Abstract
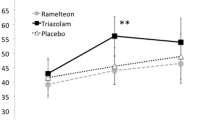
Fifty healthy male subjects were administered zolpidem (5, 10, or 20 mg), triazolam (0.5 mg) or placebo, then attempted to sleep in a non-sleep-conductive environment. Subjects were awakened at 90 min post-drug (near peak blood concentration for both drugs) and tested on several cognitive tasks, including Two Column Addition, Logical Reasoning, and a Simulated Escape Task. This was followed by a second, 3.5-h sleep period. Hypnotic efficacy of the 20 mg zolpidem (Z-20) dose was similar to that of the 0.5 mg triazolam (TRIAZ) dose, as indicated by comparably shortened sleep latencies and lengthened total sleep times. Though accuracy on most performance measures was not affected by either drug, a reduction in speed of responding on logical reasoning and addition tasks was evident for the TRIAZ group at 90 min post-drug (Ps<0.05). On the simulated escape task, only triazolam significantly increased the mean number of errors, and interfered with subsequent memory of the task. Thus, zolpidem had milder effects on performance than triazolam. However, 60% of the Z-20 subjects experienced mild, adverse physical reactions. Performance differences between somnogenically comparable doses of zolpidem and triazolam may be due to their differential affinities for the BZ1 and BZ2 receptor subtypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albin H, Vincon G, Vincon J, Herrmann P, Thiercelin JP (1988) Study of the pharmacokinetics of zolpidem in healthy volunteers after repeated administration: effect on antipyrine clearance. In: Bartholini G, Friedmann JC, Sanger SZ, Morselli PL, Wick A (eds) Imidazopyridines in sleep disorders: a novel experimental and therapeutic approach. Raven Press, New York, pp 369–370
Balkin TJ, O'Donnell VM, Kamimori GH, Redmond DP, Belenky G (1989) Sleep inertia following triazolam-induced recovery sleep. Hum Psychopharmacol 4:291–296
Bonnet MH (1986) Performance and sleepiness as a function of frequency and placement of sleep disruption. Psychophysiology 23:263–271
Dennis T, Dubois A, Benavides J, Scatton B (1988) Distribution of central omega 1 (benzodiazepine 1; BZD1) and omega 2 (BZD2) receptor subtypes in the monkey and human brain: an autoradiographic study with [3H]flunitrazepam and the omega 1 selective ligand [3H]zolpidem. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:309–22
Dorian P, Sellers EM, Kaplan HL, Hamilton HL, Greenblatt DJ, Abernathy D (1985) Triazolam and ethanol interaction: kinetic and dynamic consequences. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37:558–562
Englund CE, Reeves DL, Shingledecker CA, Thorne DR, Wilson KP, Hegge FW (1987) Unified tri-service cognitive performance assessment battery (UTC-PAB) 1. Design and specification of the battery (Report no. 87-10). Naval Medical Research and Development Command, Bethesda MD
Hoddes E, Zarcone V, Smythe H, Phillips R, Dement WC (1973) Quantification of sleepiness: a new approach. Psychophysiology 10:431–436
Horne J (1988) Why we sleep. Oxford University Press, London New York
Kales A (1990) Benzodiazepine hypnotics and insomnia. Hosp Pract Suppl 3:7–23
Mendelson WB (1990) The search for the hypnogenic center. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 14:1–12
O'Donnell VM, Balkin TJ, Andrade JR, Simon LM, Kamimori GH, Redmond DP, Belenky G (1988) Effects of triazolam on sleep and performance in a model of transient insomnia. Hum Perform 1:145–160
Oswald I (1989) Triazolam syndrome 10 years on (letter). Lancet II(8664):680
Palminteri R, Narbonne G (1988) Safety profile of zolpidem. In: Bartholini G, Friedmann JC, Sanger SZ, Morselli PL, Wick A (eds) Imidazopyridines in sleep disorders: a novel experimental and therapeutic approach. Raven Press, New York, pp 351–362
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardized terminology, techniques, and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Brain Information Service/Brain Research Institute, UCLA
Richardson GS, Carskadon MA, Orav EJ, Dement WC (1982) Circadian variation in sleep tendency in elderly and young adult subjects. Sleep 5:S82-S94
Roth T, Kramer M, Lutz T (1976) Intermediate use of triazolam: a sleep laboratory study. J Int Med Res 4:59–63
Seidel WF, Roth T, Roehrs T, Zorick F, Dement WC (1984) Treatment of a 12 hour shift of sleep schedule with benzodiazepines. Science 224:1262–1264
Stroop JR (1935) Factors affecting speed in serial verbal reactions. Psychol Monogr 50:38–48
Wechsler D (1958) Measurement and appraisal of adult intelligence, 4th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This material has been reviewed by the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, and there is no objection to its presentation and/or publication. The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the author and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the position of the Department of the Army or the Department of Defense.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balkin, T.J., O'Donnell, V.M., Wesensten, N. et al. Comparison of the daytime sleep and performance effects of zolpidem versus triazolam. Psychopharmacology 107, 83–88 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244970
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244970