxiety. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:741–750
Kršiak M (1975) Timid singly-housed mice: their value in prediction of psychotropic activity of drugs. Br J Pharmacol 55:141–150
Kršiak M (1979) Effects of drugs on behaviour of aggressive mice. Br J Pharmacol 65:525–533
Kršiak M (1980) The study of neuropsychotropic effects of drugs by ethological analysis of behavior (DSc Thesis, in Czech). Institute of Pharmacology, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Prague
Kršiak M (1989) Effects of muscimol, cetyl-GABA, pentetrazol and picrotoxin on timidity during intraspecies conflict in mice. Act Nerv Super (Praha) 31:64–66
Kršiak M, Šulcová A (1990) Differential effects of six structurally related benzodiazepines on some ethological measures of timidity, aggression and locomotion in mice. Psychopharmacology 101:396–402
Kršiak M, Šulcová A, Tomašíková Z, Dlohožková N, Kosař E, Mašek K (1981) Drug effects on attack, defense and escape in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 14 [Suppl 1]:47–52
Kršiak M, Šulcová A, Donát P, Tomašíková N, Kosař E, Mašek K (1984) Can social and agonistic interactions be used to detect anxiolytic activity of drugs? In: Miczek KA, Kruk MR, Olivier B (eds) Ethopharmacological aggression research. Liss, New York, pp 93–114
Ongini E (1983) Behavioral and EEG effects of benzodiazepines and their antagonists in the cat. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) Benzodiazepine recognition site ligands: biochemistry and pharmacology. Raven Press, New York, pp 211–225
Petersen EN, Jensen LH, Honoré T, Braestrup C (1983) Differential pharmacological effects of benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonists. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) Benzodiazepine recognition site ligands: biochemistry and pharmacology. Raven Press, New York, pp 57–64
Piret B, Depaulis A, Vergnes M (1991) Opposite effects of agonist and inverse agonist ligands of benzodiazepine receptor on self-defensive and submissive postures in the rat. Psychopharmacology 103:56–61
Poshivalov VP (1978) Ethological analysis of the action exerted by medazepam and diazepam on the zoosocial behavior of isolated mice (in Russian). Farmakol Toksikol 41:263–265
Skolnick P, Schweri MM, Paul SM, Martin JV, Wagner RL, Mendelson WB (1983) 3-Carboethoxy-β-carboline (β-CCE) elicits electroencephalographic seizures in rats: reversal by the benzodiazepine antagonist CGS 8216. Life Sci 32:2439–2445
Skolnick P, Reed GF, Paul SM (1985) Benzodiazepine-receptor mediated inhibition of isolation-induced aggression in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:17–20
Šulcová A, Kršiak M (1985) Effects of ethyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate and diazepam on aggressive and timid behaviour in mice. Act Nerv Super (Praha) 27:308–310
Šulcová A, Kršiak M (1986) β-Carbolines (β-CCE, FG 7142) and diazepam: synergistic effects on aggression and antagonistic effects on timidity in mice. Act Nerv Super (Praha) 28:312–314
Šulcová A, Kršiak M (1990) Flumazenil antagonizes antiaggressive and “anxiogenic” effects of FG 7142 on intraspecies conflict in mice. Act Nerv Super (Praha) 32:217–219
Thiébot MH, Soubrié P, Sanger D (1988) Anxiogenic properties of beta-CCE and FG 7142: a review of promises and pitfalls. Psychopharmacology 94:452–463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šulcová, A., Kršiak, M. & Donát, P. Beta-CCE and FG 7142 increase defensiveness during intraspecies encounters in mice. Psychopharmacology 108, 205–209 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245308
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245308