Summary
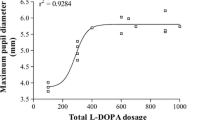
In order to assess the course of methadone (Heptadone) substitution therapy, 29 inpatients at the Vienna Psychiatric University Clinic (21 males, mean age=27 years, SD 4 years; 8 females, mean age 29.75 years, SD 5.28 years) who were addicted to opium tea or to a mixture of opium and heroin were investigated by means of computer-assisted “static”- and “light-evoked dynamic” pupillometry. Pupillary measurements were carried out before the start of withdrawal, on the 2nd day 48 h after the administration of 10 mg methadone, and again after the maximum and half of the maximum dose of methadone had been administered. The constricted pupils (the effect of opiate) showed dilatation after the withdrawal syndrome appeared, but immediately after the start of the detoxification treatment, as well as 1 day after administration of the maximum methadone dose a decrease of pupillary diameter was observed. The narrowing of the pupil was followed by an increase in pupillary diameter, which peaked 48 h after the last minimal dose of methadone and nearly reached the normal level. The widening of the pupil reflects an increase of noradrenergic activity under conditions of opiate withdrawal. An increase of spontaneous fluctuations was observed during withdrawal and was only inhibited by the maximum dose of methadone. Finally, pupillary dynamics (shortening of latency time and increase of relative changes) improved during therapy. The pupillary measurement coresponded with clinical observations as well as with self-evaluation during treatment. Thus pupillometry seems to be a useful instrument for assessment of treatment of opiate-addicted patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1978) Tolerance of locus coeruleus neurons to morphine and suppression of withdrawal response to clonidin. Nature 276:186–187
Cooley WW, Lohnes RP (1971) Multivariate data analysis. Wiley, New York
Gold MS, Redmond DE Jr (1977) Pharmalogical activation and inhibition of noradrenergic activity alter specific behaviours in nonhuman primates (abstract). Neurosci Abstr 3:250
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Saletu B (1984a) Psychodiagnostik mit Hilfe psychophysiologischer Verfahren. Wien Med Wochenschr 2:29
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Saletu B, Stöhr H (1984b) Mikrocomputer im Einsatz bei Routineuntersuchungen und Forschungsaufgaben im Bereich der klinischen Psychodiagnostik. Biomed Tech 29:283
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Saletu B, Stöhr H (1984c) Zur Methodologie der Pupillenmessung. Psychiatr Clin 3:157
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Gathmann P, Saletu B (1985) Computerassistierte “statische” und lichtevozierte “dynamische” Pupillometrie bei psychosomatischen Patienten. Wien Klin Wochenschr 20-775
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Cepko H, Saletu B (1986a) Pupillometrie im psychopharmakologischen Experiment. Arzneim Forsch 1:141
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Küfferle B, Saletu B (1986b) Pupillometrie bei schizophrenen Patienten. In: Keup W (ed) Biologische Psychiatrie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 199
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Cepko H, Saletu B (1987a) Lichtevozierte dynamische Pupillometrie zur Differenzierung psychotroper Substanzen. Arzneim Forsch 3:357
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Witek R, Saletu B (1987b) Faktorenanalytische Untersuchungen und Reliabilitätsbestimmung der statischen und dynamischen Pupillometrie. Wien Med Wochenschr 7:135–139
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Gasic S, Saletu B (1988) Computerassistierte statische und dynamische Pupillometrie zur Charakterisierung des trizyklischen Antidepressivums Cianopramin. Arzneim Forsch 3:383–387
Grünberger J, Linzmayer L, Suletu B, Lesch OM (1989) Klinische psychologische Diagnostik bei ambulanten Alkoholikern: Statische und lichtevozierte dynamische Pupillometrie. Wien Z Suchtforsch 12:53–62
Kolb L, Himmelsbach CK (1938) Clinical studies of drug addiction. III. A critical review of the withdrawal treatments method of evaluating abstinence syndromes. Am J Psychiatry 94:759–799
Loimer N, Linzmayer L, Grünberger J, Presslich O (1988) Objektivierung des Entzugssyndroms während der Ultrakurzentzugsbehandlung mit hohen Naloxondosen bei Opiatabhängigkeit. Therapiewoche Österreich 12. pp 1125–1130
Sachs L (1977) Statistische Auswertungsmethoden. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grünberger, J., Linzmayer, L., Fodor, G. et al. Static and dynamic pupillometry for determination of the course of gradual detoxification of opiate-addicted patients. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Nuerosci 240, 109–112 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02189980
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02189980